Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article helps to resolve the issue in which the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server answers delayed or doesn't respond to DHCP requests, even though the request volume won't cause DHCP performance issues.
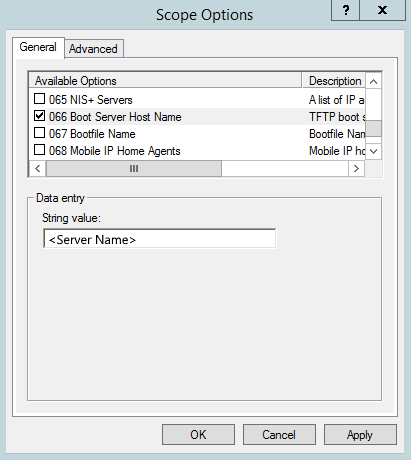
When a DHCP server has the DHCP server or scope option (066 Boot Server Host Name) configured to a server name that isn't resolvable, the DHCP clients can't get an IP address from the DHCP server in time.
When you check the DHCP packets on the DHCP server side, only a part of the incoming DHCP requests gets replies.
When you filter on the NetBIOS or LLMNR requests, you see lots of the name resolution requests are sent to a particular host name, but the IP address can't be resolved.
Unresolvable boot server host name
When the DHCP server responds to a DHCP Discover packet under a certain type of request, the DHCP server needs to check BOOTP (Bootstrap Protocol) information. The information includes the BOOTP server IP address and the boot filename.
If option 66 is configured as a server name, the DHCP server will perform name resolution over broadcast protocols (NetBIOS and LLMNR). In this period, the DHCP server ProcessingLoop thread hangs until the name resolution completes, which is by design.
When the server name is unresolvable, the name resolution takes time to fail. This action blocks the DHCP server from processing new incoming DHCP requests because all DHCP ProcessingLoop threads are synchronized by one critical section.
Check the server side DHCP option 66
You can delete the option if it isn't necessary. If the option is needed, make sure the name resolution can succeed. To fix the name resolution, edit the host file or replace the server name with the IP address for the option value.