You cannot open file shares or Group Policy snap-ins on a domain controller
This article describes how to resolve a problem that occurs when SMB signing is disabled for the Workstation or Server service on a domain controller.
Applies to: Windows Server 2003
Original KB number: 839499
Summary
You cannot open file shares or the Group Policy snap-ins on a Windows Server 2003 domain controller or on a Windows 2000 Server domain controller. When you log on to the domain controller locally and then try to open shares on the domain controller, you receive repeated password prompts, and you cannot open the shares. You can resolve this problem by changing the registry.
Warning
Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly by using Registry Editor or by using another method. These problems might require that you reinstall the operating system. Microsoft cannot guarantee that these problems can be solved. Modify the registry at your own risk.
Symptoms
Scenario 1 - Server Message Block (SMB) signing is disabled for the Workstation service on a domain controller, but SMB signing is required for the Server service on the same domain controller
Windows Server 2003
When you try to open Group Policy snap-ins on the domain controller, you receive an error message that resembles the following:
You do not have permission to perform this operation. Access is denied.
The domain controller logs the following events in the application event log every five minutes:
Windows 2000 Server
When you try to open Group Policy snap-ins on the domain controller, you receive an error message that resembles the following:
You do not have permission to perform this operation.
Access is denied. The domain controller logs the following event in the application event log:
When you log on to the domain controller locally and then try to open shares on the domain controller, you receive repeated password prompts, and you cannot open the shares.
Scenario 2 - SMB signing is disabled for the Server service on a domain controller, but SMB signing is required for the Workstation service on the same domain controller
Windows Server 2003
Failed to open the Group Policy Object. You may not have the appropriate rights.
The account is not authorized to log in from this station.
In a network trace, if SMB signing is enabled and required at the client and is disabled at the server, the connection to the TCP session is gracefully closed after the Dialect Negotiation, and the client receives the following error:
1240 (ERROR_LOGIN_WKSTA_RESTRICTION)
The domain controller logs the following events in the application event log every five minutes: When you log on to the domain controller locally and then try to open file shares on the domain controller, you receive an error message that resembles the following:
\\Server_Name\Share_Name is not accessible. You might not have permission to use this network resource. Contact the administrator of this server to find out if you have access permissions.
The account is not authorized to log in from this station.
Note
In a network trace, if SMB signing is enabled, and if SMB signing is required at the client and is disabled at the server, the connection to the TCP session is gracefully closed after the dialect negotiation. Also, the client receives the following error message: 1240 (ERROR_LOGIN_WKSTA_RESTRICTION)
Windows 2000 Server
When you try to open Group Policy snap-ins on the domain controller, you receive an error message that is similar to the following:
Failed to open the Group Policy Object. You may not have the appropriate rights.
The account is not authorized to log in from this station.
The domain controller logs the following event in the application event log: When you log on to the domain controller locally and then try to open file shares on the domain controller, you receive an error message that is similar to the following:
\\Server_Name\Share_Name is not accessible.
The account is not authorized to log in from this station.
Note
In a network trace, if SMB signing is enabled, and if SMB signing is required at the client and is disabled at the server, the connection to the TCP session is gracefully closed after the dialect negotiation. Also, the client receives the following error message: 1240 (ERROR_LOGIN_WKSTA_RESTRICTION)
Resolution
To resolve this behavior, follow these steps:
Important
This section, method, or task contains steps that tell you how to modify the registry. However, serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully. For added protection, back up the registry before you modify it. Then, you can restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up and restore the registry, see How to back up and restore the registry in Windows XP.
Step 1 - Change the registry
Change the value of the enablesecuritysignature registry entry. To do this, follow these steps:
On the domain controller, click Start, and then click Run.
Copy and then paste (or type) the regedit command in the Open box, and then press Enter.
Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\lanmanserver\parametersIn the right pane, double-click enablesecuritysignature, type 1 in the Value data box, and then click OK.
Double-click requiresecuritysignature, type 1 in the Value data box, and then click OK.
Locate and then click the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\lanmanworkstation\parametersIn the right pane, double-click enablesecuritysignature, type 1 in the Value data box, and then click OK.
