Track software update compliance assessment
Applies to: Configuration Manager
Before you can deploy software updates to clients, the clients must run a software updates compliance scan. We recommend that you allow enough time for clients to complete the scan and report compliance results so that you can review the compliance results and deploy only the updates that are required on the clients.
When the software update point (SUP) is installed and synchronized, a site-wide machine policy is created that informs client computers that Configuration Manager Software Updates was enabled for the site. When a client receives the machine policy, a compliance assessment scan is scheduled to start randomly within the next two hours. When the scan is started, a Software Updates Client Agent process clears the scan history, submits a request to find the Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server that should be used for the scan, and updates the local Group Policy with the WSUS location.
For an overview of the compliance assessment process, see Software updates compliance assessment.
Software update scan policy
Before a client can try to scan for updates, it needs the UpdateSource policy. This policy is created on the site server after a successful synchronization of the SUP. This section discusses how this policy is created by the following process:
Step 1: After a successful synchronization, WSyncMgr updates the Content Version and Last Sync Time in the database
After a successful synchronization on a primary site, WSyncMgr updates Last Sync Time and Content Version in the database for the SUP. This is done by executing the spProcessSUMSyncStateMessage stored procedure. In the following sample SQL Server Profiler trace, this stored procedure is executed to update the content version to 36:
declare @Error int; exec spProcessSUMSyncStateMessage N'2014-01-17 17:59:54', N'PS1', N'{C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}', 1, 0, '36', @Error output, N'PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM'
Step 2: SMSDBMON gets triggered and drops a .STN file in policypv.box
spProcessSUMSyncStateMessage updates the Update_SyncStatus table with the new Content Version and Sync Time. This update to the Update_SyncStatus table triggers SMSDBMON to drop a <UpdateSource_UniqueID>.STN file (STN stands for Scan Tool Notification) in policypv.box to indicate a change in the scan tool definition. The following are logged in SMSDBMON.log:
RCV: UPDATE on Update_SyncStatus for UpdSyncStatus_iu [{C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}][46680] SMS_DATABASE_NOTIFICATION_MONITOR
SND: Dropped E:\ConfigMgr\inboxes\policypv.box{C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}.STN (non-zero) [46680] SMS_DATABASE_NOTIFICATION_MONITOR
Step 3: Policy Provider creates or updates the UpdateSource policy in the database
The <UpdateSource_UniqueID>.STN file notifies Policy Provider that it should wake up and update the UpdateSource policy in the database.
The following are logged in PolicyPv.log:
Found {C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}.STN SMS_POLICY_PROVIDER
Added Scan Tool ID {C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC} SMS_POLICY_PROVIDER
Adding to delete list: E:\ConfigMgr\inboxes\policypv.box{C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}.STN SMS_POLICY_PROVIDER
In SQL Server Profiler trace:
select PolicyID, PolicyAssignmentID, SourceCRC, PADBID from SettingsPolicy where SourceID = N'PS1' and SourceType = N'UpdateSource'
select Version from Policy where PolicyID = N'{d0855677-b0a6-4e33-9bd5-7b0d06f0a2be}'
IF EXISTS (select PolicyID from Policy where PolicyID = N'{d0855677-b0a6-4e33-9bd5-7b0d06f0a2be}') update Policy set Version = N'40.00' where PolicyID = N'{d0855677-b0a6-4e33-9bd5-7b0d06f0a2be}' ELSE insert Policy (PolicyID, Version) values (N'{d0855677- b0a6-4e33-9bd5-7b0d06f0a2be}', N'40.00')exec sp_describe_undeclared_parameters N'UPDATE Policy SET Body = @P1 where PolicyID = N''{d0855677-b0a6-4e33-9bd5- 7b0d06f0a2be}'''
IF EXISTS (select PADBID from PolicyAssignment where PADBID = 16777218) update PolicyAssignment set Version = N'40.00', InProcess = 1 , BodyHash = null where PADBID = 16777218 ELSE insert PolicyAssignment (PolicyAssignmentID, PADBID, Version, PolicyID) values (N'{375c8020-3cae-4736-89ca-ccf1ce6e3709}', 16777218, N'40.00', N'{d0855677-b0a6-4e33-9bd5-7b0d06f0a2be}')exec sp_describe_undeclared_parameters N'UPDATE PolicyAssignment SET Body = @P1 where PADBID = 16777218'
update PolicyAssignment set InProcess = 0, BodySignature = N'<BodySignatureTruncated>', TombstoneBodySignature = N'<TombstoneBodySignatureTruncated>', HashAlgOID = N'1.2.840.113549.1.1.11', HashAlgId = 32780, BodyHash = N'<BodyHashTruncated>', TombstoneBodyHash = N'<TombstoneBodyHashTruncated>' where PADBID = 16777218
To see this policy in the database, run the following query:
SELECT CONVERT(XML, Body, 1), * FROM Policy WHERE PolicyID = (SELECT PolicyID FROM SettingsPolicy WHERE SourceType = 'UpdateSource')
This policy contains the content version of the update server which is used to find the location of the WSUS computer that the client can scan against. After this policy is created or updated in the database, the clients get the new or updated UpdateSource policy during the next policy evaluation cycle.
