Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Please note: This document reflects the changes made in 2005 recommendations for Indic-script OpenType font and shaping-engine implementations. While Indic fonts made according to the earlier recommendations will still function properly in the new versions of Uniscribe, font developers may choose to update their fonts, particularly if they wish to avoid certain limitations of the earlier implementation.
This document presents information that will help font developers create or support OpenType fonts for all Bengali script languages covered by the Unicode Standard. The Bengali script, closely related to the Devanagari script, is used to write Bengali, Assamese and Manipuri.
Introduction
This document targets developers implementing Indic shaping behavior compatible with Microsoft OpenType specification for Indic scripts. It contains information about terminology, font features and behavior of the Indic shaping engine in regards to the Bengali script. While it does not contain instructions for creating Bengali fonts, it will help font developers understand how the Indic shaping engine processes Indic text. In addition, registered features of the Bengali script are defined and illustrated with examples.
The new Indic shaping engine allows for variations in typographic conventions, giving a font developer control over shaping by the choice of designation of glyphs to certain OpenType features. For example, the location where the reph and pre-pended matra are re-ordered within a syllable cluster is affected by the presence of a half form. See illustrations below.
In the example below (Ra + halant + Da+ halant + Ka + I-matra), Ra + halant will form the reph, but how the Da is classified will determine the position of the reph as well as the location of the pre-pended matra.
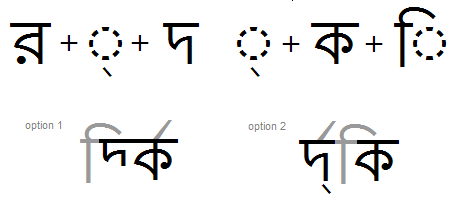
Option 1= The re-ordering behavior of the shaping engine for Bengali where the 'Da' has a half form; the reph will be positioned on the first main consonant; and the I-matra will be positioned immediately in front of the "half-form" D(a).
Option 2= If the Da did not have a half form and was NOT listed in the half feature, the halant-form will display and the shaping engine will treat it as the first main consonant on which to position the reph. And the I-matra will be positioned immediately in front of the base (or half-form) preceding it, which in this case is the Ka.
Glossary
The following terms are useful for understanding the layout features and script rules discussed in this document.
Above-base form of consonants - A variant form of a consonant that appears above the base glyph. In Bengali, only the consonant Ra has an above-base form, known as "reph".
Akhand ligatures - Required consonant ligatures that may appear anywhere in the syllable, and may or may not involve the base glyph. Akhand ligatures have the highest priority and are formed first; some languages include them in their alphabets. Akhand ligatures may be displayed in either half- or full-form.
Base glyph - The only consonant or consonant conjunct in the syllable that is written in its "full" (nominal) form. In Bengali, the last consonant of the syllable (except for syllables ending with letter "Ra") usually forms the base glyph. In "degenerate" syllables that have no vowel (last letter of a word), the last consonant in halant form serves as the base consonant and is mapped as the base glyph. Layout operations are defined in terms of a base glyph, not a base character, since the base can often be a ligature.
Below-base form of consonants - A variant form of a consonant that appears below the base glyph. In Bengali, the consonant Ra and Ba have below-base forms. In the glyph sequence, the below-base form comes after the consonant(s) that form the base glyph. Below-base forms are represented by a non-spacing mark glyph.
Bengali syllable - Effective orthographic "unit" of Bengali writing systems. Syllables are composed of consonant letters, independent vowels, and dependant vowels. In a text sequence, these characters are stored in phonetic order (although they may not be represented in phonetic order when displayed). Once a syllable is shaped, it is indivisible. The cursor cannot be positioned within the syllable. Transformations discussed in this document do not cross syllable boundaries.
Cluster - a group of characters that form an integral unit in Indic scripts, often times a syllable.
Consonant - Each represents a single consonant sound. Consonants may exist in different contextual forms and have an inherent vowel (usually, the short vowel "a"). For example, "Ka" and "Ta", rather than just "K" or "T."
Consonant conjuncts (aka 'conjuncts') - Ligatures of two or more consonants. Consonant conjuncts may have both full and half forms, or only full forms.
Halant (Virama) - The character used after a consonant to "strip" it of it's inherent vowel. A halant follows all but the last consonant in every Bengali syllable; a halant also follows the last consonant if the syllable has no vowel.
