Examine Microsoft Defender for Cloud usage scenarios
You can integrate Microsoft Defender for Cloud into your workflows and use it in many ways. For example, use Microsoft Defender for Cloud as part of your incident response plan.
Many organizations only respond to security incidents after an attack has occurred. To reduce costs and damage, it's necessary to have an incident response plan before an attack occurs.
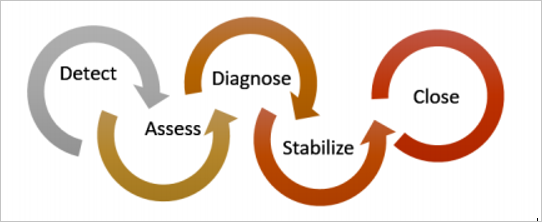
The following examples show how to use Microsoft Defender for Cloud to detect, assess, and diagnose your incident response plan stages.
- Detect. Review the first indication of an event investigation. For example, use the Microsoft Defender for Cloud dashboard to review a high-priority security alert's initial verification.
- Assess. Do the initial assessment to obtain more information about suspicious activity. For example, you can get more information about a security alert from Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
- Diagnose. Conduct a technical investigation and identify containment, mitigation, and workaround strategies. For example, you can follow the remediation steps described by Microsoft Defender for Cloud for a particular security alert.
- Use Microsoft Defender for Cloud recommendations to enhance security.
You can reduce the chances of a significant security event by configuring a security policy and then implementing the recommendations provided by Microsoft Defender for Cloud. A security policy defines the controls recommended for resources within a specified subscription or resource group. You can define policies in Microsoft Defender for Cloud according to your company's security requirements.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud analyzes the security state of your Azure resources. When identifying potential security vulnerabilities, it creates recommendations based on the controls set in the security policy.
The suggestions guide you through the process of configuring the corresponding security controls.
For example, if you have workloads that don't require the Azure SQL Database Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) policy, turn off the policy at the subscription level and enable it only on the resource groups where SQL Database TDE is required.
You can read more about the Microsoft Defender for Cloud at the Microsoft Defender for Cloud. More implementation and scenario details are available in the Microsoft Defender for Cloud planning and operations guide.