Step 4: Policy is downloaded and evaluated on the client
The following are logged in PolicyAgent.log on the client:
Successfully initiated download of policy 'CCM_Policy_Policy5.PolicyID="{d0855677-b0a6-4e33-9bd5- 7b0d06f0a2be}",PolicySource="SMS:PS1",PolicyVersion="40.00"' PolicyAgent_ReplyAssignments
Policy 'CCM_Policy_Policy5.PolicyID="{d0855677-b0a6-4e33-9bd5-7b0d06f0a2be}",PolicyVersion="40.00",PolicySource="SMS:PS1"' successfully compiled PolicyAgent_PolicyDownload
In PolicyEvaluator.log on the client:
Updating policy CCM_Policy_Policy5.PolicyID="{d0855677-b0a6-4e33-9bd5- 7b0d06f0a2be}",PolicySource="SMS:PS1",PolicyVersion="40.00" PolicyAgent_PolicyEvaluator
Applied policy CCM_Policy_Policy5.PolicyID="{d0855677-b0a6-4e33-9bd5- 7b0d06f0a2be}",PolicySource="SMS:PS1",PolicyVersion="40.00" PolicyAgent_PolicyEvaluator
Policy state for [CCM_Policy_Policy5.PolicyID="{d0855677-b0a6-4e33-9bd5-7b0d06f0a2be}",PolicyVersion="40.00",PolicySource="SMS:PS1"] is currently [Active] PolicyAgent_PolicyEvaluator
To find the PolicyID of the UpdateSource policy on a client, run the following WQL query:
- Namespace:
ROOT\ccm\Policy\Machine\RequestedConfig - Query:
SELECT * FROM CCM_Policy_Policy5 WHERE PolicyCategory = 'UpdateSource'
Once this policy is compiled on the client, the UpdateSource information is stored in the following WMI Class:
Namespace: ROOT\ccm\Policy\Machine\ActualConfig
Class: CCM_UpdateSource
Tip
If you compare the instance of CCM_UpdateSource class on the client with the XML body retrieved from the policy table, you will notice that the content of the XML looks identical to the instance.
Step 5: Scan Agent is notified that the UpdateSource policy is updated
The following are logged in ScanAgent.log on the client:
Inside CScanAgent::Notify() ScanAgent
CScanAgent::OnPolicyChange- Policy InstanceModificationEvent notification received ScanAgent
WSUS server location
After receiving the UpdateSource policy, the client has the necessary configuration to initiate a scan. However, policy updates won't initiate immediate scans. A scan can be triggered manually through the Configuration Manager control panel or occur automatically at the next scheduled time. At this point, the client locates the WSUS computer with the content version specified in the policy. This process is very similar to the way that the client finds the location of a distribution point for a specific package and version.
Step 1: Scan Agent creates a scan request based on the available policy
The following are logged in ScanAgent.log:
CScanAgent::ScanByUpdates- Policy available for UpdateSourceID={C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC} ContentVersion=38 ScanAgent
CScanAgent::ScanByUpdates- Added Policy to final ScanRequest List UpdateSourceID={C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}, Policy-ContentVersion=38, Required-ContentVersion=38 ScanAgent
Step 2: Scan Agent sends a request for the WSUS location to Location Services
Scan Agent now requests the WSUS location from Location Services and waits for a response. In this example, the location request ID is {C2BB9710-C548-49D0-9DF8-5F9CFC5F3862}. The following are logged in ScanAgent.log:
Inside CScanAgent::ProcessScanRequest() ScanAgent
CScanJobManager::Scan- entered ScanAgent
ScanJob({4CD06388-D509-46E4-8C00-75909EDD9EE8}): CScanJob::Initialize- entered ScanAgent
ScanJob({4CD06388-D509-46E4-8C00-75909EDD9EE8}): CScanJob::Scan- entered ScanAgent
ScanJob({4CD06388-D509-46E4-8C00-75909EDD9EE8}): CScanJob::RequestLocations- entered ScanAgent
- - - - - -Requesting WSUS Server Locations from LS for {C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC} version 38 ScanAgent
- - - - - -Location Request ID = {C2BB9710-C548-49D0-9DF8-5F9CFC5F3862} ScanAgent
CScanAgentCache::PersistInstanceInCache- Persisted Instance CCM_ScanJobInstance ScanAgent
ScanJob({4CD06388-D509-46E4-8C00-75909EDD9EE8}): - - - - - -Locations requested for ScanJobID={4CD06388-D509-46E4-8C00-75909EDD9EE8} (LocationRequestID={C2BB9710-C548-49D0-9DF8-5F9CFC5F3862}), will process the scan request once locations are available. ScanAgent
Each scan job is stored in WMI in the CCM_ScanJobInstance class:
Namespace: root\CCM\ScanAgent
Class: CCM_ScanJobInstance
Step 3: Location Services sends the location request to the management point
Location Services creates a location request and sends it to the management point. The package ID for a WSUS location request is the UpdateSource unique ID. The following are logged in LocationServices.log:
