Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
When you try to enroll a certificate on a Windows Server, it fails with the error 0x800706ba, "The RPC Server is unavailable." This article introduces steps to resolve this issue.
Applies to: Supported versions of Windows Server
Original KB number: 4042719, 4516764, 5021150
Identify the issue
When you encounter this issue, you may see one or more of the following symptoms.
Note
When the issue occurs, if we add the user account that's used to request the certificate to the local administrators group on the certificate authority (CA), the enrollment succeeds for a user-based template. However, enrollment against a machine-based template still returns the same error.
Error messages
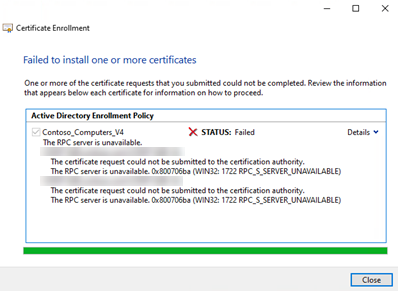
You receive error messages that resemble the following during certificate enrollment.
Error 1
An error occurred whilst enrolling for a certificate. The certificate request could not be submitted to the certification authority.
Url: <certificate server FQDN>\MyPKI
Error: The RPC server is unavailable. 0x800706ba (WIN32: 1322 RPC_S_SERVER_UNAVAILABLE)
Error 2
Error 3
Network capture
The network trace shows the successful Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) queries to the configuration partition in Active Directory; the templates available are revealed in the trace.
Then, the requesting server tries to do a remote procedure call (RPC) to the CA and gets the response "ACCESS DENIED."
For example:
10167 <time> <requesting server IP address> <CA IP address> ISystemActivator 918 RemoteCreateInstance request
10174 <time> <CA IP address> <requesting server IP address> DCERPC 86 Fault: call_id: 3, Fragment: Single, Ctx: 1, status: nca_s_fault_access_denied
Additionally, you can find the Microsoft Remote Procedure Call (MSRPC) bind attempt and error:
1093 <time> 92.5590216 (0) SourceIP 52237 (0xCC0D) DestIP 135 (0x87) MSRPC MSRPC:c/o Bind: IRemoteSCMActivator(DCOM) UUID{000001A0-0000-0000-C000-000000000046} Call=0x3 Assoc Grp=0x8A9E Xmit=0x16D0 Recv=0x16D0
1097 <time> 92.5940283 (652) SourceIP 135 (0x87) DestIP 52237 (0xCC0D) MSRPC MSRPC:c/o Bind Nack: Call=0x3 Reject Reason: invalid_checksum
In a network trace, you find the following error:
Status : MSRPC:c/o Fault: Call=0x3 Context=0x1 Status=0x5 (Access is denied)
For example:
<Certificate_Server> <Client> DCOM DCOM:RemoteCreateInstance Request, DCOM Version=5.7 Causality Id={7CFF2CD3-3165-4098-93D6-4077D1DF7351}
<Client> <Certificate_Server> MSRPC MSRPC:c/o Fault: Call=0x3 Context=0x1 Status=0x5 Cancels=0x0
Event log
If auditing is enabled, a Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) error can be observed on the CA server detailing an ANONYMOUS LOGON attempt:
Log Name: System
Source: Microsoft-Windows-DistributedCOM
Date: <date>
Event ID: 10027
Task Category: None
Level: Warning
Keywords: Classic
User: ANONYMOUS LOGON
Computer: <CA FQDN>
Description:
The machine wide limit settings do not grant Remote Activation permission for COM Server applications to the user NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGON SID (S-1-5-7) from address <IP address> running in the application container Unavailable SID (Unavailable). This security permission can be modified using the Component Services administrative tool.
Note
Event ID 82 is logged in Application logs if auto-enrollment is failing with the same error.
Other symptoms and logs
- The call should be made with dce_c_authn_level_pkt_integrity RPC Integrity level that enforces Kerberos or New Technology LAN Manager (NTLM) as an authentication mechanism. This behavior is enforced by default starting 6B.22 KB5004442—Manage changes for Windows DCOM Server Security Feature Bypass (CVE-2021-26414).
- When the client sends a KRB_AP_REQ request, it's rejected by the server side.
- The server tries to procure an access token for the user who presented the Kerberos Ticket Granting Service (TGS) and fails with error 0xc000015b, "STATUS_LOGON_TYPE_NOT_GRANTED."
Cause 1: Incorrect group policy configurations
This issue can occur because of one of the following reasons:
- The group policy Access this computer from the network is set, and the user account used to enroll the certificate isn't added. By default, the policy is populated by the groups: Administrators, Backup Operators, Everyone, and Users.
