Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: ✔️ Linux VMs
Misconfigurations at the networking layer can cause common issues to occur in the Red Hat Update Infrastructure (RHUI). This article helps you identify and resolve some of these issues.
Overview
Access to the Microsoft Azure-hosted RHUI is limited to virtual machines (VMs) that are within the Azure Datacenter IP address ranges. For more information, see Red Hat Update Infrastructure for on-demand Red Hat Enterprise Linux VMs in Azure.
Red Hat configured these Azure-hosted RHUI servers to allow traffic only from Azure public IP ranges. Because of this setup, it's implied that if you use a virtual private network (VPN) or other means to reroute the traffic between Azure and the Azure-hosted RHUI servers, the Azure-hosted RHUI servers block that traffic.
Important
RHUI is intended only for pay-as-you-go (PAYG) images. For golden images, also known as bring your own subscription (BYOS), you can receive updates only if the system is attached to Red Hat Subscription Manager (RHSM) or Red Hat Satellite. For more information, see How to register and subscribe a RHEL system.
Symptoms
The yum repository list that RHUI manages is configured in your Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) instance during provisioning. You don't have to do any extra configuration. Just run yum update after your RHEL VM is ready for the latest updates. However, during the yum update operation, the connection eventually times out, and you see an error message that resembles one of the following output strings:
Output 1
https://rhui-3.microsoft.com/pulp/repos/microsoft-azure-rhel7/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 12] Timeout on https://rhui-3.microsoft.com/pulp/repos/microsoft-azure-rhel7/repodata/repomd.xml: (28, 'Operation timed out after 30000 milliseconds with 0 out of 0 bytes received')
Output 2
https://rhui4-1.microsoft.com/pulp/repos/content/dist/rhel8/rhui/8/x86_64/baseos/os/repodata/repomd.xml [OpenSSL SSL_connect: SSL_ERROR_SYSCALL in connection to http://rhui4-1.microsoft.com:443 ]
Output 3
DEBUG error: Curl error (28): Timeout was reached for https://rhui-1.microsoft.com/pulp/repos/content/dist/rhel8/rhui/8/x86_64/baseos/os/repodata/repomd.xml [Operation timed out after 30000 milliseconds with 0 out of 0 bytes received] (https://rhui-1.microsoft.com/pulp/repos/content/dist/rhel8/rhui/8/x86_64/baseos/os/repodata/repomd.xml).
Output 4
https://rhui-3.microsoft.com/pulp/repos/microsoft-azure-rhel7/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 14] curl#56 - "Network error recv()" [Errno 12] Timeout on https://rhui-3.microsoft.com/pulp/repos/microsoft-azure-rhel7/repodata/repomd.xml: (28, 'Operation timed out after 30000 milliseconds with 0 out of 0 bytes received')
Troubleshooting checklist
Troubleshooting step 1: Update IP addresses for RHUI version 4
Do you use a network configuration (custom firewall or UDR configurations) to further restrict https access from RHEL pay-as-you-go (PAYG) VMs? In this case, make sure that the correct IP addresses are allowed for yum update to work, depending on your environment. The following table shows the IP addresses to use for different regions in Azure Global for RHUI version 4.
| Region | IP address |
|---|---|
| West Europe | 52.136.197.163 |
| South Central US | 20.225.226.182 |
| East US | 52.142.4.99 |
| Australia East | 20.248.180.252 |
| Southeast Asia | 20.24.186.80 |
Note
As of October 12, 2023, all PAYG clients are directed to the RHUI 4 IP addresses in phase over the next two months. During this time, the RHUI 3 IP addresses remain in use for continued updates but will be removed at a future date. For uninterrupted access to packages and updates, you must update existing routes and rules that allow access to the RHUI 3 IP addresses so that they also include the RHUI 4 IP addresses. In order for you to continue to receive updates during the transition period, we recommend that you don't remove the RHUI 3 IP addresses.
All Azure government PAYG instances use the same RHUI IP addresses that were previously covered.
Troubleshooting step 2: Run a validation script
Azure makes available an RHUI repository validation script in GitHub. One of the many functions of the script is to validate the connectivity of the repository server and provide recommendations for a fix if it discovers a connectivity error. This Python script has the following features:
- Validates the RHUI client certificate.
- Validates RHUI rpm consistency.
- Does a consistency check between EUS, non-EUS repository configuration, and their requirements.
- Validates connectivity to the RHUI repositories. Reports that repository connectivity is successful if no errors are observed.
- Validates SSL connectivity to the RHUI repositories.
- Focuses exclusively in the RHUI repositories.
- Validates a found error by using the defined conditions and provides recommendations for a fix.