CCCMWSUSLocation::GetLocationsAsyncEx LocationServices
Attempting to persist WSUS location request for ContentID='{C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}' and ContentVersion='38' LocationServices
Persisted WSUS location request LocationServices
Attempting to send WSUS Location Request for ContentID='{C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}' LocationServices
WSUSLocationRequest : <WSUSLocationRequest SchemaVersion="1.00"><Content ID="{C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3- 12D7205B39CC}" Version="38"/><AssignedSite SiteCode="PS1"/><ClientLocationInfo OnInternet="0"><ADSite Name="CM12-R2- PS1"/><Forest Name="CONTOSO.COM"/><Domain Name="CONTOSO.COM"/><IPAddresses><IPAddress SubnetAddress="192.168.2.0" Address="192.168.2.62"/></IPAddresses></ClientLocationInfo></WSUSLocationRequest> LocationServices
Created and Sent Location Request '{C2BB9710-C548-49D0-9DF8-5F9CFC5F3862}' for package {C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3- 12D7205B39CC} LocationServices
Step 4: CCM Messaging sends the location request message to the management point
The following are logged in CcmMessaging.log:
Sending async message '{76453CC6-76BA-4B68-BE30-BA70754570BB}' to outgoing queue 'mp:[http]mp_locationmanager' CcmMessaging
Sending outgoing message '{76453CC6-76BA-4B68-BE30-BA70754570BB}'. Flags 0x200, sender account empty CcmMessaging
Step 5: The management point parses the request, obtains the WSUS location from the database, and sends a response
The management point parses this request and calls the MP_GetWSUSServerLocations stored procedure to get the WSUS locations from the database. The following are logged in MP_Location.log:
MP LM: Message Body : <WSUSLocationRequest SchemaVersion="1.00"><Content ID="{C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3- 12D7205B39CC}" Version="38"/><AssignedSite SiteCode="PS1"/><ClientLocationInfo OnInternet="0"><ADSite Name="CM12-R2- PS1"/><Forest Name="CONTOSO.COM"/><Domain Name="CONTOSO.COM"/><IPAddresses><IPAddress SubnetAddress="192.168.2.0" Address="192.168.2.62"/></IPAddresses></ClientLocationInfo></WSUSLocationRequest> MP_LocationManager
MP LM: calling MP_GetWSUSServerLocations MP_LocationManager
In SQL Server Profiler trace:
exec MP_GetMPSitesFromAssignedSite N'PS1'
exec MP_GetSiteInfoUnified N'<ClientLocationInfo OnInternet="0"><ADSite Name="CM12-R2-PS1"/><Forest Name="CONTOSO.COM"/><Domain Name="CONTOSO.COM"/><IPAddresses><IPAddress SubnetAddress="192.168.2.0" Address="192.168.2.62"/></IPAddresses></ClientLocationInfo>'
exec MP_GetWSUSServerLocations N'{C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}',N'38',N'PS1',N'PS1',N'0',N'CONTOSO.COM'
After getting the results from the stored procedure, the management point sends a response to the client. The following is logged in MP_Location.log:
MP LM: Reply message body:
<WSUSLocationReply SchemaVersion="1.00"><Sites><Site><MPSite SiteCode="PS1"/><LocationRecords><LocationRecord WSUSURL="http://PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM:8530" ServerName="PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM" Version="38"/><LocationRecord WSUSURL="https://PS1SYS.CONTOSO.COM:8531" ServerName="PS1SYS.CONTOSO.COM" Version="38"/></LocationRecords></Site></Sites></WSUSLocationReply> MP_LocationManager
Step 6: CCM Messaging receives the response and sends it back to Location Services
The CcmMessaging.log file on the client shows that a reply was received. This message was delivered to Location Services:
Message '{76453CC6-76BA-4B68-BE30-BA70754570BB}' got reply '{8E6D05EF-B77F-4AD0-AF64-1C6F3069A29C}' to local endpoint queue 'LS_ReplyLocations' CcmMessaging
OutgoingMessage(Queue='mp_[http]mp_locationmanager', ID={76453CC6-76BA-4B68-BE30-BA70754570BB}): Delivered successfully to host 'PS1SYS.CONTOSO.COM'. CcmMessaging
Message '{8E6D05EF-B77F-4AD0-AF64-1C6F3069A29C}' delivered to endpoint 'LS_ReplyLocations' CcmMessaging
Step 7: Location Services parses the response and sends the location back to Scan Agent
The following are logged in LocationServices.log:
Processing Location reply message LocationServices 1/20/2014 12:18:09 PM
WSUSLocationReply : <WSUSLocationReply SchemaVersion="1.00"><Sites><Site><MPSite SiteCode="PS1"/><LocationRecords><LocationRecord WSUSURL="http://PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM:8530" ServerName="PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM" Version="38"/><LocationRecord WSUSURL="https://PS1SYS.CONTOSO.COM:8531" ServerName="PS1SYS.CONTOSO.COM" Version="38"/></LocationRecords></Site></Sites></WSUSLocationReply> LocationServices
