Ensure business continuity with Azure SQL Managed Instance
Running and maintaining a Disaster Recovery (DR) solution on-premises can be challenging, costly, and time consuming.
SQL Server 2025 provides the flexibility to extend your on-premises disaster recovery environment to Azure, allowing you to fail over and fail back between SQL Server instances and Azure SQL Managed Instance by using the link feature. This capability has been enhanced in SQL Server 2025 with improved performance, better monitoring, and streamlined configuration options.
Azure SQL Managed Instance offers a fully functional instance of SQL Server on Azure that is highly compatible with SQL Server 2025, supporting your hybrid disaster recovery solution.
Extended capabilities to the cloud
There are several ways to use the link feature and use Azure services and resources:
Offload read-only workloads. You can configure secondary replicas on your SQL Server to Azure to offload reporting needs. The link feature is database scoped, allowing for consolidation of read-only workloads in Azure, bringing data closer to customers in any supported region worldwide.
Migrate workloads. Azure SQL Managed Instance link feature offers an online migration option. Organizations can adopt a phased approach to cloud migration by partially running workloads on Azure.
Automated backups. Secondary replicas running on Azure SQL Managed Instance are automatically backed up to your Azure Blob Storage account, which reduces administrative efforts and improves reliability. SQL Server 2025 introduces enhanced backup capabilities for Always On availability groups, allowing full and differential backups to be performed on secondary replicas in addition to the existing copy-only and transaction log backups. This enhancement, enabled through trace flags (TF 3261 for differential and TF 3262 for full backups), provides flexibility in offloading backup workloads from the primary replica, reducing I/O strain on production systems while maintaining backup consistency across your hybrid environment.
Business continuity. As a disaster recovery solution, the link feature in SQL Server 2025 allows you to fail over to Azure SQL Managed Instance and fail back after the disaster is mitigated. SQL Server 2025 enhances this capability with improved monitoring dashboards and health checks.
Tip
For organizations requiring real-time data replication for analytics purposes, consider using Mirroring in Fabric in conjunction with Azure SQL Managed Instance Link. The link feature focuses on disaster recovery and business continuity, while Fabric Mirroring provides low-latency replication for analytical workloads.
Hybrid flexibility with Azure SQL Managed Instance link feature
Azure SQL Managed Instance link feature allows you to replicate your SQL Server databases hosted anywhere to Azure, and failover to the cloud in the event of a disaster or business disruption. The link feature provides failover between the primary and secondary databases.
One of the advantages of using Azure SQL Managed Instance is that it's a platform as a service (PaaS), which means that hardware maintenance, patching, and updates are applied and managed automatically by Azure. This ensures that your database environment is up-to-date and secure, while reducing the risk of downtime due to hardware failures or software vulnerabilities.
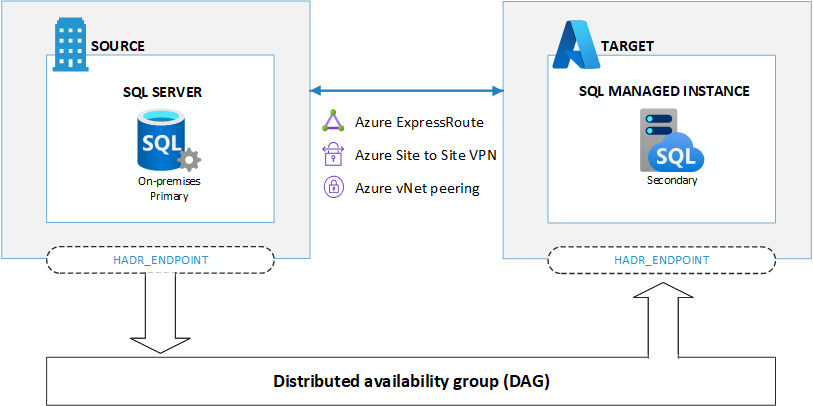
The link feature uses distributed availability group (DAG) and is scoped per database (one link per database). This allows you to consolidate multiple parallel SQL Server databases into an Azure SQL Managed Instance or scale them out across multiple instances and regions worldwide.
The link feature provides two types of replication:
One-way replication. One-way replication is available for SQL Server versions 2016, 2019, and 2022, allowing you to replicate data one way from a SQL Server instance to your managed instance.
Two-way replication. SQL Server 2025 provides enhanced two-way replication capabilities, where you can replicate data between your managed instance and SQL Server instances, manually fail over during a disaster, and fail back after the disaster is mitigated. SQL Server 2025 includes improvements to the failback process with better performance monitoring and reduced downtime during failover operations.
Note
SQL Server 2025 supports both online failover and failback capabilities. Check the latest Azure SQL Managed Instance documentation for current feature availability and enhancements.
Enable the link feature
To configure the link feature, follow the same steps regardless of whether you're migrating to Azure SQL Managed Instance, configuring disaster recovery on the cloud, offload workloads to Azure, or reduce backup operations and management costs.
You can use either a wizard in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or scripts. The main advantage of using scripts is that they can be automated, which can improve your deployment process. SQL Server 2025 benefits from the latest SSMS enhancements that provide better visibility into link status and replication health.
Replicate a database by using Azure SQL Managed Instance link wizard available in SSMS.
Replicate a database by using T-SQL and PowerShell scripts.
There are a few SQL Server features that aren't supported by Azure SQL Managed Instance link. For example, you can't enable the link feature if the functionality that's used on the primary SQL Server database isn't supported on Azure SQL Managed Instance, such as file tables and file streams.
For the full list of supported features and any SQL Server 2025-specific considerations, see Limitations of Azure SQL Managed Instance link.