Define fields and their properties
A table contains several table properties that configure your table. A table also contains several fields that define what type of data that your table contains. Every field also has field properties. The following sections explain some of the important field properties.
Field No. and Name properties
Similar to table properties, every field also has a number and a name. For a field, these properties are Field No. and Name. When creating a new field, you must provide a field number to your new field. Keep in mind that when you extend an existing table with new fields, you must stick within the number ranges that are provided to you by Microsoft. Correspondingly, it's also important to give your fields an English name that can only exist once in a table.
DataType property
DataType is an important field property. The data type determines the type of data that you can store in the field.
The DataType property is found as the last part in your field definition, as follows:
field([number], [name], [datatype])
The following figure shows an example of the DataType property.
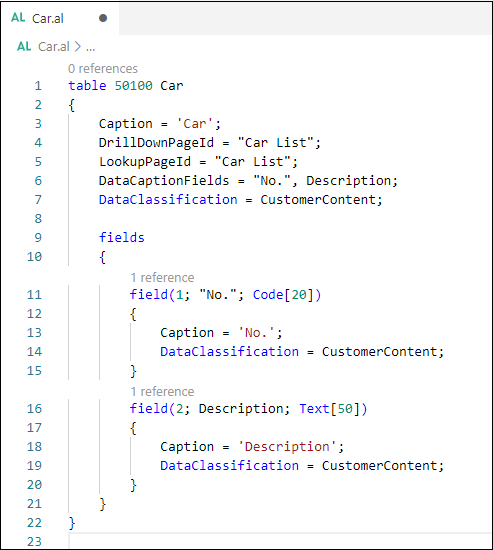
The data type can be one of the following types:
Text
Alphanumeric string
Max of 2048 characters
Corresponding SQL data type: NVARCHAR
Code
Uppercase alphanumeric string
Max of 250 characters
Corresponding SQL data type: NVARCHAR
Often used as a primary key
Decimal
Decimal number
From -999,999,999,999,999.99 to +999,999,999,999,999.99
Corresponding SQL data type: DECIMAL
Integer
Whole number
From -2,147,483,647 to 2,147,483,647
Corresponding SQL data type: INT
BigInteger
64-bit integer
Large whole numbers
Corresponding SQL data type: BIGINT
Binary
Binary data
Corresponding SQL data type: VARBINARY
Option
Option string
Comma-separated list of strings: valid values of the field
Cannot be extended by other extensions
Corresponding SQL data type: INT
Enum
Linked to an enum object
Can be extended by other extensions
Corresponding SQL data type: INT
Boolean
True or false
Formatted: Yes or No
Corresponding SQL data type: TINYINT
Date
Date value
From January 1, 1753 to December 31, 9999
Undefined date (default value): 0D
Corresponding SQL data type: DATETIME
Time
Time value
From 00:00:00 to 23:59:59.999
Undefined date (default value): 0T
Corresponding SQL data type: DATETIME
DateFormula
Holds a date formula
Ex. 30D, CM+1M, D15 (the fifteenth of each month)
DateTime
- A point in time, a combined date and time
Duration
- Difference (ms) between two points in time
BLOB
Binary Large Object
Store bitmaps and memos
Media
Store image
Optimized performance to manage images
MediaSet
A set of images
Manage a collection of images
RecordID
TableFilter
GUID
The Option data type is a comma-separated list of string with the valid values of the field. When you create a field with the Option data type, you should provide the OptionMembers property. The values of an Option field always start with zero (0). In the following example, Hatchback has value 0, Sedan has value 1, MPV has value 2, and so on.
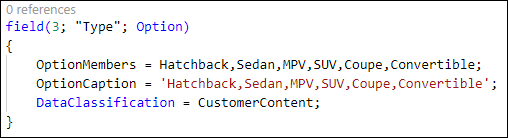
The problem with the Option data type is that it can't be extended by other AL extensions to add more values to the OptionMembers property.
An alternative to the Option data type is the Enum data type. To use this type, you first need to define the enum as a separate object with its own number and name. The Enum object is extensible.
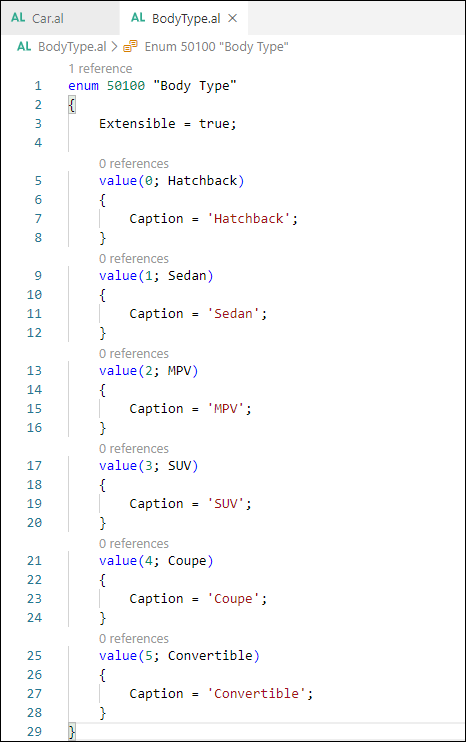
Instead of using an Option data type, you can define the field with an Enum data type.

ExtendedDataType property
The ExtendedDataType property affects the layout and behavior of controls on a page. This property can have one of following values:
None (this is the default value)
PhoneNo
URL
Email
Ratio
Masked
Person
Resource
Business Central allows users to select the value in a control and open a browser for a URL ExtendedDataType, open the email client with the Email ExtendedDataType, or start a phone call with the PhoneNo ExtendedDataType.