Troubleshooting AD Replication error 8446: The replication operation failed to allocate memory
This article describes the symptoms, cause, and resolution steps for issues when Active Directory replication fails with error 8446.
Note
Home users: This article is only intended for technical support agents and IT professionals. If you're looking for help with a problem, ask the Microsoft Community.
Applies to: Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 2693500
Symptoms
This article describes the symptoms, cause, and resolution steps for issues when Active Directory replication fails with error 8446: "The replication operation failed to allocate memory".
REPADMIN.exe reports that replication attempt has failed with error "8446" - The Replication operation failed to allocate memory
DC=Contoso,DC=com
Default-First-Site-Name\DomainController via RPC
DC object GUID: <source DCs ntds settings object object guid>
Last attempt @ <Date Time> failed, result 8446 (0x20fe):
The replication operation failed to allocate memory.
1359 consecutive failure(s).
Last success @ <Date & Time>.CN=Configuration,DC=Contoso,DC=com
Default-First-Site-Name\DomainController via RPC
DC object GUID: <source DCs ntds settings object object guid>
Last attempt @ <Date Time> failed, result 8446 (0x20fe):
The replication operation failed to allocate memory.
1358 consecutive failure(s).
Last success @ <Date & Time>.Source: Default-First-Site-Name\DomainController
******* 1359 CONSECUTIVE FAILURES since <Date Time>Last error: 8446 (0x20fe):
The replication operation failed to allocate memory.DCPROMO fails with error 1130
06/05 09:55:33 [INFO] Error - Active Directory could not replicate the directory partition CN=Configuration,DC=contoso,DC=com from the remote domain controller 5thWardDC1.contoso.com. (1130)
06/05 09:55:33 [INFO] NtdsInstall for domain.net returned 1130
06/05 09:55:33 [INFO] DsRolepInstallDs returned 1130
06/05 09:55:33 [ERROR] Failed to install to Directory Service (1130)
Non critical replication returned 1130
err.exe 1130
ERROR_NOT_ENOUGH_SERVER_MEMORY / Not enough server storage is available to process this command.NTDS Replication, NTDS General Events with the 8466 status are logged in the directory service event log.
Event Source Event ID Event String NTDS Replication 1699 The local domain controller failed to retrieve the changes requested for the following directory partition. As a result, it was unable to send the change requests to the domain controller at the following network address. 8446 The replication operation failed to allocate memory NTDS General 1079 Active Directory could not allocate enough memory to process replication tasks. Replication might be affected until more memory is available Increase the amount of physical memory or virtual memory and restart this domain controller When you try to manually initiate replication using Repadmin or Active Directory Sites and Services, you get the following error message:
The following error occurred during the attempt to synchronize naming context
Contoso.comfrom domain controller <Source DC > to domain controller <Destination DC>:
The replication Operation failed to allocate memory. This operation will not continue.The domain controller may become unresponsive and a reboot will provide a temporary workaround.
Cause
The 8446 (operation failed to allocate memory. This operation will not continue) status can occur when the Active Directory replication engine cannot allocate memory to perform Active directory replication.
These events can occur due to the following conditions
- Low available physical memory
- Low available paging file size versus physical memory (Wrong configuration of paging file): Paging file should be 1.5 times the size of physical memory
- Paged Pool or Non-Paged pool exhaustion in the kernel
- LSASS Virtual memory depletion on 32-bit domain controllers. This is where the Virtual Memory of LSASS reaches the 2-GB limit of virtual memory available for a process running in user mode.
- The Virtual Memory depletion could be a leak inside the LSASS User mode Process, or the Database Cache (ESE Cache) may be consuming all the available memory.
The following information is important to understand
Lsass.exe memory usage on domain controllers has two major components: one fixed and one variable.
The fixed component is made up of the code, the stacks, the heaps, and various fixed size data structures (for example, the schema cache). The amount of memory that LSASS uses may vary, depending on the load on the computer. As the number of running threads increases, so does the number of memory stacks. Lsass.exe usually uses 100 MB to 300 MB of memory. Lsass.exe uses the same amount of memory no matter how much RAM is installed in the computer.
The variable component is the database buffer cache. The size of the cache can range from less than 1 MB to the size of the entire database. Because a larger cache improves performance, the database engine for AD (ESENT) attempts to keep the cache as large as possible. While the size of the cache varies with memory pressure in the computer, the maximum size of the cache is limited by both the amount of physical RAM installed in the computer and by the amount of available virtual address space (VA). AD uses only a portion of total VA space for the cache.