Supported Red Hat images
This version of the validation script currently supports only the following Red Hat VMs that are deployed from the Azure Marketplace image:
- RHEL 7.x PAYG VMs
- RHEL 8.x PAYG VMs
- RHEL 9.x PAYG VMs
- RHEL 10.x PAYG VMs
How to run the validation script
To run the validation script, enter the following shell commands on a Red Hat VM:
If the virtual machine has internet access, execute the script from the VM using the following command:
curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-support-scripts/refs/heads/master/Linux_scripts/rhui-check/rhui-check.py | sudo python2 -If the virtual machine doesn't have internet access, download the RHUI check script and transfer it to the virtual machine, and then execute the following command:
sudo python2 ./rhui-check.py
The script will generate a report that identifies any specific issues. The script output is also saved in /var/log/rhuicheck.log after execution. You can also inspect that log file separately.
Cause
The following list contains the underlying causes of RHUI connection failures:
User-defined routes (UDRs) aren't configured to have a next hop IP address to the internet.
UDR rules aren't configured to access any RHUI versions on UDR rules.
An incorrect or missing network security group (NSG) is configured for the network interface.
NSG rules aren't configured to access any RHUI versions.
The following sections contain scenarios that can cause these underlying failure causes to occur, and they outline solutions that fix the connection failures.
Scenario 1: VMs are configured to use an internal load balancer
An internal load balancer doesn't provide outbound connectivity when it's configured for network interfaces.
Solution 1a: Add a public IP address
Add a public IP address on the network interface of the VMs. For more information, see Associate a public IP address to a virtual machine.
Solution 1b: Use an external load balancer
Use an external Azure Load Balancer instead of an internal Azure Load Balancer. For more information, see Quickstart: Create a public load balancer to load balance VMs using the Azure portal.
Solution 1c: Use a NAT gateway on the subnet
Use a network address translation (NAT) gateway on the VMs subnet for outbound access. For more information, see Azure NAT Gateway resource.
Solution 1d: Use an internal basic load balancer
Downgrade to use an internal basic load balancer instead of an internal standard load balancer.
Note
This solution is only a temporary fix because the basic version of the load balancer is scheduled for retirement. For more information, see Azure Basic Load Balancer will be retired on 30 September 2025—upgrade to Standard Load Balancer.
Solution 1e: Use SNAT rules
Use source network address translation (SNAT) rules. For more information, see Use SNAT for outbound connections.
Scenario 2: RHUI server connects to your on-premises network instead of an RHUI public IP address
Red Hat VMs in Azure must connect to the RHUI servers to use the RHUI repositories and complete the updates. The connection requires that the request be sent to RHUI servers. In the forced tunneling scenario (express route) or VPN, the connection fails because the server connects to your on-premises network instead of an RHUI public IP address.
Solution 2: Create a UDR
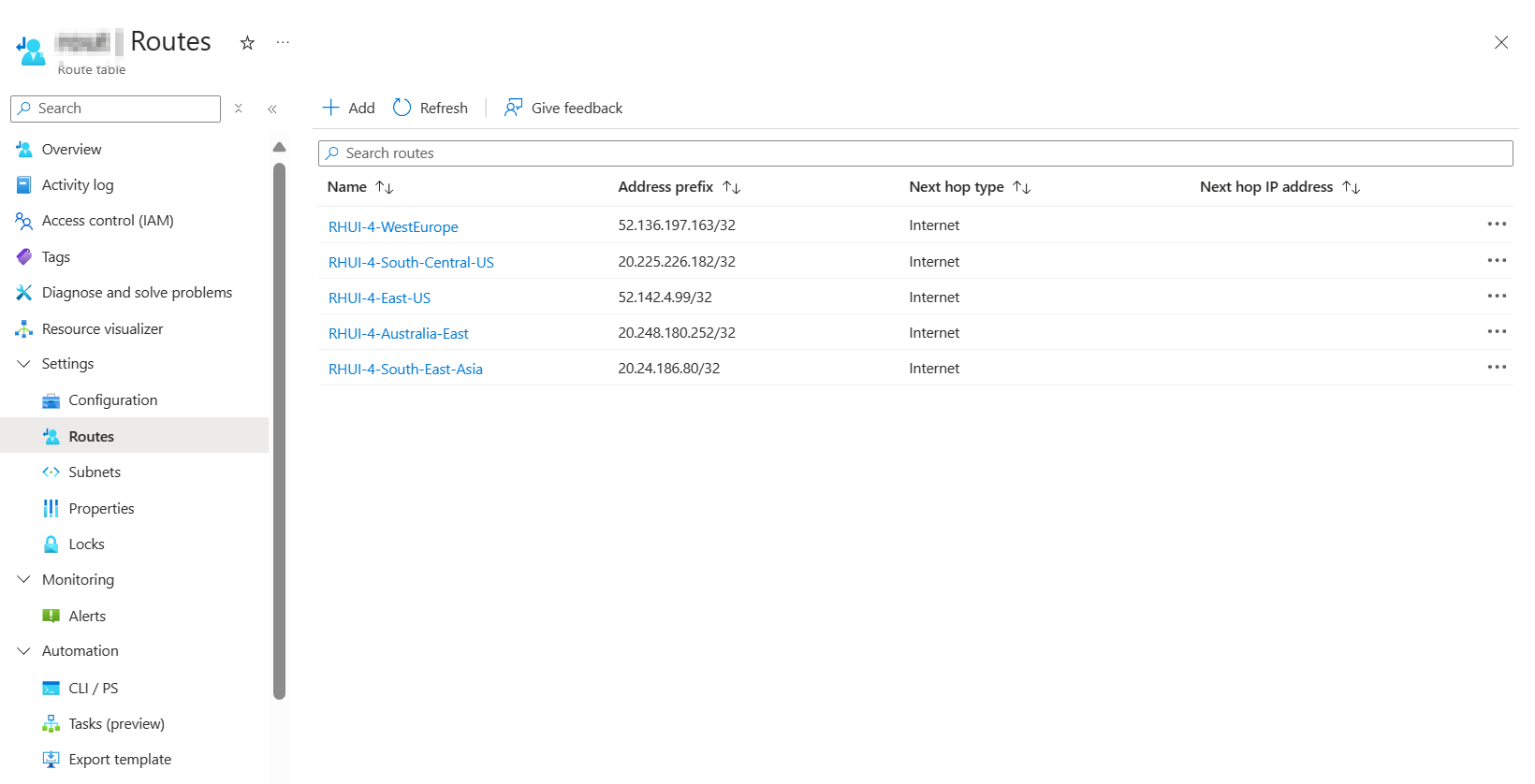