NOTE: A syllable containing halant characters may be shaped with no visible halant signs by using different consonant forms or conjuncts instead.
Halant form of consonants - The form produced by adding the halant (virama) to the nominal shape. The Halant form is used in syllables that have no vowel or as the half form when no distinct shape for the half form exists.
Half form of consonants (pre-base form) - A variant form of consonants which appear to the left of the base consonant, if they do not participate in a ligature. Consonants in their half form precede the ones forming the base glyph. Bengali has distinctly shaped half forms for most consonants. If a consonant does not have a distinct shape for the half form and does not form any ligature, it will be displayed with an explicit Virama (same shape as the halant form).
Matra (Dependent Vowel) - Used to represent a vowel sound that is not inherent to the consonant. Dependent vowels are referred to as "matras" in Sanskrit. They are always depicted in combination with a single consonant, or with a consonant cluster. The greatest variation among different Indian scripts is found in the rules for attaching dependent vowels to base characters.
New shaping behavior - Shaping behavior defined in this version of the Indic OpenType Font Specification. Information in this document relates primarily to the new implementation model. Old behavior may be mentioned in comments about compatibility.
Nukta - A combining character that alters the way a preceding consonant (or matra) is pronounced.
Old shaping behavior - Shaping behavior defined in previous versions of the Indic OpenType Font Specification.
OpenType layout engine Library responsible for executing OpenType layout features in a font. In the Microsoft text formatting stack, it is named OTLS (OpenType layout services).
OpenType tag - 4-byte identifier for script, language system or feature in the font.
Post-base form of consonants - A variant form of a consonant that appears to the right of the base glyph. A consonant that takes a post-base form is preceded by the consonant(s) forming the base glyph plus a halant (virama). Post-base forms are usually spacing glyphs.
Pre-base form of consonants - A variant form of a consonant that appears to the left of the base glyph. Note that most pre-base consonant forms are logically as well as visually before the base consonant. Half forms are examples of this kind of pre-base form. In some scripts, though, a pre-base Ra may logically follow the base consonant (that is, it follows it phonetically and in the character sequence of the text), even though it is presented visually before the base. The shaping engine detects such cases dynamically using the 'pref' feature and re-orders the pre-base-form glyph as needed.
Reph - the above-base form of the letter "Ra" that is used in Bengali when "Ra" is the first consonant in the syllable and is not the base consonant.
Shaping Engine - code that processes text strings that is aware of language rules.
Split Matra - A matra that is decomposed into pieces for rendering. Usually the different pieces appear in different positions relative to the base. For instance, part of the matra may be placed at the beginning of the cluster and another part at the end of the cluster.
Syllable - A single unit of Indic text processing. Shaping of Indic text is performed independently for each syllable. Process of identifying boundaries of each syllable is described below.
Vattu - A below-base form of a consonant.
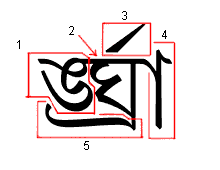
1. Pre-base form
2. The base consonant
3. Above-base form (reph)
4. Post-base (matra)
5. Below-base form (vattu)
Shaping Engine
- Analyze the text
- Reorder characters
- Shape glyph sequences (GSUB processing)
- Position glyphs sequences (GPOS processing)
- Base elements
- Invalid combining marks
- Use of ZWJ, ZWNJ and NBSP
The Indic shaping engine processes Bengali text in stages. The stages are:
- Analyze the text sequence; breaking it into syllable clusters
- Reorder the characters as necessary
- Apply OpenType GSUB font features to get the correct glyph shape
- Apply OpenType GPOS features to position glyphs or marks
The descriptions which follow will help font developers understand the rationale for the Bengali feature encoding model, and help application developers better understand how layout clients can divide responsibilities with operating system functions.
Analyze the syllables
Character properties
The shaping engine divides the text into syllable clusters and identifies character properties.
Character properties are used in parsing syllables and identifying its parts, in determining proper character or glyph reordering and in OpenType feature application. Properties for each character are divided into two types: static properties and dynamic properties.
Static properties define basic characteristics that do not change from font to font: character type (consonant, matra, vedic sign, etc.) or type of matra reordering. They differ from script to script, but can't be controlled by font developer.
Dynamic properties are font dependent and are retrieved by the shaping engine as the font is loaded. These properties affect shaping and reordering behavior.
