Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Microsoft System Center Operations Manager depends on SQL Server Service Broker to implement all task operations. If SQL Server Service Broker is disabled, all task operations are affected. The resulting behavior may vary according to the task that's initiated. For example, you may experience the following issues:
- The Discovery Wizard seems to be running endlessly, even though the task in the background has finished.
- Resetting the health of a monitor never finishes, even though the task in the background has finished.
This article provides common troubleshooting steps for SQL Server Service Broker issues.
Note
The SQL queries in this article use a default name of OperationsManager for the operational database. Replace OperationsManager with the name of your operational database if you use a different database name.
Check whether SQL Server Service Broker is enabled
Run the following SQL query:
SELECT is_broker_enabled FROM sys.databases WHERE name = 'OperationsManager'If the returned value of the
is_broker_enabledfield is 1 (one), SQL Server Service Broker is enabled. Otherwise, run the following SQL queries to enable it:ALTER DATABASE OperationsManager SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE ALTER DATABASE OperationsManager SET ENABLE_BROKER ALTER DATABASE OperationsManager SET MULTI_USER
Restart System Center Data Access Service
After SQL Server Service Broker is enabled, restart System Center Data Access Service (OMSDK).
In SQL Server Management Studio, go to Databases > OperationsManager > Service Broker.
Expand Queues and Services.
Verify that there's a queue and service whose name contains the following values:
- The IP address of the management server that created the queue and service.
- The process ID of the OMSDK service (Microsoft.Mom.Sdk.ServiceHost.exe) that's running on that management server.
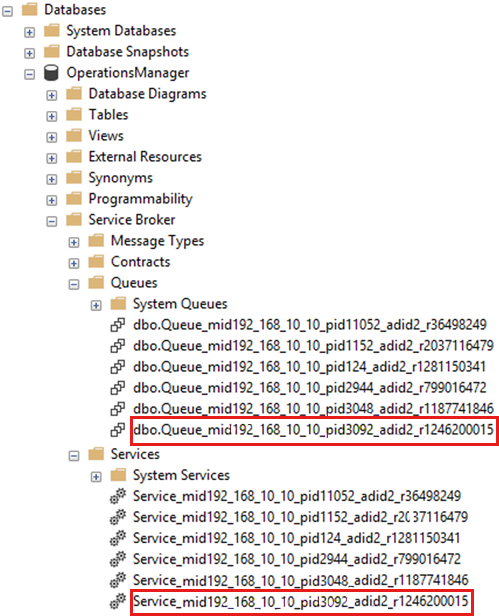
In this example, the IP address of the management server is 192.168.10.10. The PID of the OMSDK service is 3092.
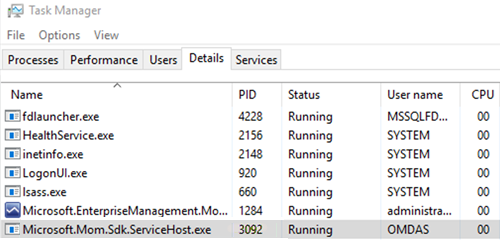
If you have more than one management server, each management server will have a separate Service Broker queue and service.
If you can't find the corresponding queue and service, restart the OMSDK service again.
If you still can't find the queue and service, the current Service Broker may be corrupted. Go to the next step to re-create the SQL Server Service Broker.