Calling back with the following WSUS locations LocationServices
WSUS Path='http://PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM:8530', Server='PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM', Version='38' LocationServices
WSUS Path='https://PS1SYS.CONTOSO.COM:8531', Server='PS1SYS.CONTOSO.COM', Version='38' LocationServices
Calling back with locations for WSUS request {C2BB9710-C548-49D0-9DF8-5F9CFC5F3862} LocationServices
Step 8: Scan Agent notifies WUAHandler to add the update source to the registry
Scan Agent now has the policy and the update source location with the appropriate content version. The following are logged in ScanAgent.log:
*****WSUSLocationUpdate received for location request guid={C2BB9710-C548-49D0-9DF8-5F9CFC5F3862} ScanAgent
ScanJob({4CD06388-D509-46E4-8C00-75909EDD9EE8}): CScanJob::OnLocationUpdate- Received Location=http://PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM:8530, Version=38 ScanAgent
ScanJob({4CD06388-D509-46E4-8C00-75909EDD9EE8}): CScanJob::Execute- Adding UpdateSource={C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}, ContentType=2, ContentLocation=http://PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM:8530, ContentVersion=38 ScanAgent
Scan Agent notifies WUAHandler to add the update source. WUAHandler adds the update source to the registry and initiates a Group Policy refresh (if the client is in domain) to see whether Group Policy overrides the update server that we just added. The following are logged in WUAHandler.log on a new client showing a new update source being added:
Its a WSUS Update Source type ({C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}), adding it. WUAHandler
Its a completely new WSUS Update Source. WUAHandler
Enabling WUA Managed server policy to use server:http://PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM:8530WUAHandler
Policy refresh forced. WUAHandler
Waiting for 2 mins for Group Policy to notify of WUA policy change... WUAHandler
Waiting for 30 secs for policy to take effect on WU Agent. WUAHandler
Added Update Source ({C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}) of content type: 2 WUAHandler
During this time, the Windows Update Agent sees a WSUS configuration change. The following are logged in WindowsUpdate.log:
2014-01-20 12:18:11:520 968 9d0 Agent * WSUS server:
http://PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM:8530(Changed)
2014-01-20 12:18:11:520 968 9d0 Agent * WSUS status server:http://PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM:8530(Changed)
2014-01-20 12:18:11:520 968 9d0 AU Sus server changed through policy.
The following registry keys are checked and set:
| Registry subkey | Value name | Type | Data |
|---|---|---|---|
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate |
WUServer | REG_SZ | The full WSUS server URL including the port. For example, http://PS1Site.Contoso.com:8530 |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate |
WUStatusServer | REG_SZ | The full WSUS server URL including the port. For example, http://PS1Site.Contoso.com:8530 |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\AU |
UseWUServer | REG_DWORD | 0x1 |
For an existing client, we could expect to see the following in WUAHandler.log to denote when content version has incremented:
Its a WSUS Update Source type ({C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}), adding it. WUAHandler
WSUS update source already exists, it has increased version to 38. WUAHandler
Step 9: Scan Agent initiates the scan
After the update source is successfully added, Scan Agent raises a state message and initiates the scan. The following are logged in ScanAgent.log:
ScanJob({4CD06388-D509-46E4-8C00-75909EDD9EE8}): Raised UpdateSource ({C2D17964-BBDD-4339-B9F3-12D7205B39CC}) state message successfully. StateId = 2 ScanAgent
ScanJob({4CD06388-D509-46E4-8C00-75909EDD9EE8}): CScanJob::Execute - successfully requested Scan, ScanType=1 ScanAgent
Software update scan on clients
After the update source policy and the update source location are available, Scan Agent initiates the scan. Software update scan is actually performed by the Windows Update Agent. However, the Configuration Manager client interacts with the Windows Update Agent to perform a scan and obtain the scan results. This interaction is handled by the Windows Update Agent Handler (WUAHandler) component, which communicates with the Windows Update Agent.