Create a UDR to route the traffic to the RHUI servers. The following screenshot shows the UDRs that you have to create in a route table on the Azure portal. The UDRs are based on the Azure Global regions and IP addresses listed in Troubleshooting step 1: Update IP addresses for RHUI version 4. For more information, see Create, change, or delete a route table.
Scenario 3: An Azure firewall or virtual appliance is between your virtual network and the internet
An Azure firewall or virtual appliance might exist that acts as a protective barrier between your Azure virtual network and the internet. This barrier enforces security policies and provides features to control and monitor traffic effectively, by sending all traffic to the firewall. In this case, the firewall is blocking the communication to RHUI servers.
Solution 3: Make sure that the RHUI IP addresses can be accessed
Make sure that the RHUI IP addresses are fully accessible by taking the following actions:
Verify that the destination RHUI IP addresses are allowed in firewall policies.
Verify that RHUI IP addresses are allowed if Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) inspection is active.
If an NSG is used, make sure that RHUI IP addresses are added to the allow list of the outbound rule of the network interface NSG or subnet NSG. The priority should be higher than the
Block_Internet_Access_outboundrule.
Scenario 4: A checkpoint firewall runs an SSL inspection
If the networking traffic route goes through a checkpoint firewall device that runs an SSL inspection, this process might alter the manner in which the RHUI certificate affects communication to the RHUI servers.
Solution 4: Add RHUI IP addresses and URLs to the allow list
Make sure that the RHUI IP addresses and URLs are included in the allow list if SSL inspection is active.
Scenario 5: A proxy is used for communication
Internet communication goes through a customer proxy that affects communication to the RHUI servers.
Solution 5: Fix the proxy configuration settings
If a proxy server is configured in Microsoft Azure between the RHEL VM and RHUI, use the correct proxy configuration settings in the /etc/yum.conf or /etc/dnf.conf files, as shown in the following snippet:
Important
If the configured proxy server has a private IP address, make sure that it has connectivity within the Azure public address space.
proxy=http://myproxy.mydomain.com:3128
proxy_username=proxy-user
proxy_password=password
Important
If no proxy server exists between the RHEL VM and RHUI, search for and remove any proxy configuration settings that are in the /etc/yum.conf or /etc/dnf.conf files.
Third-party information disclaimer
The third-party products that this article discusses are manufactured by companies that are independent of Microsoft. Microsoft makes no warranty, implied or otherwise, about the performance or reliability of these products.
Third-party contact disclaimer
Microsoft provides third-party contact information to help you find additional information about this topic. This contact information may change without notice. Microsoft does not guarantee the accuracy of third-party contact information.
Contact us for help
If you have questions or need help, create a support request, or ask Azure community support. You can also submit product feedback to Azure feedback community.