Re-create the SQL Server Service Broker
Run the following SQL queries in order:
declare @i int set @i=0 DECLARE @handle UNIQUEIDENTIFIER declare @service_id int declare @service_name nvarchar (100) declare @far_service nvarchar (70) DECLARE conv_cur CURSOR FAST_FORWARD FOR SELECT CONVERSATION_HANDLE, service_id, far_service FROM SYS.CONVERSATION_ENDPOINTS OPEN conv_cur; FETCH NEXT FROM conv_cur INTO @handle, @service_id, @far_service; while (@@FETCH_STATUS = 0 and (@i<500000)) BEGIN select top 1 @service_name=name from sys.services where service_id=@service_id begin END CONVERSATION @handle WITH CLEANUP end FETCH NEXT FROM conv_cur INTO @handle, @service_id, @far_service; set @i=@i+1 END CLOSE conv_cur DEALLOCATE conv_cur go declare @servicename sysname declare @queuename sysname declare @cmd nvarchar(200) declare @serverqid nvarchar(25) set @serverqid='%Queue_mid%' while ((select count(*) from sys.service_queues WHERE name like @serverqid )>1) begin set @servicename= (select top 1 s.name from sys.service_queues as q join sys.services as s on q.object_id=s.service_queue_id WHERE q.name like @serverqid order by q.create_date asc) set @cmd= 'DROP SERVICE '+@servicename exec sp_sqlexec @cmd set @queuename= (select top 1 Object_name(object_id) from sys.service_queues WHERE name like @serverqid order by create_date asc) set @cmd= 'DROP QUEUE '+@queuename exec sp_sqlexec @cmd end go ALTER DATABASE OperationsManager SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE ALTER DATABASE OperationsManager SET NEW_BROKER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE ALTER DATABASE OperationsManager SET MULTI_USER go ALTER DATABASE OperationsManager SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE ALTER DATABASE OperationsManager SET ENABLE_BROKER ALTER DATABASE OperationsManager SET MULTI_USER goRestart the OMSDK service on the management servers to re-create the Service Broker, and the queue and service. This process might require two restarts:
- The first restart re-creates the Service Broker
- The second restart re-creates the service queue
Verify that the SQL Server Service Broker is still enabled. If it's disabled, enable it.
Verify that the Service Broker queue and service are generated, as described in step 4 in Restart System Center Data Access Service.
Advanced troubleshooting
If the previous steps don't resolve the issue, collect a SQL Server Profiler trace that includes Service Broker events.

Sample trace when the OMSDK service creates the service and queue when it's restarted:
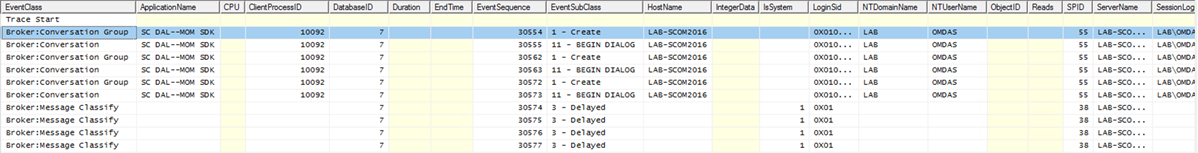
Sample trace when resetting the health of a monitor:

Sample trace when the Service Broker is disabled:
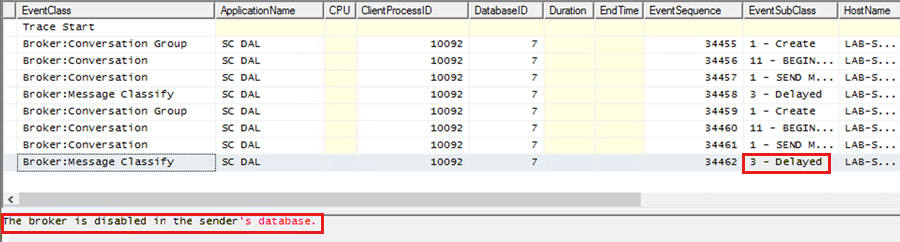
Additionally, run the following SQL script against the operational database to collect diagnostic logs.