*Note: in old shaping-engine implementations, all consonant properties were static: consonants were assumed to have particular conjoining forms. In the new implementation model, consonant conjoining behavior is a dynamic property.
Retrieving dynamic character properties from Indic fonts
Fonts define dynamic properties for consonants through implementing standard features. Consonant types (and corresponding feature tags) that the shaping engine reads from the font are:
- Reph 'rphf'
- Half forms 'half'
- Pre-base-reordering forms of Ra/Rra 'pref'
- Below-base forms 'blwf'
- Post-base forms 'pstf'
Each of the features above is applied together with 'locl' feature to input sequences consisting of two characters: for 'rphf' and 'half', features are applied to Consonant + Halant combinations; for 'pref', 'blwf' and 'pstf', features are applied to Halant + Consonant combinations. This is done for each consonant. If these two glyphs form a ligature, with no additional glyphs in context, this means the consonant has the corresponding form. For instance, if a substitution occurs when the 'half' and 'locl' features are applied to a sequence Da + Halant, then Da is classified as having a half form.
Note that a font may be implemented to re-order a Ra to pre-base position only in certain syllables and display it as a below-base or post-base form otherwise. This means that the Pre-base-form classification is not mutually exclusive with either Below-base-form or Post-base-form classifications. However, all classifications are determined as described above using context-free substitutions.
Font-dependent character classification only defines consonant types. Reordering positions, however, are fixed for each character class.
*Note: for fonts that support the old implementation, all features are applied to Consonant + Halant sequences.
Indic input processing
The following steps should be repeated while there are characters left in the input sequence. All shaping operations are done on a syllable-by-syllable basis, independent from other characters.
Find next syllable in the input
Engine should find the character sequence matching one of the patterns below:
Consonant syllable
- {C+[N]+<H+[<ZWNJ|ZWJ>]|<ZWNJ|ZWJ>+H>} +
- C+[N]+[A] + [< H+[<ZWNJ|ZWJ>] | {M}+[N]+[H]>]+[SM]+[(VD)]
Vowel-based syllable:
- [Ra+H]+V+[N]+[<[<ZWJ|ZWNJ>]+H+C|ZWJ+C>]+[{M}+[N]+[H]]+[SM]+[(VD)]
Stand Alone cluster (at the start of the word only):
- [Ra+H]+NBSP+[N]+[<[<ZWJ|ZWNJ>]+H+C>]+[{M}+[N]+[H]]+[SM]+[(VD)]
Where
| { } | zero or more occurrences |
| [ ] | optional occurrence |
| <|> | 'one of' |
| ( ) | one or two occurrences |
| C | consonant |
| V | independent vowel |
| N | nukta |
| H | halant/virama |
| ZWNJ | zero width non-joiner |
| ZWJ | zero width joiner |
| M | matra (up to one of each type: pre-, above-, below- or post- base) |
| SM | syllable modifier sign |
| VD | vedic |
| A | anudatta (U+0952) |
| NBSP | NO-BREAK SPACE |
Identify key positions inside syllable
Syllable structure consists of the following parts:
Reph + HalfConsonant(s) + MainConsonant(s) + BelowBaseConsonant(s) + PostBaseConsonant(s) + PreBaseReorderingRa + MatrasAndSigns
The consonant parts include all associated halants and nuktas. (For example, an instance of BelowBaseConsonant consists of a sequence of Halant + Below-base-forming Consonant.) All parts are optional, except the main consonant.
All parts are shown in the order they would occur within a syllable, with one qualification: depending on a font implementation, PreBaseReorderingRa may occur before all BelowBaseConsonants, after BelowBaseConsonants and before PostBaseConsonants, or after PostBaseConsonants. Also, a font may be implemented to re-order a Ra to pre-base position only in certain syllables and display it as a below-base or post-base form otherwise. Thus, final determination of whether an occurrence of Ra in a specific syllable can be treated as a pre-base reordering Ra can be made only after the 'pref' feature has been applied to that syllable.
There could be several main consonants in the case where more than one consonant doesn't have a half-, below-base, post-base or pre-base form. In a case of a cluster where the first consonant does not have a half form, the shaping engine will recognize it as the 1st 'full form' and go on to identify the 2nd full form consonant, if there is one. This information will then be used to determine the reordering behavior of the reph or any matras, vowel modifiers or stress marks.
All other elements are classified by their position relative to the base: pre-base (half forms and reordering pre-base Ra forms), below-base, above-base and post-base.
Indic clusters are subject to the following constraints:
- Only one reph is allowed per syllable.
- Only one pre-base reordering Ra is allowed per syllable.
- A nukta can be placed on a consonant, matra or independent vowel. It cannot be placed on a pre-composed nukta character.
- One matra from each positioning class is permitted (exception in the Kannada script). A composite matra is treated as belonging to all the classes from which its components belong.
- One syllable modifier sign is allowed per cluster.
- Vedic signs are combining marks (used for Sanskrit) that should be included in all Indic scripts.
- Danda and Double Danda are punctuation marks that should be included in all Indic scripts.
Reorder characters
Once the Indic shaping engine has analyzed the cluster as described above, it creates and manages a buffer of appropriately reordered elements (glyphs) representing the cluster, according to several rules (described below).
The OpenType lookups in an Indic font must be written to match glyph sequences after re-ordering has occurred. OpenType fonts should not have substitutions that attempt to perform the re-ordering. If a font developer attempted to encode such reordering information in an OpenType font, they would need to add a huge number of many-to-many glyph mappings to cover the general algorithms that a shaping engine will use.
- Find base consonant: The shaping engine finds the base consonant of the syllable, using the following algorithm: starting from the end of the syllable, move backwards until a consonant is found that does not have a below-base or post-base form (post-base forms have to follow below-base forms), or that is not a pre-base reordering Ra, or arrive at the first consonant. The consonant stopped at will be the base.
- If the syllable starts with Ra + Halant (in a script that has Reph) and has more than one consonant, Ra is excluded from candidates for base consonants.
- Decompose and reorder Matras: Each matra and any syllable modifier sign in the cluster aremoved to the appropriate position relative to the consonant(s) in the cluster. The shaping engine decomposes two- or three-part matras into their constituent parts before any repositioning. Matra characters are classified by which consonant in a conjunct they have affinity for and are reordered to the following positions:
- Before first half form in the syllable
- After subjoined consonants
- After post-form consonant
- After main consonant (for above marks)
- Reorder marks to canonical order: Adjacent nukta and halant or nukta and vedic sign are always repositioned if necessary, so that the nukta is first.
- Final reordering: After the localized forms and basic shaping forms GSUB features have been applied (see below), the shaping engine performs some final glyph reordering before applying all the remaining font features to the entire cluster.
- Reorder matras: If a pre-base matra character had been reordered before applying basic features, the glyph can be moved closer to the main consonant based on whether half-forms had been formed. Actual position for the matra is defined as 'after last standalone halant glyph, after initial matra position and before the main consonant'. If ZWJ or ZWNJ follow this halant, position is moved after it.
- Reorder reph: Reph's original position is always at the beginning of the syllable, (i.e. it is not reordered at the character reordering stage). However, it will be reordered according to the basic-forms shaping results. Possible positions for reph, depending on the script, are; after main, before post-base consonant forms, and after post-base consonant forms.
- If reph should be positioned after post-base consonant forms, proceed to step 5.
- If the reph repositioning class is not after post-base: target position is after the first explicit halant glyph between the first post-reph consonant and last main consonant. If ZWJ or ZWNJ are following this halant, position is moved after it. If such position is found, this is the target position. Otherwise, proceed to the next step.
Note: in old-implementation fonts, where classifications were fixed in shaping engine, there was no case where reph position will be found on this step. - If reph should be repositioned after the main consonant: from the first consonant not ligated with main, or find the first consonant that is not a potential pre-base reordering Ra.
- If reph should be positioned before post-base consonant, find first post-base classified consonant not ligated with main. If no consonant is found, the target position should be before the first matra, syllable modifier sign or vedic sign.
- If no consonant is found in steps 3 or 4, move reph to a position immediately before the first post-base matra, syllable modifier sign or vedic sign that has a reordering class after the intended reph position. For example, if the reordering position for reph is post-main, it will skip above-base matras that also have a post-main position.
- Otherwise, reorder reph to the end of the syllable.
- Reorder pre-base reordering consonants: If a pre-base reordering consonant is found, reorder it according to the following rules:
- Only reorder a glyph produced by substitution during application of the 'pref' feature. (Note that a font may shape a Ra consonant with the 'pref' feature generally but block it in certain contexts.)
- Try to find a target position the same way as for pre-base matra. If it is found, reorder pre-base consonant glyph.
- If position is not found, reorder immediately before main consonant.