Step 1: Scan Agent requests the scan and WUAHandler initiates the scan
Scan Agent requests the scan from WUAHandler, which uses the Windows Update Agent API to request a software update scan from the Windows Update Agent. The following is logged in ScanAgent.log:
ScanJob({4CD06388-D509-46E4-8C00-75909EDD9EE8}): CScanJob::Execute - successfully requested Scan, ScanType=1 ScanAgent
The following are logged in WUAHandler.log:
Scan results will include superseded updates only when they are superseded by service packs and definition updates. WUAHandler
Search Criteria is (DeploymentAction=* AND Type='Software') OR (DeploymentAction=* AND Type='Driver') WUAHandler
Running single-call scan of updates. WUAHandler
Async searching of updates using WUAgent started. WUAHandler
Step 2: Windows Update Agent (WUA) starts the scan against the WSUS computer
Windows Update Agent starts a scan after receiving a request from the Configuration Manager client (CcmExec). Because the Windows Update Server value was already set to the SUP server, this scan is performed against the WSUS server that has the SUP role installed. The following are logged in WindowsUpdate.log:
2014-01-20 12:18:42:694 3856 708 COMAPI -- START -- COMAPI: Search [ClientId = CcmExec]
2014-01-20 12:18:42:752 3856 708 COMAPI <<-- SUBMITTED -- COMAPI: Search [ClientId = CcmExec]
2014-01-20 12:18:47:511 968 f58 PT + ServiceId = {3DA21691-E39D-4DA6-8A4B-B43877BCB1B7}, Server URL =http://PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM:8530/ClientWebService/client.asmx
2014-01-20 12:18:48:662 968 f58 Agent ** START ** Agent: Finding updates [CallerId = CcmExec]
2014-01-20 12:18:48:662 968 f58 Agent * Include potentially superseded updates
2014-01-20 12:18:48:662 968 f58 Agent * Online = Yes; Ignore download priority = Yes
2014-01-20 12:18:48:662 968 f58 Agent * Criteria = "(DeploymentAction=* AND Type='Software') OR (DeploymentAction=* AND Type='Driver')"
2014-01-20 12:18:48:662 968 f58 Agent * ServiceID = {3DA21691-E39D-4DA6-8A4B-B43877BCB1B7} Managed
2014-01-20 12:18:48:662 968 f58 Agent * Search Scope = {Machine}
Windows Update Agent now scans against the WSUS server and reports the results to CcmExec (specifically WUAHandler). The following are logged in WindowsUpdate.log:
2014-01-20 12:18:49:175 968 f58 PT + ServiceId = {3DA21691-E39D-4DA6-8A4B-B43877BCB1B7}, Server URL =
http://PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM:8530/ClientWebService/client.asmx
2014-01-20 12:18:52:680 968 f58 Agent * Added update {4AE85C00-0EAA-4BE0-B81B-DBD7053D5FAE}.104 tosearch result
2014-01-20 12:18:52:683 968 f58 Agent * Added update {57260DFE-227C-45E3-9FFC-2FC77A67F95A}.104 to search result
2014-01-20 12:18:52:694 968 f58 Agent * Found 163 updates and 70 categories in search; evaluated appl. rules of 622 out of 1150 deployed entities
2014-01-20 12:18:52:745 968 f58 Agent ** END ** Agent: Finding updates [CallerId = CcmExec]
2014-01-20 12:18:52:755 3856 708 COMAPI >>-- RESUMED -- COMAPI: Search [ClientId = CcmExec]
2014-01-20 12:18:53:137 3856 708 COMAPI - Updates found = 163
2014-01-20 12:18:53:137 3856 708 COMAPI -- END -- COMAPI: Search [ClientId = CcmExec]
Step 3: WUAHandler receives the results from the Windows Update Agent and marks the scan as complete
The following are logged in WUAHandler.log:
Async searching completed. WUAHandler
Finished searching for everything in single call. WUAHandler
Step 4: WUAHandler parses the scan results
WUAHandler then parses the results, which include the applicability state for each update. As part of this process, superseded updates are pruned out. The following are logged in WUAHandler.log:
Pruning: update id (70f4f236-0248-4e84-b472-292913576fa1) is superseded by (726b7201-862a-4fde-9b12-f36b38323a6f). WUAHandler
...
Update (Installed): Security Update for Windows 7 for x64-based Systems (KB2584146) (4ae85c00-0eaa-4be0-b81b-dbd7053d5fae, 104) WUAHandler
Update (Missing): Security Update for Windows 7 for x64-based Systems (KB2862152) (505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773, 200) WUAHandler
...
Successfully completed scan. WUAHandler
Step 5: Update store records the status and raises a state message for each update in WMI
Once the scan results are available, these results are stored in the updates store. Update store records the current state of each update and creates a state message for each update. These state messages are forwarded to the site server in bulk at the end of the status message reporting cycle (which is 15 minutes, by default).
UpdatesStore.log showing state for missing update (KB2862152) being recorded and a state message being raised:
Processing update status from update (505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773) with ProductID = 0fa1201d-4330-4fa8-8ae9- b877473b6441 UpdatesStore
Update status from update (505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773) hasn't been reported before, creating new instance. UpdatesStore
Successfully raised state message for update (505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773) with state (Missing). UpdatesStore
Successfully added WMI instance of update status (505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773). UpdatesStore
StateMessage.log showing state message being recorded with State ID 2 (missing):
Adding message with TopicType 500 and TopicId 505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773 to WMI StateMessage
State message(State ID : 2) with TopicType 500 and TopicId 505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773 has been recorded for SYSTEM StateMessage
For each update, an instance of the CCM_UpdateStatus class is created or updated, and this stores the current status of the update. The CCM_UpdateStatus class is located in the ROOT\CCM\SoftwareUpdates\UpdatesStore namespace.
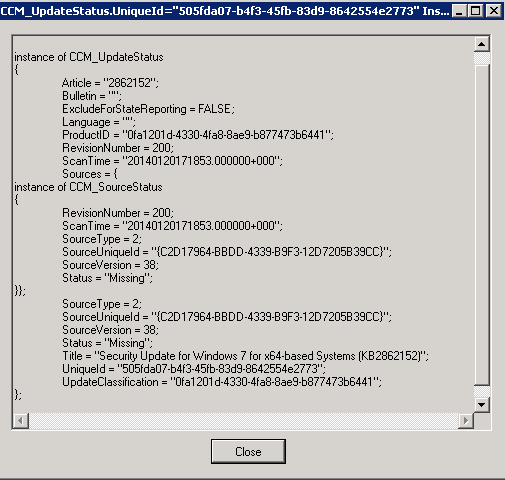
Similarly, an instance of the CCM_StateMsg class is created or updated, and this stores the current state of the update. The CCM_StateMsg class is located in the ROOT\CCM\StateMsg namespace.
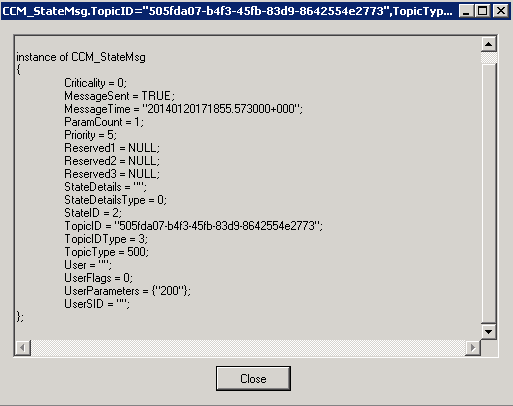
Step 6: State messages are sent to the management point
As mentioned earlier, state messages are sent to the management point based on the state message reporting cycle schedule, which is configured to 15 minutes by default. Once a state message is sent to the management point, the MessageSent property for the state message instance in the CCM_StateMsg class is set to True.
In StateMessage.log:
StateMessage body: <XML Report Body Truncated> StateMessage
Successfully forwarded State Messages to the MP StateMessage
The following is how the state message body looks like for our update. Normally this XML body is too large for the log and is truncated in CMTrace. However, you can see the whole XML body in Notepad.
StateMessage body: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-16"?>
<Report><ReportHeader><Identification><Machine><ClientInstalled>1</ClientInstalled><ClientType>1</ClientType><ClientID>GUID: A1006D0E-CF56-41D1-A006-6330EFC39381</ClientID><ClientVersion>5.00.7958.1000</ClientVersion><NetBIOSName>PS1WIN7X64</NetBIOSName><CodePage>437</CodePage><SystemDefaultLCID>1033</SystemDefaultLCID><Priority>5</Priority></Machine></Identification><ReportDetails><ReportContent>State Message Data</ReportContent><ReportType>Full</ReportType><Date>20140120194656.903000+000</Date><Version>1.0</Version><Format>1.0</Format></ReportDetails></ReportHeader><ReportBody><StateMessage MessageTime="20140120171855.573000+000" SerialNumber="232"><Topic ID="505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773" Type="500" IDType="3" User="" UserSID=""/><State ID="2" Criticality="0"/><UserParameters Flags="0" Count="1"><Param>200</Param></UserParameters></StateMessage></ReportBody></Report> StateMessage
Successfully forwarded State Messages to the MP StateMessage
State message processing flow
We now know how a state message is recorded and the WMI location where these state messages are stored. We also know that unsent state messages on a client are sent to the management point every 15 minutes by default, per the state message reporting cycle. This schedule can be modified in the State Messaging of the custom or default client settings.
Although StateMessage.log reports Successfully forwarded State Messages to the MP, the State Message component isn't actually sending these messages itself. All messages sent and received from the management point are handled by the CCM Messaging component on the client. CCM Messaging is the actual component that communicates with the management point for sending and receiving data. The management point has various queues defined to handle different kinds of incoming traffic. For state messages, the queue that handles this traffic is the MP_RelayEndpoint queue.
Step 1: The State Message component starts sending messages to the management point
In StateMessage.log:
StateMessage body: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-16"?> <Report><ReportHeader><Identification><Machine><ClientInstalled>1</ClientInstalled><ClientType>1</ClientType><ClientID>GUID: A1006D0E-CF56-41D1-A006-6330EFC39381</ClientID><ClientVersion>5.00.7958.1000</ClientVersion><NetBIOSName>PS1WIN7X64</NetBIOSName><CodePage>437</CodePage><SystemDefaultLCID>1033</SystemDefaultLCID><Priority>5</Priority></Machine></Identification><ReportDetails><ReportContent>State Message Data</ReportContent><ReportType>Full</ReportType><Date>20140120194656.903000+000</Date><Version>1.0</Version><Format>1.0</Format></ReportDetails></ReportHeader><ReportBody><StateMessage MessageTime="20140120171855.573000+000" SerialNumber="232"><Topic ID="505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773" Type="500" IDType="3" User="" UserSID=""/><State ID="2" Criticality="0"/><UserParameters Flags="0" Count="1"><Param>200</Param></UserParameters></StateMessage></ReportBody></Report> StateMessage
Successfully forwarded State Messages to the MP StateMessage
Step 2: CCM Messaging sends a message containing the state message XML body to the management point
CCM Messaging sends a message to the MP_RelayEndpoint queue successfully. This message doesn't have a reply, unlike the one we noticed earlier in the WSUS Location Request section where the message with the Location Request received a reply.
