Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article helps you resolve the problem that occurs when you connect to a SQL Server Always On availability group listener in a multi-subnet environment.
Original product version: SQL Server 2012 and later versions
Original KB number: 2792139
Symptoms
After you configure the availability group listener for an Always On Availability Group in Microsoft SQL Server, you might be unable to ping the listener or connect to it from an application.
For example, when you try to connect to a listener of SQL Server by using SQLCMD, the connection times out. Additionally, you receive an error message that resembles the following one:
Sqlcmd: Error: Microsoft SQL Native Client: Login timeout expired.
Note
These symptoms are intermittent, or related to failover of the availability group resource.
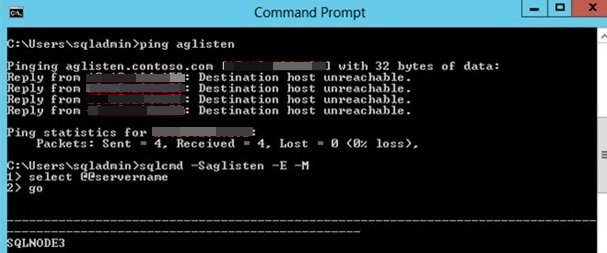
The following screenshot shows an example of what occurs when you try to ping the listener for the availability of aglisten. The screenshot also shows a successful connection to SQL Server by using the SQLCMD command when you include the multi-subnet failover parameter -M.
Note
You can use the SQLCMD command together with the -M parameter as shown in the screenshot to connect to the listener.
Cause
This issue occurs because your application either uses a legacy data provider that doesn't support the new MultiSubnetFailover parameter, or isn't configured to use this parameter.
This parameter is supported in newer versions of the SQLClient driver that is included with the .NET Framework 4 and later versions of the .NET Framework, and is back ported to the .NET Framework 3.5.
Note
The PING command is a simple connectivity testing tool that doesn't support the new parameter.
Resolution
You can use one of the following resolutions as applicable to your case:
To resolve this situation when the data providers support the
MultiSubNetFailoverparameter, add theMultiSubNetFailoverparameter to your connection string, and set it to true.To resolve this situation when your legacy clients can't use the
MultiSubnetFailoverproperty, you can change the listener'sRegisterAllProvidersIPvalue to 0 by running the following command from the Windows PowerShell command-line interface:Import-Module FailoverClusters Get-ClusterResource <*Your listener name*>|Set-ClusterParameter RegisterAllProvidersIP 0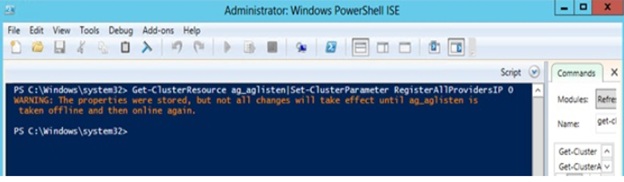
Note
After you set the RegisterAllProvidersIP value to 0, the current online IP address must be unregistered from the DNS server and the offline IP address must be registered to the DNS server when a failover occurs. This might cause a connection delay for the next failover.
More information
When you try to connect to a listener that is defined on more than one subnet, the operation might fail if the client driver tries to connect by using one of the listener's offline IP addresses.
When a listener is created, an IP address is designated for each unique subnet that an availability group replica is hosted in. For example, if a listener is created for an availability group that has replicas that exist in two subnets, two IP addresses are defined in the listener. One address is used by an application that can connect to an instance of SQL Server in subnet 1, and the other address is used when an application connects to an instance of SQL Server in subnet 2.
Behind the scenes, the listener creates a Windows cluster Client Access Point resource. One of its properties is RegisterAllProvidersIP. When a listener is created, this property is set to 1, and all the listener's IP addresses are registered in DNS server. This configuration provides reduced reconnection time for clients.
Because the DNS record contains all the IP addresses, a client that tries to connect to the listener must know how to handle this situation. The MultiSubnetFailover parameter enables the client driver to try connections in parallel to all the listener's IP addresses. Without the MultiSubnetFailover parameter, the client driver will try to connect sequentially to all IP addresses for the listener. Sequential connections might cause a long logon time or logon time-outs.
Note
The problem that is mentioned in this article also affects SharePoint environments that are configured to use an Always On Availability Group's secondary read-only replica. To resolve this issue, perform whichever of the following actions applies to your version of SharePoint:
For SharePoint 2007: This is classified as a legacy application. Therefore, SharePoint 2007 can't be configured to use the
MultiSubnetFailoverparameter. Instead, you have to use the Windows PowerShell command that is described in the Resolution section.For SharePoint 2010: Cumulative update packages are now available that add support for the
MultiSubnetFailoverparameter. For more information about the update packages, see the following article: