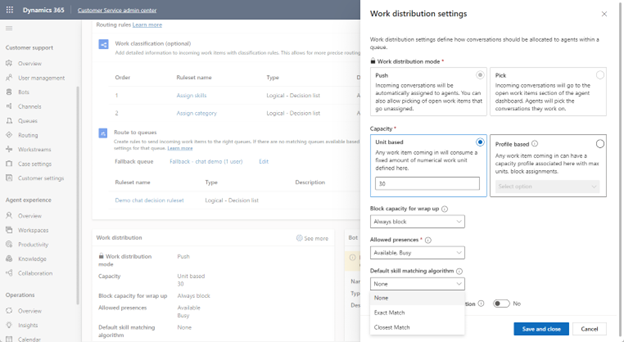
Define a default skill-matching algorithm for a workstream
Thus far, you've defined which skills will be used in your organization and have attached those skills to individual resources in your organization. Now, you'll define how skills will be attached to work items by defining skill-matching criteria. Based on the matching type that's defined and the attachment rules that have been created, the system will attach specific skills to an incoming conversation and then route them to representatives accordingly.
The two skill-matching types are exact skill matching and closest skill matching. The primary difference between the two is what the system does when it's unable to locate representatives with the appropriate skill proficiency levels. It's important to understand the steps that the system uses for distribution based on which skill-matching type is selected to ensure that conversations reach the most efficient location.
Exact skill matching
Exact skill matching works in a way that you might expect. The attachment logic identifies the skill(s) and the proficiency level for the skill that a representative should have to work on the conversation. The defined skills and proficiency levels represent the minimum requirements that the representative must have to receive the conversation. The distribution system searches for a representative who meets the minimum proficiency levels for the attached skills, as defined in the skill attachment logic. If the system is unable to find a representative who meets the minimum proficiency criteria, it will search for a representative who has a higher proficiency level. By first trying to find someone with the minimum proficiency level, the system can try to keep the higher qualified technicians available for potential calls that lower-level technicians couldn't work on. If the system doesn't find a representative with a higher proficiency level, it won't route the conversation to anyone; therefore, the conversation will remain in the queue until a representative selects it.
The following example shows how exact skill matching works in two different scenarios based on the Xbox 360 scenario that was previously mentioned. In the first scenario, only a single skill and proficiency are defined. In the second scenario, the system needs to match the Xbox 360 skills, the language skills, and the proficiency skills.
| Skill scenario | Skill & proficiency criteria | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Single | Xbox 360 = 4 | The system searches for a representative with Xbox 360 = 4, which represents the minimum criteria. If no representative with a proficiency of 4 is available, then the system will search for a representative with an Xbox 360 proficiency that's greater than 4. If the criteria aren't met, then the conversation (work item) remains in the queue that it was initially routed to. |
| Multiple | Xbox 360 = 4 Spanish = 5 | The system searches for a representative with Xbox 360 = 4 and Spanish = 5, the minimum criteria for each. When the criteria aren't met, the system will search for a representative with Xbox 360 proficiency that's greater than 4 and a Spanish proficiency that's greater than 5. If the criteria aren't met, then the conversation (work item) will remain in the queue. |
In both scenarios, if the system can't find a match, then the work item will remain in the queue. This reason is the primary one for selecting exact matching. Typically, you'd use exact matching in scenarios where it's more important that you have the appropriate representative working on a conversation and when you're willing to take more time to route the work item rather than sending it to anyone. You might use this approach when you're dealing with more advanced technical support issues.
Closest skill matching
Unlike exact matching, with closest skill matching, the conversation will always end with distribution to a representative. Similar to exact matching, with closest skill matching, the skill attachment logic identified proficiency level is set to the minimum criteria while the system searches for the representatives. When the system finds representative who has the skill and minimum proficiency levels, it will assign the conversation to that representative. Also, as with exact matching, if the minimum proficiency criteria aren't met, the system will search for representative who has a higher proficiency level.
Where closest matching differs is that, if the system can't find a representative with a higher proficiency level, it will look for representatives with the defined skill but will accept a lower proficiency level than the minimum criteria. The system will assign the conversation to a representative if they have at least one of the skills that matches the criteria. If the system is unable to find anyone who meets the skill proficiency level criteria, the distribution system will assign the conversation based on the capacity and availability of the representative.
The following table shows how closest matching would impact the previous Xbox 360 example.
| Skill scenario | Skill & proficiency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Single | Xbox 360 = 4 | The system searches for an agent who has Xbox 360 = 4 because it's the minimum criteria. When the criteria aren't met, the system will search for an agent who has an Xbox 360 proficiency that's greater than 4. If the agent is found, the system will assign the conversation to the agent. When the greater than criteria aren't met, the system will search for an agent who has an Xbox 360 proficiency that's less than 4. If the agent is found, the system will assign the conversation to the agent. When the criteria aren't met, the system will assign the conversation based on the capacity and availability of the agent. |
| Multiple | Xbox 360 = 4 Spanish = 5 | The system searches for an agent who meets the Xbox 360 = 4 and Spanish = 5 minimum criteria. When the criteria aren't met, the system will search for an agent who has an Xbox 360 proficiency that's greater than 4 and a Spanish proficiency that's greater than 5. When the greater than criteria aren't met, the system will search for an agent who has an Xbox 360 proficiency that's less than 4 and a Spanish proficiency that's less than 5. If an agent is found, the system will assign the conversation to the agent. When the less than criteria isn't met, the system will search for an agent who has an Xbox 360 proficiency that's less than 4 or a Spanish proficiency that's less than 5. If an agent is found, the system will assign the conversation to the agent. When the criteria aren't met, the system will assign the conversation based on the capacity and availability of the agent. |
You can specify which matching algorithm that you want to apply at the workstream level. In the Work distribution section, select more options and then set the Default skill matching algorithm to Exact Match, Closest Match, or None.