Resolution
Determine if there is depletion of following resources and fix the underlying cause:
- Physical RAM
- Paging File
- Paged Pool or Non-Paged Pool Depletion
LSASS Virtual memory fragmentation
If the root cause is not memory, then the problem may be caused by a lack of available continuous address space for memory allocation. Due to memory fragmentation, the available address segments are too small to satisfy request.
The fragmentation problem is not apparent on 64-bit systems since it has much larger virtual address space 16 TB. Therefore, a solution is replacing 32-bit domain controllers with DC's running 64-bit hardware and a 64-bit version of operation system.
Domain Controller Scalability
If there is no apparent memory leak or resource depletion:
Check the size of the NTDS.DIT file on the domain controller; if the size is beyond 2 GB on a 32- bit domain controller, then a likely solution is to move to a 64-bit operating system and hardware.
There are many cases where administrators have moved onto to x64 Bit hardware and not faced a repeat of the 8446 (Replication failed to allocate memory) error.
For 32-bit operating systems, depending on the size of the NTDS.DIT, the /USERVA boot.ini switch that increases the virtual mode address space on domain controllers may provide relief, but this might cause kernel mode depletion as this reduces the size of the kernel mode address space. Prior to implementing the /UserVA switch, it is best to consult with a Windows memory performance tuning expert for an analysis of kernel mode and user mode memory usage.
Database cache consumes all available virtual memory for the LSASS process.
Run Performance Monitor with database counters, review the following counters:
- LSASS - Working Set
- LSASS - Virtual Bytes
- Database - "Database Cache Size"
Note
By default you will not be able to view the database counters on a Windows 2003 Domain controller. Use the following steps to add the database counters on Windows Server 2003.
These steps are not needed for Window Server 2008 and later.
Import the following registry settings: (copy the following text to notepad and save as a .reg file, and then import the settings on the DC)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ESENT]
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ESENT\Performance]
"Open"="OpenPerformanceData"
"Collect"="CollectPerformanceData"
"Close"="ClosePerformanceData"
"Library"="C:\\Windows\\System32\\esentprf.dll"
"Show Advanced Counters"=dword:00000001Run the following command from a command prompt to back up your existing performance counters:
Lodctr /s: backup.iniRun the following command from a command prompt to register the database counters:
Lodctr c:\windows\system32\esentprf.iniOpen Perfmon or restart performance monitor if already open.
You should by now be able to view a new performance object in Perfmon called Database.
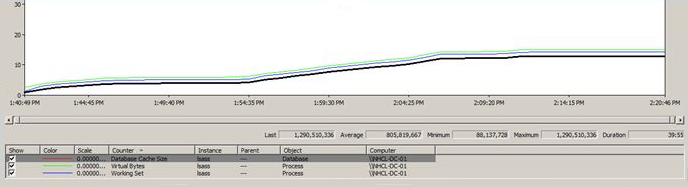
Add the "Database Cache Size" counter. In the following example, the database cache size grows at an increasing trend of Virtual Bytes and Working Set of the LSASS Process eventually consuming all 2 GB of available virtual memory allocated to the LSASS process. You will encounter the 8446 replication failure once this virtual address space is consumed. Refer to the " LSASS ESE Database cache is not limited by default" section of the article for detailed instructions on how to avoid this condition.
LSASS ESE Database cache is not limited by default
If you determine it is the database cache that is consuming memory using performance monitor, you can add the following registry value to limit the database cache.
You can use the "EDB max buffers" registry value for limiting ESE cache allocation (number of pages is 8912 bytes) to prevent the conditions.
Value Name: EDB max buffers
Type: reg_dword
Setting: <refer to the values below>
Registry key: HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NTDS\Parameters
Caution
Ensure that you set an optimal value to the registry value (EDB max buffers), if the cache limit is too low then it might cause performance degradation. You may apply the following values as start for an optimization, depending is the /3GB boot.ini switch is use or not:
Without /3GB switch: "EDB max buffers", Reg_DWord: 157286 (1.2 GB); expected LSASS consumption ~1.5 GB With /3GB switch: "EDB max buffers", Reg_DWord: 235929 (1.8 GB); expected LSASS consumption ~2.1 GB
Data collection
If you need assistance from Microsoft support, we recommend you collect the information by following the steps mentioned in Gather information by using TSS for Active Directory replication issues.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for