Double-click requiresecuritysignature, type 0 in the Value data box, and then click OK.
Step 2 - Restart the Server service and the Workstation service After you change the registry values, restart the Server service and the Workstation service.
Important
Do not restart the domain controller, because this action may cause Group Policy to change the registry values back to the earlier values.
To restart the Server service and the Workstation service, follow these steps:
Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Services.
Right-click Server, and then click Restart.
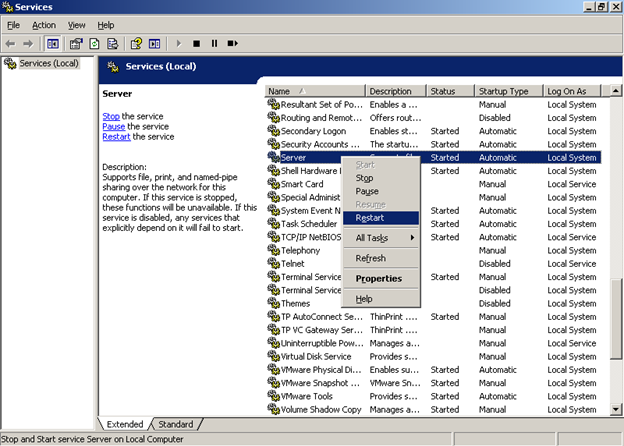
Right-click Workstation, and then click Restart.
Note
If you are prompted to restart other services, click Yes.
Step 3 - Update the Sysvol share
Update the domain controller's Sysvol share. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open the domain controller's Sysvol share. To do this, click Start, click Run, type \\Server_Name\Sysvol in the Open box, and then press Enter.
- If the Sysvol share does not open, repeat Step 1 - Change the registry and Step 2 - Restart the Server and Workstation services .
- Repeat Step 1 - Change the registry and Step 2 - Restart the Server and Workstation services on each affected domain controller to make sure that each domain controller can access its own Sysvol share.
Step 4 - Set up the SMB policy settings
After you connect to the Sysvol share on each domain controller, open the Domain Controller Security Policy snap-in, and then set up the SMB signing policy settings. To do this, follow these steps:
Click Start, point to Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Domain Controller Security Policy.
In the left pane, expand Local Policies, and then click Security Options.
In the right pane, double-click Microsoft network server: Digitally sign communications (always).
Note
In Windows 2000 Server, the equivalent policy setting is Digitally sign server communication (always).
Important
If you have client computers on the network that do not support SMB signing, you must not enable the Microsoft network server: Digitally sign communications (always) policy setting. If you enable this setting, you must have SMB signing for all client communication, and client computers that do not support SMB signing will not be able to connect to other computers. For example, clients that are running Apple Macintosh OS X or Microsoft Windows 95 do not support SMB signing. If your network includes clients that do not support SMB signing, set this policy to disabled.