In CcmMessaging.log:
Sending async message '{95F79010-D0EB-49A6-8A1E-3897883105F2}' to outgoing queue 'mp:mp_relayendpoint' CcmMessaging
Sending outgoing message '{95F79010-D0EB-49A6-8A1E-3897883105F2}'. Flags 0x200, sender account empty CcmMessaging
POST: Host=PS1SYS.CONTOSO.COM, Path=/ccm_system/request, Port=443, Protocol=https, Flags=512, Options=480 CcmMessaging
Message '{95F79010-D0EB-49A6-8A1E-3897883105F2}' doesn't have reply CcmMessaging
OutgoingMessage(Queue='mp_mp_relayendpoint', ID={95F79010-D0EB-49A6-8A1E-3897883105F2}): Delivered successfully to host 'PS1SYS.CONTOSO.COM'. CcmMessaging
Step 3: The message is received on the management point, and then MP_Relay processes the message and creates an SMX file
As all messages are sent using HTTP/HTTPS and are received by IIS. In this example, this request is made to the CCM_System virtual directory.
In IIS log:
192.168.2.12 CCM_POST /ccm_system/request - 443 - 192.168.2.62 ccmhttp - 200 0 0 542 31
Once the message is received successfully on the management point, the MP_Relay component processes this message, converts the message into an SMX file, and moves the SMX file to the appropriate location depending on whether the management point is colocated on the site server or not.
- On a remote management point: \SMS\mp\outboxes\StateMsg.box
- On a management point colocated on the site server: \inboxes\auth\StateSys.box\incoming
In MP_Relay.log on a management point co-located on the site server:
Mp Message Handler: start message processing for Relay----------------------- MP_RelayEndpoint
Mp Message Handler: FileType=SMX MP_RelayEndpoint
Message Body : <XML Body Truncated> MP_RelayEndpoint
Relay: Outbox dir: E:\ConfigMgr\inboxes\auth\statesys.box\incoming MP_RelayEndpoint
Priority in the message = 5 MP_RelayEndpoint
State Priority Directory = E:\ConfigMgr\inboxes\auth\statesys.box\incoming MP_RelayEndpoint
Inv-Relay: Task completed successfully MP_RelayEndpoint
In MP_Relay.log on a remote management point:
Mp Message Handler: start message processing for Relay------------------------------ MP_RelayEndpoint
Mp Message Handler: FileType=SMX MP_RelayEndpoint
Message Body :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-16"?>
<Report><ReportHeader><Identification><Machine><ClientInstalled>1</ClientInstalled><ClientType>1</ClientType><ClientID>GUID: A1006D0E-CF56-41D1-A006-6330EFC39381</ClientID><ClientVersion>5.00.7958.1000</ClientVersion><NetBIOSName>PS1WIN7X64</NetBIOSName><CodePage>437</CodePage><SystemDefaultLCID>1033</SystemDefaultLCID><Priority>5</Priority></Machine></Identification><ReportDetails><ReportContent>State Message Data</ReportContent><ReportType>Full</ReportType><Date>20140120194656.903000+000</Date><Version>1.0</Version><Format>1.0</Format></ReportDetails></ReportHeader><ReportBody><StateMessage MessageTime="20140120171855.573000+000" SerialNumber="232"><Topic ID="505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773" Type="500" IDType="3" User="" UserSID=""/><State ID="2" Criticality="0"/><UserParameters Flags="0" Count="1"><Param>200</Param></UserParameters></StateMessage></ReportBody></Report> MP_RelayEndpoint
Inv-Relay Task: Processing message body MP_RelayEndpoint
Relay: Outbox dir: C:\SMS\mp\outboxes\StateMsg.box MP_RelayEndpoint
Priority in the message = 5 MP_RelayEndpoint
State Priority Directory = C:\SMS\mp\outboxes\StateMsg.box MP_RelayEndpoint
Inv-Relay: Task completed successfully MP_RelayEndpoint
The XML body looks identical to what's logged in StateMessage.log on the client.
Step 4: MP File Dispatch Manager sends the SMX file to the site server (only when the management point isn't colocated on-site server)
When the management point is remote to the site server, after the file arrives in outboxes\StateMsg.box, MP File Dispatch Manager (MPFDM) is responsible for moving these files to the StateMsg.box inbox on the site server. When the management point is colocated on the site server, these files are moved directly to the appropriate Inbox folder, so MPFDM isn't involved.
In MPFDM.log on a remote management point:
Moved file C:\SMS\MP\OUTBOXES\statemsg.box\TAZGYTSJ.SMX to \\PS1SITE.CONTOSO.COM\SMS_PS1\inboxes\auth\statesys.box\incoming\TAZGYTSJ.SMX SMS_MP_FILE_DISPATCH_MANAGER
For MPFDM to move the files to the appropriate inbox, the remote management point must be able to access the registry of the site server to determine the Inbox source locations. Therefore, the Remote Registry service must be running, and Registry Access should not be blocked by Group Policy. MPFDM determines the Inbox locations by accessing the following registry key on the site server:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SMS\Inbox Source
Step 5: StateSys component on the site server processes the state message to the database
After the file arrives in \inboxes\auth\StateSys.box on the site server, the State System Manager (StateSys) component wakes up and processes the SMX file(s).