Character reordering Classes for Bengali:
| Characters | Reorder Class |
|---|---|
|
09B0, 09F0 (reph) |
AfterSubscript |
|
09BF, 09C7, 09C8 |
BeforeHalf |
|
09C1-09C4, 09E2, 09E3 |
AfterSubscript |
|
09BE, 09C0, 09D7 |
AfterPostscript |
|
0981 |
AfterPostscript |
Shape glyph sequences (GSUB processing)
All characters from a string are first mapped to their nominal glyphs using the cmap lookup. The shaping engine then proceeds to shape (substitute) the glyphs using GSUB lookups.
The features for localized forms and basic shaping forms are applied one at a time to the cluster or a relevant portion of the cluster.
The results after basic shaping forms features have been applied impact the final syllable analysis in terms of final designation of Ra as a pre-base reordering form and final reordering positions for reph and matras. Next, the features for presentation forms are applied to the entire cluster simultaneously. Note: since the presentation form features are applied simultaneously over the entire cluster, several features are operationally equivalent to a single feature. Multiple features are provided as an aid for font developers to organize the lookups they implement.
Note: final reordering occurs after features for basic shaping forms have been applied and before features for presentation forms are applied. Font developers must consider the effects of initial reordering (before any features are applied) and final reordering (after basic shaping forms features have applied) when they create GSUB feature and lookup tables.
These predefined features are described and illustrated in the Features section and are applied in the order below.
Shaping features:
Localized forms
- Apply feature 'locl' to select language-specific forms.
Basic Shaping forms
- Apply feature 'nukt' to substitute nukta forms of consonants.
- Apply feature 'akhn' to substitute required akhand ligatures, or to substitute forms that take precedence over forms produced by features applied later.
- Apply feature 'rphf' to substitute reph glyph (above-base form of 'Ra').
- Apply feature 'blwf' to substitute below-base forms (ba + ra phala).
- Apply feature 'half' to substitute half forms of pre-base consonants.
- Apply feature 'pstf' to substitute post-base forms of consonants.
- Apply feature 'vatu' to substitute ligature consonant-vattu or conjunct-vattu forms for sequences of a consonant or conjunct glyph (full or half form) followed by the below-base mark.
- Apply feature 'cjct' to substitute conjunct forms. (This is needed particularly for ligature conjuct forms when the pre-base consonant does not have a half form.)
Presentation forms
- Apply feature 'init' to substitute initial forms
- Apply feature 'pres' to substitute pre-base consonant conjuncts and pre-base matra conjuncts. (ie. consonant and matra conjuncts to the left of the base glyph).
- Apply feature 'abvs' to substitute above-base matra conjuncts, reph conjuncts, above-base vowel modifiers and above-base stress and tone marks.
- Apply feature 'blws' to substitute below-base consonant conjuncts, below-base matra conjuncts, below-base vowel modifier forms and below-base stress and tone mark forms.
- Apply feature 'psts' to substitute post-base consonant conjuncts, post-base matra conjuncts and post-base vowel modifiers.
- Apply feature 'haln' to substitute the halant form of base (or conjunct base) glyph in syllables ending with a halant.
- Apply feature 'calt' to substitute the contextual alternate of a consonant.
Position glyph sequences (GPOS processing)
The shaping engine next processes the GPOS (glyph positioning) table, applying features concerned with positioning. All features are applied simultaneously to the entire cluster.
The font developer must consider the effects of re-ordering when creating the GPOS feature and lookup tables (i.e., the glyphs will be in the order they were in after the GSUB presentation forms features were applied).
Positioning features:
Kerning
- Apply feature 'kern' to adjust distances (e.g., to provide kerning between post- or pre-base elements and the base glyph).
- Apply feature 'dist' to adjust distances. (NOTE - the feature 'dist' can be used in the same way as the 'kern' feature. The advantage of using the 'dist' feature is that it does not rely on the application to enable kerning. Therefore, if you want to make sure certain spacing adjustments will always be displayed, you should use the 'dist' feature).
Above-base marks
- Apply feature 'abvm' to position above-base marks (above-base consonant forms, matras, vowel modifiers or stress/tone marks) on base glyphs or post-base matra.
Below-base marks
- Apply feature 'blwm' to position below-base marks (below-base consonant forms, matras, vowel modifiers or stress/tone marks) on base glyphs or post-base matra.
Base elements
Commonly, a feature is required for dealing with the base glyph and one of the post-base, pre-base or above-base elements. Since it is not possible to reorder ALL of these elements next to the base glyph, we need to skip over the elements "in the middle" (reordering-wise).
The solution is to assign different mark attachment classes to different elements of the syllable and positional forms, and in any given lookup work with one mark type only. For example, in above-base substitutions we need only consider above-base elements most of the time.
Generally, it is good practice to label as "mark" glyphs that are denoted as marks in the Unicode Standard as well as below-base/above-base forms of consonants. Then, different attachment classes should be assigned to different marks depending on their position with respect to the base.
For example, after the shaping engine has re-ordered elements within the cluster, matras will always occur before syllable modifiers such as the candrabindu. In an actual sequence, though, potentially some other mark glyph, such as nukta, may occur between the matra and the candrabindu. Thus, when processing the matra and candrabindu, you may need to allow for the possibility that some other mark glyphs may occur between them. Using lookup flags, you can specify that a lookup should process only a certain class of marks, such as 'above-base marks', and ignore all other marks. In that way, a match will occur whether or not a mark from another class is present. Otherwise, the lookup would fail to apply.
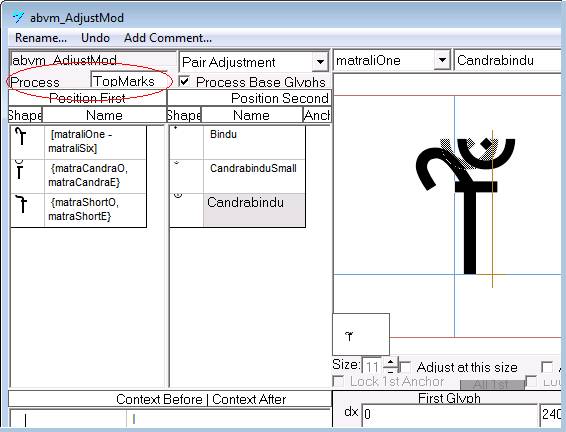
Using Microsoft VOLT, you can assign glyphs to attachment classes.
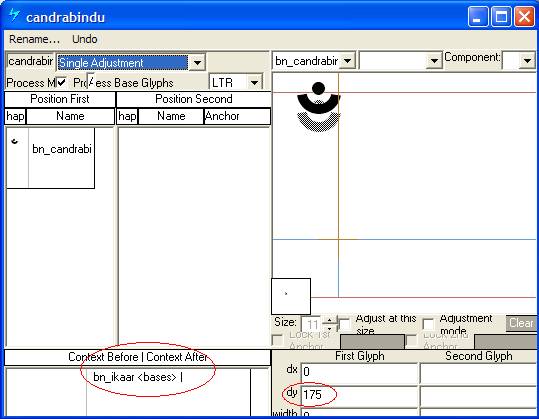
In the example below this 'abvm' feature was set to process only TopMarks, therefore the presence of another mark class would be ignored. If Process ALL was used and another mark glyph followed the matra, this positioning lookup would fail to apply. This example comes from the Devanagari font Mangal.
Invalid combining marks
Combining marks and signs that do not occur in conjunction with a valid base are considered invalid. Shaping engine implementations may adopt different strategies for how invalid marks are handled. For example, a shaping engine implementation might treat an invalid mark as a separate cluster and display the stand-alone mark positioned on some default base glyph, such as a dotted circle. (See Fallback Rendering in section 5.13 of the Unicode Standard 4.0.) Shaping engine implementations may vary somewhat with regard to what sequences are or are not considered valid. For instance, some implementations may impose a limit of at most one above-base vowel mark while others may not.
To allow for shaping engine implementations that expect to position an invalid mark on a dotted circle, it is recommended that a Bengali OT font contain a glyph for the dotted circle character, U+25CC. If this character is not supported in the font, such implementations will display invalid signs on the missing glyph shape (white box).
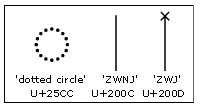
In addition to the 'dotted circle' other Unicode code points that are recommended for inclusion in any Bengali font are the ZWJ (zero width non-joiner; U+200C), the ZWNJ (zero width joiner; U+200D) and the ZWSP (zero width space; U+200B). For more information see the Suggested glyphs section of the OpenType Font Development document.
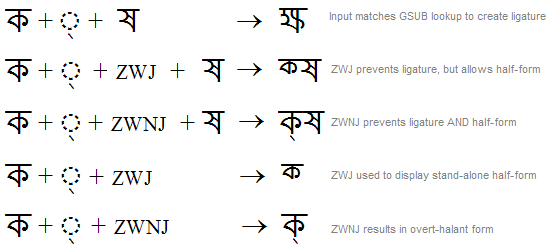
Effect of ZWJ, ZWNJ and NBSP on Consonant Shaping
Unicode defines specific behaviors for zwj and zwnj in relation to Indic scripts. The Indic-specific behavior retains the general behavior that zwj requests connection between text elements while zwnj inhibits connection between text elements.
- The main intent of using ZWJ in this context is to prevent a ligature-conjunct from forming (and in Devanagari or Gujuarati, to request a half form, below-base form or post-base form instead). The Indic engine does not need to take any action to prevent ligature-conjuct formation: the presence of ZWJ will prevent GSUB substitution lookups from matching the input glyph sequence. If the first consonant does not have a half form, an overt-halant form should result, which would also happen with no particular action by the engine.
- A secondary intent of using ZWJ in this context is to prevent the display of reph in the case that the first consonant is RA. If a cluster begins with RA H (halant) ZWJ, the engine must ensure that the 'rphf' feature is not applied, and that re-ordering for reph does not take place. Note that use of either joiner in this context should prevent formation and re-ordering of reph when RA is the first consonant.
- The main intent of using ZWNJ is to prevent conjunct ligature or half forms from forming, and to display an explicit halant form instead. The shaping engine must take specific actions to prevent half forms for a sequence of Consonant + Halant + ZWNJ.
The following example illustrates these behaviors:
Just as the zwj can be used to display a half form in isolation, it can also be used to display a mark, sub- or post-base form in isolation. Unlike the stand-alone half form, however, sequences to display them must begin with a no-break space (NBSP). This is because marks, sub- and post-base forms have a 'zero-width' so must be placed on the NBSP. For example, to get a shape of I-matra without the dotted circle one should type NBSP + I-matra.
In the illustration below the I-matra is displayed without the dotted circle by using the NBSP.
The combination of NBSP and ZWJ is used to display the below-base form of Ra in isolation.
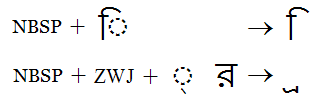
Features
The features listed below have been defined to create the basic forms for the languages that are supported on Bengali systems. Regardless of the model an application chooses for supporting layout of complex scripts, the shaping engine requires a fixed order for executing features within a run of text to consistently obtain the proper basic form.
The features of the basic shaping forms are applied one at a time to the cluster or portion of the cluster. The result impacts the analysis in terms of the conjoining behavior and final reordering. The features of the presentation forms are applied next, to the entire cluster simultaneously. Mandatory features must always be applied; the discretionary presentation-forms features listed should be applied by default, but can be suppressed by a client (normally at the discretion of the user).
The order of the lookups within each feature is also very important. For more information on lookups and defining features in OpenType fonts, see the Encoding section of the OpenType Font Development document.
OpenType features used for Bengali scripts, applied in the following order:
| Feature | Feature function | Layout operation |
|---|---|---|
|
Localized forms: |
||
|
locl |
Localization form substitution |
GSUB |
|
Basic shaping forms: |
||
|
nukt |
Nukta form substitution |
GSUB |
|
akhn |
Akhand ligature substitution |
GSUB |
|
rphf |
Reph form substitution |
GSUB |
|
blwf |
Below-base form substitution |
GSUB |
|
half |
Half-form substitution |
GSUB |
|
pstf |
Post-base form substitution |
GSUB |
|
vatu |
Vattu variants |
GSUB |
|
cjct |
Conjunct form substitution |
GSUB |
|
Mandatory presentation forms: |
||
|
init |
Initial form |
GSUB |
|
pres |
Pre-base substitution |
GSUB |
|
abvs |
Above-base substitution |
GSUB |
|
blws |
Below-base substitution |
GSUB |
|
psts |
Post-base substitution |
GSUB |
|
haln |
Halant form substitution |
GSUB |
|
Discretionary presentation forms: |
||
|
calt |
Contextual alternates |
GSUB |
|
Positioning features: |
||
|
kern |
Kerning |
GPOS |
|
dist |
Distances |
GPOS |
|
abvm |
Above-base mark positioning |
GPOS |
|
blwm |
Below-base mark positioning |
GPOS |
| [GSUB = glyph substitution, GPOS = glyph positioning] | ||
Feature examples
Many of the registered features described and illustrated in this document are based on the Microsoft OpenType font Vrinda. Vrinda contains layout information and glyphs to support all of the required features for the Bengali script and language systems supported.