USE master
go
SET NOCOUNT ON
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON;
DECLARE @StartTime datetime
select @@version as 'Version'
select GETDATE() as 'RunDateTime', GETUTCDATE() as 'RunUTCDateTime', SYSDATETIMEOFFSET() as 'SysDateTimeOffset'
select @@servername as 'ServerName'
PRINT '-- sys.databases --'
select * from master.sys.databases where is_broker_enabled = 1 and name not in('tempdb', 'model', 'AdventureWorks', 'AdventureWorksDW')
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.dm_broker_activated_tasks --'
select * from sys.dm_broker_activated_tasks
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.dm_broker_connections --'
select * from sys.dm_broker_connections
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- COUNT Broker Connections --'
SELECT count(*) as Cnt, state_desc, login_state_desc from sys.dm_broker_connections GROUP BY state_desc, login_state_desc ORDER BY state_desc
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.dm_broker_forwarded_messages --'
select * from sys.dm_broker_forwarded_messages
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.service_broker_endpoints --'
select * from sys.service_broker_endpoints
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.tcp_endpoints --'
select * from sys.tcp_endpoints
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.certificates --'
select * from sys.certificates
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.database_mirroring --'
select * from sys.database_mirroring where mirroring_guid is not null
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.dm_db_mirroring_connections --'
select * from sys.dm_db_mirroring_connections
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.dm_os_memory_clerks (broker) --'
select * from sys.dm_os_memory_clerks where type like '%BROKER%' order by type desc
-- Loop Through DBs and Gather SSB information specific to each DB
DECLARE tnames_cursor CURSOR
FOR SELECT name
FROM master.sys.databases
WHERE is_broker_enabled = 1
and state = 0
and name not in('tempdb', 'model', 'AdventureWorks', 'AdventureWorksDW')
ORDER BY [name]
OPEN tnames_cursor;
DECLARE @dbname sysname;
DECLARE @SCI int; -- Checking for Broker activity
DECLARE @cmd3 nvarchar(1024); -- New Command
FETCH NEXT FROM tnames_cursor INTO @dbname;
WHILE (@@FETCH_STATUS = 0)
BEGIN
SELECT @SCI = 0; -- service_contract_id
select @dbname = RTRIM(@dbname);
EXEC ('USE [' + @dbname + ']');
SELECT @cmd3 = N'SELECT @SCI_OUT = MAX(service_contract_id) FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.service_contracts';
EXEC sp_executesql @cmd3, N'@SCI_OUT INT OUTPUT', @SCI_OUT = @SCI OUTPUT;
IF @SCI > 7
BEGIN
PRINT ''
PRINT '====================================================================================='
PRINT 'Begin Database: ' + @dbname
SELECT @StartTime = GETDATE()
PRINT 'Start Time : ' + CONVERT(Varchar(50), @StartTime)
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.service_message_types --'
EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.service_message_types');
-- PRINT ''
-- PRINT '-- sys.service_contract_message_usages --'
-- EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.service_contract_message_usages');
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.service_contracts --'
EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.service_contracts');
-- PRINT ''
-- print '-- sys.service_contract_usages --'
-- EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.service_contract_usages');
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.service_queues --'
EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.service_queues');
-- PRINT ''
-- PRINT '-- sys.service_queue_usages --'
-- EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.service_queue_usages');
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.services --'
EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.services');
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.routes --'
EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.routes');
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.remote_service_bindings --'
EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.remote_service_bindings');
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.certificates --'
EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.certificates');
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- sys.dm_qn_subscriptions --'
EXEC ('SELECT * FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.dm_qn_subscriptions');
PRINT '-- sys.dm_broker_queue_monitors, current state, last activation, current backlog in transmission queue --'
EXEC ('USE ' + @dbname + ';SELECT t1.name AS [Service_Name], t3.name AS [Schema_Name], t2.name AS [Queue_Name],
