Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how the different Network Load Balancing (NLB) operation modes affect network infrastructure, and the best ways in which the network can support each mode.
Original KB number: 4494444
Summary
Based on our experience, the most common issue that users encounter when they use NLB is that they are not informed enough about the technology. Therefore, the deployments and implementations usually lack some mandatory settings, or don't consider the most important factor in every network: Bandwidth consumption.
NLB can operate in any of three modes: unicast, multicast, and multicast that uses Internet Group Membership Protocol (IGMP multicast). Each of these modes has different requirements and places different demands on the network infrastructure.
Important
All of the nodes in a cluster must use the same operation mode.
The following table summarizes the requirements, advantages, and disadvantages of each mode.
| NLB operation mode | Special requirements | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unicast | NLB must be able to change the MAC adapter address. |
|
|
| Multicast | The network infrastructure must use a static ARP entry and a static MAC address table entry. |
|
More complex to configure than unicast |
| Multicast with IGMP | The network switches must be capable of IGMP snooping. |
|
Requires that the network hardware have specific capabilities that the other modes do not need |
You can configure an NLB cluster in one of three operation modes: Unicast, multicast, or IMGP multicast. All three modes work very well if your infrastructure is correctly configured. However, serious problems can develop if you haven't prepared your network infrastructure to support the mode that you are using. Each mode has different implications for the network infrastructure.
Unicast
Unicast is the simplest operation mode to configure. In theory, you don't have to do anything else in your network infrastructure. In actuality, you may have to modify the infrastructure to manage network traffic.
In unicast mode, NLB uses the NLB MAC address to replace the original hardware MAC address of each adapter in each node of the cluster. Because multiple adapters now have the same address, any physical switches in the network can no longer correctly maintain their MAC address tables. Because they cannot determine which traffic goes to which switch port, the switches start sending all traffic to all ports to make sure that the traffic reaches its destination. This is known as a unicast flood scenario.
A unicast flood can seriously affect the network performance. In addition to the regular network traffic, every NLB node sends out a heartbeat packets (each heartbeat packet contains about 1500 bytes of data). By default, a node sends a heartbeat packet each second and waits for five of those packets to be received until it considers the node as converged. In a unicast flood situation, any switches rebroadcast this heartbeat traffic to all switch ports just like the regular network traffic. For example, if your network has a 24-port or 48-port switch, and only two of those ports connect to NLB nodes, the switch may end up broadcasting significant network traffic to 22 (or 46) servers that don't need it.
To avoid a unicast flood, you have the following options:
Option 1: Insert a hub between the network switch and the NLB nodes. The hub uses the NLB unicast MAC address and connects to a single switch port, so the switch can correctly manage its MAC address table. The hub forwards traffic to the NLB nodes, and servers that connect to the other switch ports don't receive the extra NLB traffic.
Option 2: Create a separate VLAN for the NLB servers. Make sure that other subnets can reach the VLAN. This configuration isolates NLB traffic to the switch ports that are assigned to that VLAN.
Configure computers that have dual NICs in unicast mode
In some cases, you want to have two network interface cards (NICs) on your computer. If you are running Windows Server 2008 or later, you must enable IP forwarding on the NICs in order to ensure that traffic gets routed properly. IP forwarding is enabled by default in earlier versions of Windows.
Before you enable IP forwarding, you have to get the index of the Cluster NIC. On the computer that you want to configure, open a Command Prompt window and run the following command:
netsh interface ipv4 show int
The output of this command lists the interfaces on the computer, as follows.
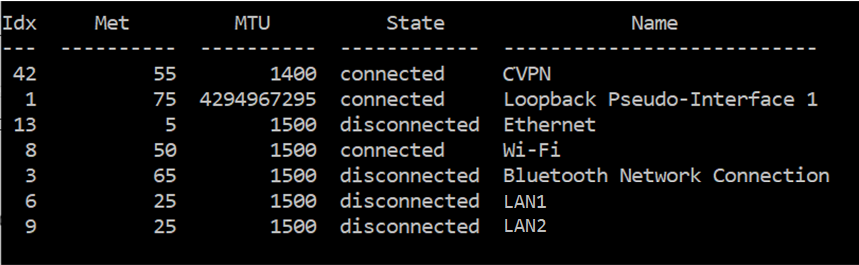
In the Command Prompt window, run the following command:
netsh interface ipv4 set interface <Cluster Idx> forwarding=enabled
In this command, <Cluster Idx> represents the index of the cluster interface.
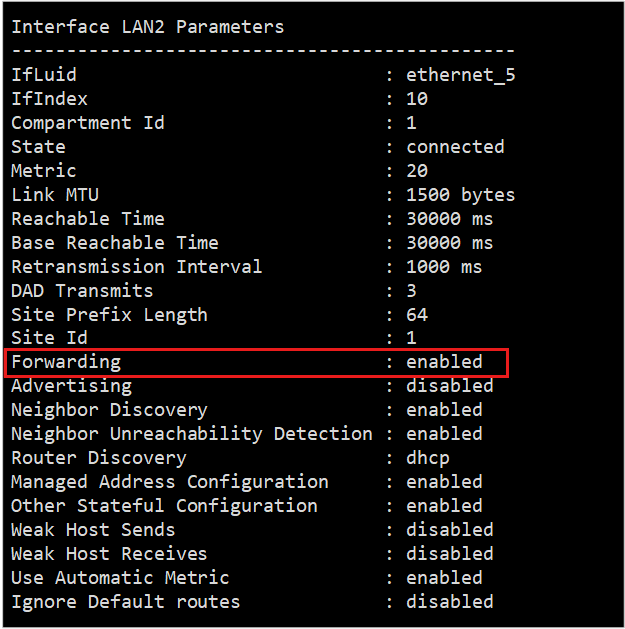
To verify that the setting has changed, run the following command:
netsh interface ipv4 show interface <Cluster Idx> l=verbose
In this command, <Cluster Idx> represents the index of the cluster interface.
The output shows that forwarding is now enabled.
Configure virtual environments in unicast mode
By default, the virtual switches in virtual environments usually prevent unicast flooding. For more configuration information, see the following resources:
If you are using Hyper-V to run your virtual environment, open the Hyper-V management console. Select the virtual machine settings, select the NIC settings, and then select Enable spoofing of MAC addresses. Select OK. For more information, see Tip: Configure MAC Address Spoofing for Virtual Network Adapters.
If you are using VMware to run your virtual environment, refer to the VMware article Microsoft NLB not working properly in Unicast Mode (1556). This article explains how to configure the virtual network infrastructure. Remember to contact VMware if you have questions about their documentation.
If you are using another virtual environment (such as XenServer or VirtualBox) and you are experiencing similar issues, contact the manufacturer for guidance.
Multicast
Multicast mode differs from unicast mode. Instead of changing the MAC addresses on the network adapters, NLB converts the NLB virtual IP (VIP) address to an NLB multicast MAC address. This MAC has the format of 03-BF-XX-XX-XX-XX. NLB also makes sure that the cluster's primary IP address resolves to this multicast address as part of the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). Although the individual network adapters retain their original MAC addresses, the NLB traffic is addressed to the NLB multicast MAC address.
To support this configuration, you must configure the network infrastructure to use static ARP entries and MAC address table entries. Network switches cannot learn the NLB multicast MAC address in the course of their usual operations. If you skip the manual configuration step, the network switches may flood NLB traffic to all ports or drop packets. The network may seem to function correctly at first, but problems increase over time.
The articles that are listed in the following table explain clearly what you have to do to correctly configure your network infrastructure, based on your network infrastructure vendor. Remember that we don't maintain these articles. Therefore, we cannot guarantee that they are accurate or available. If you have any questions about these articles, please contact the appropriate vendor.
Configure virtual environments in multicast mode
In a virtual environment, the network switches connect to the hypervisor host servers. In a high-availability virtual environment, a group of hypervisor hosts supports a group of virtual machines. An individual virtual machine may reside on any of the hypervisor hosts, and it may migrate to a different hypervisor host under specific circumstances. The network traffic must be able to reach the correct virtual machine regardless of which hypervisor host that virtual machine runs on.