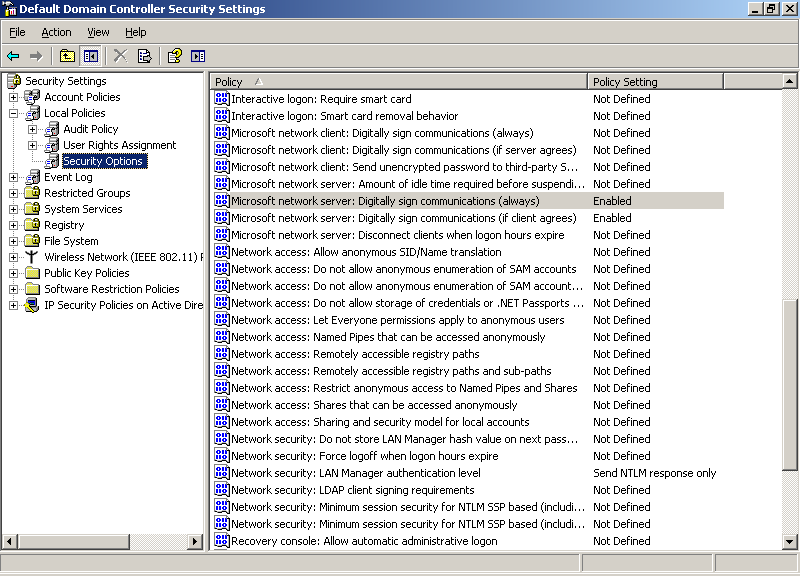
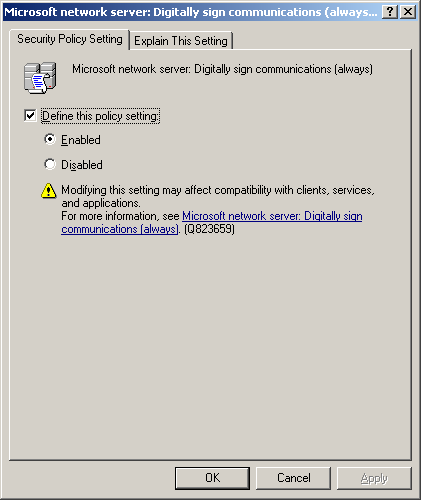
Click to select the Define this policy setting check box, click Enabled, and then click OK.
Double-click Microsoft network server: Digitally sign communications (if client agrees).
Note
For Windows 2000 Server, the equivalent policy setting is Digitally sign server communication (when possible).
Click to select the Define this policy setting check box, and then click Enabled.
Click OK.
Double-click Microsoft network client: Digitally sign communications (always).
Click to clear the Define this policy setting check box, and then click OK.
Double-click Microsoft network client: Digitally sign communications (if server agrees).
Click to clear the Define this policy setting check box, and then click OK.
Step 5 - Run the Group Policy Update utility
Run the Group Policy Update utility (Gpupdate.exe) with the force switch. To do this, follow these steps:
Click Start, and then click Run.
Copy and paste (or type) the cmd command in the Open box, and then press Enter.
At the command prompt, type
gpupdate /force, and then press Enter.Note
The Group Policy Update utility does not exist in Windows 2000 Server. In Windows 2000 Server, the equivalent command is
secedit /refreshpolicy machine_policy /enforce.
Step 6 - Check the application event log
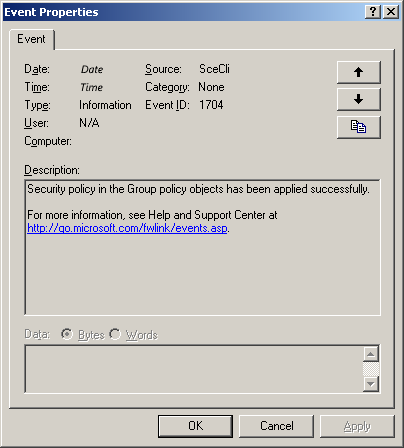
After you run the Group Policy Update utility, check the application event log to make sure that the Group Policy settings were updated successfully. After a successful Group Policy update, the domain controller logs Event ID 1704. To open the Application log in Event Viewer, follow these steps:
Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Event Viewer.
In the left pane, click Application.
Double-click event ID 1704 and confirm that the Group Policy setting was applied successfully.
Note
The source of the event is SceCli.
Step 7 - Check the registry values
Check the registry values that you changed in Step 1 - Change the registry to make sure that the registry values have not changed.
Note
This step makes sure that a conflicting policy setting is not applied at another group or organizational unit (OU) level. For example, if the Microsoft network client: Digitally sign communications (if server agrees) policy is configured as "Not Defined" in Domain Controller Security Policy, but this same policy is configured as disabled in Domain Security Policy, SMB signing will be disabled for the Workstation service.
Step 8 - Check the SMB signing policy settings by using the Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) snap-in
If the registry values have changed after you run the Group Policy Update utility, check the SMB signing policy settings by using the RSoP snap-in in Windows Server 2003. To do this, follow these steps:
Click Start, click Run, type rsop.msc in the Open box, and then click OK.
In the RSoP snap-in, the SMB signing settings are located in the following path: Computer Configuration/Windows Settings/Security Settings/Local Policies/Security Options
Note
If you are running Windows 2000 Server, install the Group Policy Update utility from the Windows 2000 Server Resource Kit, and then type the following at the command prompt:
gpresult /scope computer /vAfter you run this command, the Applied Group Policy Objects list appears. This list shows all Group Policy Objects that are applied to the computer account. Check the SMB signing policy settings for all these Group Policy Objects.
Additional resources
This behavior occurs if the SMB signing settings for the Workstation service and for the Server service contradict each other. When you configure the domain controller in this way, the Workstation service on the domain controller cannot connect to the domain controller's Sysvol share. Therefore, you cannot start Group Policy snap-ins. Also, if SMB signing policies are set by the default domain controller security policy, the problem affects all the domain controllers on the network. Therefore, Group Policy replication in the Active Directory directory service will fail, and you will not be able to edit Group Policy to undo these settings.
Scenario 1 - If you run the domain controller diagnostic tool (DcDiag.exe), you receive errors that are similar to the following for Windows 2000 Server and for Windows Server 2003
Starting test: MachineAccount
Could not open pipe with [SERVERNAME]:failed with 5: Access is denied.
Could not get NetBIOSDomainName
Failed cannot test for HOST SPN
Failed cannot test for HOST SPN
* Missing SPN :(null)
* Missing SPN :(null)
......................... SERVERNAME failed test MachineAccount
Starting test: Services
Could not open Remote ipc to [SERVERNAME]:failed with 5: Access is denied.
......................... SERVERNAME failed test Services
Starting test: ObjectsReplicated
......................... SERVERNAME passed test ObjectsReplicated
Starting test: frssysvol
[SERVERNAME] An net use or LsaPolicy operation failed with error 5, Access is denied..
......................... SERVERNAME failed test frssysvol
Starting test: frsevent
......................... SERVERNAME failed test frsevent
Starting test: kccevent
Failed to enumerate event log records, error Access is denied.
......................... SERVERNAME failed test kccevent
Starting test: systemlog
Failed to enumerate event log records, error Access is denied.
......................... SERVERNAME failed test systemlog
Scenario 2 - If you run the domain controller diagnostic tool, you receive errors that are similar to the following for Windows 2000 Server and for Windows Server 2003
Testing server: Default-First-Site-Name\SERVERNAME
Starting test: Replications
......................... SERVERNAME passed test Replications
Starting test: NCSecDesc
......................... SERVERNAME passed test NCSecDesc
Starting test: NetLogons
[SERVERNAME] An net use or LsaPolicy operation failed with error 1240, The account is not authorized to log in from this station..
......................... SERVERNAME failed test NetLogons
Starting test: Advertising
......................... SERVERNAME passed test Advertising
Starting test: KnowsOfRoleHolders
......................... SERVERNAME passed test KnowsOfRoleHolders
Starting test: RidManager
......................... SERVERNAME passed test RidManager
Starting test: MachineAccount
Could not open pipe with [SERVERNAME]:failed with 1240: The account is not authorized to log in from this station.
Could not get NetBIOSDomainName
Failed cannot test for HOST SPN
Failed cannot test for HOST SPN
* Missing SPN :(null)
* Missing SPN :(null)
......................... SERVERNAME failed test MachineAccount
Starting test: Services
Could not open Remote ipc to [SERVERNAME]:failed with 1240: The account is not authorized to log in from this station.
......................... SERVERNAME failed test Services
Starting test: ObjectsReplicated
......................... SERVERNAME passed test ObjectsReplicated
Starting test: frssysvol
[SERVERNAME] An net use or LsaPolicy operation failed with error 1240, The account is not authorized to log in from this station..
......................... SERVERNAME failed test frssysvol
Starting test: frsevent
......................... SERVERNAME failed test frsevent
Starting test: kccevent
Failed to enumerate event log records, error The account is not authorized to log in from this station. ......................... SERVERNAME failed test kccevent
Starting test: systemlog
Failed to enumerate event log records, error The account is not authorized to log in from this station. ......................... SERVERNAME failed test systemlog