CASE WHEN t4.state IS NULL THEN ''Not available''
ELSE t4.state
END AS [Queue_State],
CASE WHEN t4.tasks_waiting IS NULL THEN ''--''
ELSE CONVERT(VARCHAR, t4.tasks_waiting)
END AS tasks_waiting,
CASE WHEN t4.last_activated_time IS NULL THEN ''--''
ELSE CONVERT(varchar, t4.last_activated_time)
END AS last_activated_time ,
CASE WHEN t4.last_empty_rowset_time IS NULL THEN ''--''
ELSE CONVERT(varchar,t4.last_empty_rowset_time)
END AS last_empty_rowset_time,
(
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM sys.transmission_queue t6 WITH (NOLOCK)
WHERE (t6.from_service_name = t1.name)
) AS [Tran_Message_Count],
DB_NAME() AS DB_NAME
FROM sys.services t1 WITH (NOLOCK) INNER JOIN sys.service_queues t2 WITH (NOLOCK)
ON ( t1.service_queue_id = t2.object_id )
INNER JOIN sys.schemas t3 WITH (NOLOCK) ON ( t2.schema_id = t3.schema_id )
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.dm_broker_queue_monitors t4 WITH (NOLOCK)
ON ( t2.object_id = t4.queue_id AND t4.database_id = DB_ID() )
INNER JOIN sys.databases t5 WITH (NOLOCK) ON ( t5.database_id = DB_ID() );')
PRINT ''
PRINT ''
PRINT 'sys.transmission_queue (toal count, group count, and top 500)'
-- Using count against MetaData columns rather than COUNT(*) because it is faster, and we don't need exact counts
PRINT '-- TOTAL COUNT sys.transmission_queue --'
EXEC ('SELECT p.rows as TQ_Count FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.objects as o join ' + @dbname + '.sys.partitions as p on p.object_id = o.object_id where o.name = ''sysxmitqueue''')
-- EXEC ('SELECT count(*) as TQ_Count FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.transmission_queue with (nolock)'); -- more accurate count
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- GROUP COUNT sys.transmission_queue --'
SELECT COUNT(*) as TQ_GroupCnt, transmission_status FROM sys.transmission_queue GROUP BY transmission_status
PRINT ''
PRINT 'TOP 500'
print '-- sys.transmission_queue --'
EXEC ('USE ' + @dbname + ';SELECT top 500 conversation_handle, to_service_name, to_broker_instance, from_service_name,
service_contract_name, enqueue_time, message_sequence_number, message_type_name, is_conversation_error,
is_end_of_dialog, priority, transmission_status, DB_NAME() as DB_Name FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.transmission_queue with (nolock) order by enqueue_time, message_sequence_number');
PRINT ''
print 'sys.conversation_endpoints (total count, group count, and top 500)'
-- Using count against MetaData columns rather than COUNT(*) becuase it is faster, and we don't need exact counts
PRINT '-- TOTAL COUNT sys.conversation_endpoints --'
EXEC ('SELECT p.rows as CE_Count FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.objects as o join ' + @dbname + '.sys.partitions as p on p.object_id = o.object_id where o.name = ''sysdesend''')
-- EXEC ('SELECT count(*) as count FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.conversation_endpoints with (nolock)');
PRINT ''
PRINT '-- GROUP COUNT sys.conversation_endpoints --'
EXEC ('SELECT COUNT(*) as CE_GroupCnt, state_desc FROM ' + @dbname + '. sys.conversation_endpoints GROUP BY state_desc')
PRINT ''
PRINT 'TOP 500'
PRINT '-- sys.conversation_endpoints --'
EXEC ('USE ' + @dbname + ';SELECT top 500 *, DB_NAME() as DB_Name FROM ' + @dbname + '.sys.conversation_endpoints with (nolock)');
-- Gather Activation Proc Code
/*
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER OFF;
DECLARE @cmd nvarchar(1024)
DECLARE @cmd2 nvarchar(1024)
select @cmd = 'DECLARE tproc_cursor CURSOR FOR select activation_procedure from ' + @dbname + '.sys.service_queues where activation_procedure is not null'
EXEC (@cmd)
OPEN tproc_cursor;
DECLARE @proc sysname;
DECLARE @len int
FETCH NEXT FROM tproc_cursor INTO @proc;
WHILE (@@FETCH_STATUS = 0)
BEGIN
select @proc = rtrim(@proc)
select @len = len(@proc) - 8;
select @proc = substring(@proc, 8, @len)
select @proc
EXEC ("select definition from " + @dbname + ".sys.sql_modules where definition like '%" + @proc + "%'")
FETCH NEXT FROM tproc_cursor INTO @proc;
END;
CLOSE tproc_cursor;
DEALLOCATE tproc_cursor;
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON;
*/
PRINT ''
PRINT 'End of Database: ' + @dbname
PRINT 'END Time : ' + CONVERT(Varchar(50), GetDate())
PRINT 'Data Collection Duration in milliseconds for ' + @dbname
PRINT ''
SELECT DATEDIFF(millisecond, @StartTime, GETDATE()) as Duration_ms
PRINT '====================================================================================='
PRINT '====================================================================================='
PRINT ''
END;
FETCH NEXT FROM tnames_cursor INTO @dbname;
END;
CLOSE tnames_cursor;
DEALLOCATE tnames_cursor;