- The group policy Deny access to this computer from the network is set, and Everyone, Users or a security group the user belongs to is added.
These group policies locate at Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment.
Note
You can run whoami /groups to identify the groups of the user account or use Active Directory Users and computers to identify the groups belonging to the user or the computer account.
Because the user account used for certificate enrollment fails authentication by using Kerberos, the authentication mechanism is downgraded to "anonymous logon." The logon fails on the DCOM level.
How to identify
Open an elevated command prompt on the certificate server.
Run the
gpresult /hcommand. For example,gpresult /h appliedgpo.html.Open the .html file that's generated, and review the section:
Settings \ Policies \ Windows Settings \ Local Policies \ User Rights Assignment- Access this computer from the network
- Deny access to this computer from the network
Note the Winning GPO name.
To resolve this issue, edit the Winning GPO.
Note
The settings configured on the Group Policy Objects (GPOs) are for a reason, so you should talk to your security team before making any changes.
Add the appropriate user groups to the Access this computer from the network group policy. For example:
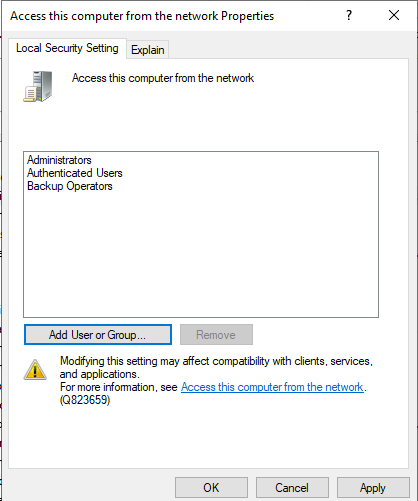
Then, remove the group that the user account or the computer account belongs to from the Deny access to this computer from the network group policy.
For more information, see Access this computer from the network - security policy setting.
Cause 2: Missing "NT Authority\Authenticated Users" in the "Users" group of the certificate server or any other default permissions
Here are the default permissions:
- Contoso\Domain Users
- NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users
- NT AUTHORITY\INTERACTIVE
To resolve this issue, open Local Users and Groups on the certificate server, locate the Users group, and add the missing groups.
Cause 3: Missing "NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users" from the "Certificate Service DCOM Access" local group of the certificate server
To resolve this issue, follow these steps:
- Open Local Users and Groups on the certificate server.
- Locate the Certificate Service DCOM Access group.
- Add NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated users.
Cause 4: EnableDCOM isn't set to Y on the Client and CA Server
To resolve this issue, follow these steps:
- Locate this registry key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\OLE. - Verify if the data of the EnableDCOM registry value is set to Y.
- If it's N, change it to Y, and then restart the computer.
Cause 5: Remote Procedure Call restrictions aren't applied on the Certificate server
To identify the issue, verify that the GPO is applied to the certificate server. Follow these steps:
Open an elevated command prompt on the certificate server.
Run the
gpresult /hcommand. For example,gpresult /h appliedgpo.html.Open the .html file, and identify the winning GPO where the Restrictions for Unauthenticated RPC Client group policy is configured to Not Configured.
The group policy locates at Administrative Templates \ System \ Remote Procedure Call \ Restrictions for Unauthenticated RPC Client.
Cause 6: Missing "Certificate Service DCOM Access" from COM Security Access Permissions or Launch and Activation Permissions
When the Active Directory Certificate Services role is installed on a server, the local Certificate Service DCOM Access group is automatically granted rights to the Component Services administrative tool. If these default permissions have been removed, you may experience the symptoms described in this article. To verify that the correct permissions are in place, follow these steps:
- Open the Component Services Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in under Windows Administrative Tools.
- In the left pane, expand Component Services > Computers.
- Right-click My Computer, select Properties, and then select the COM Security tab.
- Under Access Permissions, select Edit Limits.
- Verify that the local Certificate Service DCOM Access group appears in the Group or user names list and is granted both Local Access and Remote Access permissions. If not, add it and grant the appropriate permissions. Select OK to close the Access Permission dialog.
- Under Launch and Activation Permissions, select Edit Limits.
- Verify that the local Certificate Service DCOM Access group appears in the Group or user names list and is granted both Local Activation and Remote Activation permissions. If not, add it and grant the appropriate permissions. Select OK to close the Launch and Activation Permissions dialog.
Reference
For more information, see Restrictions for Unauthenticated RPC Clients: The group policy that punches your domain in the face.
