Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes that Windows OS running in the management partition only use up to a maximum of 64 root Virtual Processors (root VPs).
Original KB number: 2812283
Summary
Windows Server 2012 Hyper‑V supports running on systems with up to 320 logical processors (LPs). However, the Windows OS running in the management partition, known as the host, or "root" partition, will only use up to a maximum of 64 root Virtual Processors (root VPs). The Hyper‑V hypervisor will continue to manage and use all logical processors in the system to run any workload in guest Virtual Machines (VMs) on guest VPs. The Windows OS running in the management partition doesn't need more than 64 VPs to perform adequately.
More information
Observing the Number of Processors in the Windows Host OS
Because the Windows OS instance running in the Hyper-V host partition doesn't enumerate and initialize on more than 64 VPs, utilities that attempt to display the number of LPs on a system with > 64 LPs won't accurately reflect the total number of system LPs. These utilities will indicate that the host partition is only using a maximum of 64 VPs, which is correct from the perspective of software running in the host OS instance. To determine the actual number of physical processors in the system, Task Manager or Performance Monitor may be used.
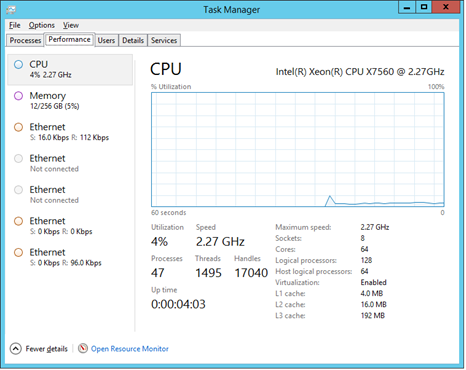
Task Manager Display of Total Host System Logical Processors
Task Manager does accurately display the total number of system logical processors, as illustrated below. The value Logical processors correctly displays 128, which is the total number of processors in the example computer system. The value Host logical processors reflects that the Hyper‑V host partition is only running on 64 VPs out of the total 128 system logical processors.
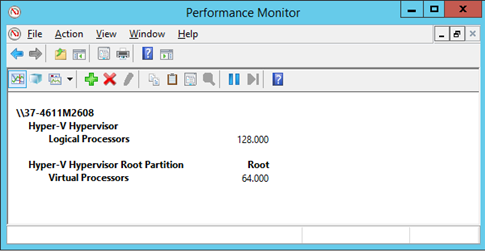
Determining the Number of Logical Processors in Performance Monitor
Windows Performance Monitor may also be used to observe the total number of system logical processors, and the number of VPs in the root partition, as illustrated below. The counter Hyper‑V Hypervisor\Logical Processors indicates the total number of system logical processors that the hypervisor is using. The counter Hyper‑V Hypervisor Root Partition\Virtual Processors indicates the total number of virtual processors allocated to the host partition.
NUMA Topologies
The original and adjusted NUMA topologies of the system can be viewed using the Debugging Tools for Windows. The !numa command displays the configuration of the host partition. The !numa_hal command displays the configuration of the system.