Manage models in Microsoft Fabric
The integration of MLflow in Microsoft Fabric makes it easy to track and manage your machine learning models.
Track model artifacts with MLflow
After you train a model, you want to use the model for scoring and generating new predictions. To easily integrate your model, you need to store your model so that you can load the model in a different environment. A common approach is to store a model as a pickle file, a serialized object.
Note
The format of your stored model depends on the machine learning framework you're using. For example, when training a deep learning model, you may opt to store your model using the Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) format instead.
MLflow adds another layer to your model's output by adding the MLmodel file. The MLmodel file specifies the model's metadata, like how and when the model was trained, as well as the model's expected input and output.
Understand the MLmodel file
When you log a model with MLflow, all relevant model assets are stored in the model folder with your experiment run.
The model folder includes the MLmodel file, a single source of truth about how the model should be loaded and consumed.
The MLmodel file may include:
artifact_path: During training, the model is logged to this path.flavor: The machine learning library with which the model was created.model_uuid: The unique identifier of the registered model.run_id: The unique identifier of job run during which the model was created.signature: Specifies the schema of the model's inputs and outputs:inputs: Valid input to the model. For example, a subset of the training dataset.outputs: Valid model output. For example, model predictions for the input dataset.
Imagine you trained a regression model to predict diabetes in patients, the logged MLmodel file may look like:
artifact_path: model
flavors:
python_function:
env:
conda: conda.yaml
virtualenv: python_env.yaml
loader_module: mlflow.sklearn
model_path: model.pkl
predict_fn: predict
python_version: 3.10.10
sklearn:
code: null
pickled_model: model.pkl
serialization_format: cloudpickle
sklearn_version: 1.2.0
mlflow_version: 2.1.1
model_uuid: 8370150f4e07495794c3b80bcaf07e52
run_id: 14cdf02f-119b-4b8d-90f3-044987c29bce
signature:
inputs: '[{"type": "tensor", "tensor-spec": {"dtype": "float64", "shape": [-1, 10]}}]'
outputs: '[{"type": "tensor", "tensor-spec": {"dtype": "float64", "shape": [-1]}}]'
When you choose to use MLflow's autologging function in Microsoft Fabric, the MLmodel file is automatically created for you. If you want to change the file to change the model's behavior during scoring, you can change how the MLmodel file is logged.
Tip
Learn more about MLflow model files and how to customize the fields.
Manage models in Microsoft Fabric
When you track a model with MLflow during training in Microsoft Fabric, all model artifacts are stored in the model folder. You can find the model folder in the experiment run:

The model folder contains:
MLmodel: Contains the model's metadata.conda.yaml: Contains the Anaconda environment needed to run the model.model.pkl: Contains the trained modelpython_env.yaml: Describes the Python environment needed to run the model. References therequirements.txtfile.requirements.txt: Lists Python packages required to run the model.
All these model artifacts are necessary when you want to use your model to generate predictions on new data.
Save a model your workspace
When you choose the model you want to use, you can save the model in the workspace from the experiment run. By saving a model, you create a new versioned model in the workspace that contains all the model artifacts and metadata.
Select the experiment run that represent the model you trained, and select the Save option to save the run as a model.
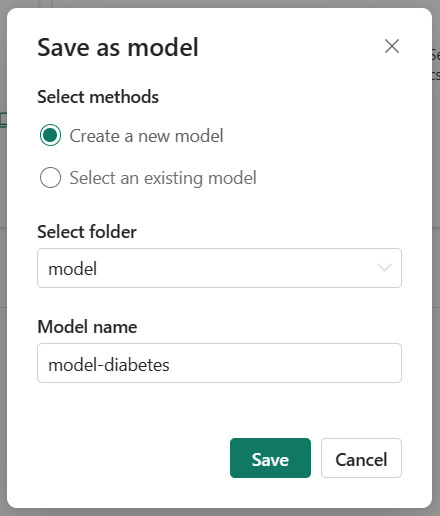
By selecting an existing model, you create a new version of a model under the same name. Model versioning allows you to compare models that serve a similar purpose, after which you can choose the best performing model to generate predictions.