To use multicast mode in such an environment, you have to configure the MAC address tables of the network switches so that each port that connects to a hypervisor host uses a static entry to map to the NLB multicast MAC address. For example, consider an environment that contains eight hypervisor hosts. Each hypervisor host has two network adapters, and all of the adapters connect to a switch. The MAC address table for the switch requires static entries that map each port to the NLB Multicast MAC address.
IGMP multicast
To use IGMP multicast, the network switches must be capable of IGMP snooping.
This mode is basically the same as multicast mode, except that the switches can automatically build their MAC address tables in this mode.
When you enable IGMP multicast, the NLB nodes send IGMP Join messages to the 239.255.x.y multicast address (in this address, x.y represents the last two octets of the NLB VIP). For example, if the NLB VIP is 10.0.0.1, the multicast address for IGMP Join messages is 239.244.0.1. These messages indicate the group membership of the NLB nodes. The switches use this information to configure the MAC address table.
Some of the articles that are listed in the Multicast section include the correct configuration parameters for their devices for multicast with IGMP. To verify that your equipment can support this mode, contact your hardware vendor.
Note
Up until Windows Server 2022, NLB supports IGMP Version 1 on any Windows versions that include IGMP multicast mode.
Configure the NLB operation mode
From an NLB standpoint, the configuration is straightforward: Install the role, open the console, create a load-balancing cluster, select the nodes, set the NLB mode, and then set the ports and affinity.
Note
To configure a cluster node by using NLB Manager, you must be a member of the Administrators group on the cluster node.
To configure the NLB cluster operation mode, use the following steps:
- In Server Manager, select Administrative tools and then select Network Load Balancing Manager.
- If NLB Manager does not already list the cluster, connect to the cluster.
- Right-click the cluster and select Cluster Properties.
- On the Cluster Parameters tab, select Unicast or Multicast in Cluster operation mode. If appropriate, you can also enable Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) support by selecting the IGMP multicast check box.
To configure the MAC addressing for NLB (which depends on the NLB mode), the most important tool is NLB IP2MAC. This tool is available on any computer that has NLB installed, and it is very easy to use. To start the tool, open a Command Prompt window and run the following command:
NLB IP2MAC <VIP of NLB>
In this command, <VIP of NLB> represents the NLB virtual IP address.
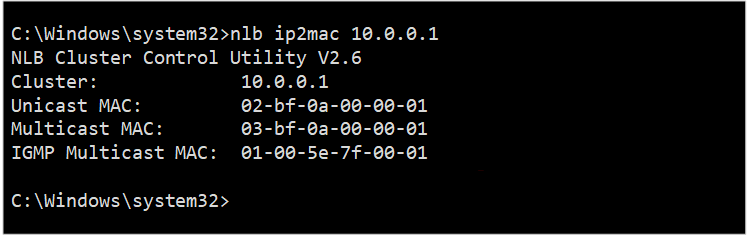
As the screenshot shows, you can get the MAC address for each mode easily by using this command. As an alternative, you can do your math, considering the following guidelines (the numbers correspond to the red numbers in the screenshot):
In Unicast mode, the MAC address starts as 02-BF. This is followed by a series of hexadecimal codes that represent each octet of the VIP address.
In Multicast mode, the MAC address starts as 03-BF. Again, this is followed by a series of hexadecimal codes that represent each octet of the VIP address.
In Multicast with IGMP mode, the MAC address starts as 01-00-5E-7F. The last two parts of the address are the last two octets of the VIP address.
For more information about how to deploy and maintain NLB, see the following resources:
Third-party information disclaimer
The third-party products that this article discusses are manufactured by companies that are independent of Microsoft. Microsoft makes no warranty, implied or otherwise, about the performance or reliability of these products.
Third-party contact disclaimer
Microsoft provides third-party contact information to help you find additional information about this topic. This contact information may change without notice. Microsoft does not guarantee the accuracy of third-party contact information.