In StateSys.log with verbose logging enabled:
Inbox notification triggered, pause for 10 seconds...... SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
Found new state messages to process, starting processing thread SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
Thread "State Message Processing Thread #0" id:4316 started SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
total chucks loaded (1) SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
CMessageProcessor - Processing file: YCE2H3VD.SMX SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
CMessageProcessor - Processed 1 records with 0 invalid records. SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
CMessageProcessor - Processed 1 message files in this batch, with 0 bad files. SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
total chucks loaded (0) SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
Thread "State Message Processing Thread #0" id:4316 terminated normally SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
In StateSys.log without verbose logging enabled:
Found new state messages to process, starting processing thread SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
Thread "State Message Processing Thread #0" id:1988 started SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
total chucks loaded (1) SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
total chucks loaded (0) SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
Thread "State Message Processing Thread #0" id:1988 terminated normally SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
The StateSys.log file doesn't log the file name unless verbose logging is enabled for State System Manager.
The SMX file that's moved to the StateSys.box folder contains the message body XML. When StateSys processes this file, it calls the spProcessStateReport stored procedure and passes this XML body on to the stored procedure as a parameter.
In SQL Server Profiler trace:
exec dbo.spProcessStateReport N'<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-16"?>
<Report><ReportHeader><Identification><Machine><ClientInstalled>1</ClientInstalled><ClientType>1</ClientType><ClientID>GUID: A1006D0E-CF56-41D1-A006-6330EFC39381</ClientID><ClientVersion>5.00.7958.1000</ClientVersion><NetBIOSName>PS1WIN7X64</NetBIOSName><CodePage>437</CodePage><SystemDefaultLCID>1033</SystemDefaultLCID><Priority>5</Priority></Machine></Identification><ReportDetails><ReportContent>State Message Data</ReportContent><ReportType>Full</ReportType><Date>20140120220131.071000+000</Date><Version>1.0</Version><Format>1.0</Format></ReportDetails></ReportHeader><ReportBody><StateMessage MessageTime="20140120171855.573000+000" SerialNumber="239"><Topic ID="505fda07-b4f3-45fb-83d9-8642554e2773" Type="500" IDType="3" User="" UserSID=""/><State ID="2" Criticality="0"/><UserParameters Flags="0" Count="1"><Param>200</Param></UserParameters></StateMessage></ReportBody></Report>'
spProcessStateReport is a CLR stored procedure, and the CLR definition has the logic to determine the type of state message being processed. Depending on the type of state message, it processes the state message appropriately and inserts the data in the database.
You can find friendly names of all state message Topic Types and IDs by querying the SR_StateNames table with the following command:
SELECT * FROM SR_StateNames
Software update summarization
Before software update compliance data can be presented in the console or reports, the software update compliance data must be summarized. This is necessary because the console and reports usually display only summarized data. The State System component on the site server performs the software update summarization along with summarization for other components, such as applications, DCM deployments and client health. You can find information about all the summarization tasks that State System performs by querying the vSR_SummaryTasks view in the Configuration Manager database. State System runs these tasks on a configured schedule and logs detail about each task in StateSys.log:
Started task '<TaskName>' SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
Task '<TaskName>' completed successfully after running for 15 seconds, with status 8. SMS_STATE_SYSTEM
For most of these tasks, the status logged by StateSys.log isn't an error code. Instead, it's the number of rows returned by the appropriate SQL Server stored procedure that performs the summarization.
Summarization tasks specific to software updates are:
SUM Assignment Compliance Evaluator
Summarizes state messages for all software update group assignments (deployments). This task runs every hour by default. It can be initiated manually for a specific deployment in Configuration Manager console > Monitoring > Deployments, right-click the deployment, and then click Run Summarization.
SUM Update Group Status Summarizer
Summarizes status of Update Groups. This task runs every hour by default. It can be initiated manually for a specific Update Group in Configuration Manager console > Software Library > Software Updates > Software Update Groups, right-click the update group, and then click Run Summarization.
You can also change the schedule of this task by right-clicking Software Update Groups or by selecting Schedule Summarization in the ribbon.
SUM Update Status Summarizer
Summarizes status of updates for all clients. This task runs every hour by default. It can be initiated manually in Configuration Manager console > Software Library > Software Updates, then click Run Summarization. You can also change the default schedule by selecting Schedule Summarization.
SUM Migrate Update Status
Migrates update status internally within the database. This task runs every 24 hours by default. It can't be initiated manually from the Configuration Manager console.
SUM Delete Aged Status
Deletes aged status from software update specific tables in the database. This task runs every 24 hours by default. It can't be initiated manually from the Configuration Manager console.
Software update point switching
In System Center 2012 Configuration Manager SP1 and later versions, a site can have multiple SUPs. This provides fault tolerance for situations when a SUP becomes unavailable. For more information about SUPs' failover and switching, see the following articles:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for