The illustrations in the following examples show the result of that particular feature being applied. Features must be written to match glyph sequences after re-ordering has occurred. Note that the input context for a feature may be the result of a previous feature having already been applied.
Localized forms
Feature Tag: "locl"
This feature is used in association with OpenType language system tags to trigger lookups that will select alternate glyphs needed for language-specific typographic conventions. The 'locl' should not be used in association with the default language system, but only used with other language system tags. See the Appendix of this document for language system tags associated with the Bengali script.
Basic shaping forms
Nukta
Feature Tag: "nukt"
The nukta alters the way a preceding consonant or vowel is pronounced. The most common nukta forms have been defined as separate characters in Unicode with their own code points. All consonants, as well as akhand forms should have an associated nukta form.
Note - Rather than using substitution, nukta forms can also be created by positioning the nukta as a below-base mark on the base glyph using the 'blwm' positioning feature.
The input context for the nukt feature always consists of the full form of the consonant. The half form of nukta consonants will be substituted using the half feature.
Nukta feature used to substitute pre-composed glyph (Yya) for Ya + Nukta:
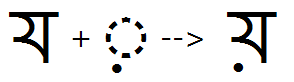
Akhand
Feature Tag: "akhn"
An akhand is a required consonant ligatures that may appear anywhere in the syllable, and may or may not involve the base glyph. Akhand ligatures have the highest priority and are formed first; some languages include them in their alphabets.
The input context for the akhand feature always consists of the full form of the consonant. The half forms of Akhand ligatures will be called later in the half feature.
Because the akhand feature is applied early in the sequence of features and is applied over the entire cluster, it can also be used to create certain forms that must take priority in particular contexts over forms that would be created during subsequent feature application.
Ka + halant + Ssa is substituted with the KaSsa ligature:
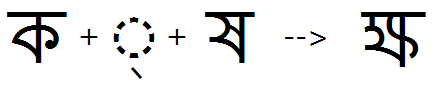
Ja + halant + Nya is substituted with the JaNya ligature:
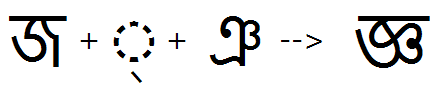
Reph
Feature Tag: "rphf"
Applying this feature substitutes the Reph glyph. If the first consonant of the cluster consists of the full form of Ra + Halant, this feature substitutes the combining-mark form of Reph. In addition, the position of the Reph glyph is adjusted with the 'abvm' GPOS feature.
The input context for the Reph feature always consists of the full form of Ra + Halant.
Example 1- Reph feature substitutes the mark glyph form of Ra. After final reordering, positioning is adjusted in the 'abvm' GPOS feature:
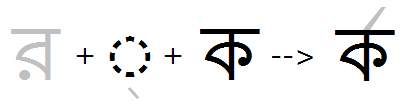
Example 2 - Reph feature applied with multiple consonants. Note- reph is re-ordered to position on the 1st main consonant, not the half-form:
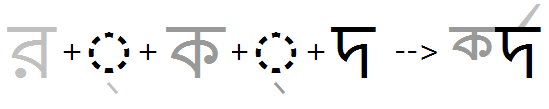
Below form of consonant
Feature Tag: "blwf"
This feature substitutes the below-base forms of Consonants like the Ra + Ba in Bengali, when they do not form a ligature with the preceding consonant.
Halant + Ra (preceded by a consonant which does not form a ligature) substitutes a below-base Ra:
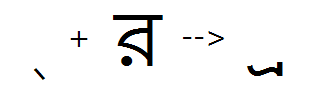
Halant + Ba (preceded by a consonant which does not form a ligature) substitutes a below-base Ba:
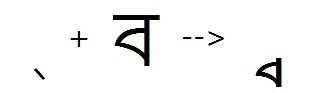
Half form of consonant
Feature Tag: "half"
Applying this feature substitutes half forms - forms of consonants used in the pre-base position. Consonants that have a half form should be listed in the 'half' feature. Bengali has distinctly shaped half forms for most of the consonants. If a consonant does not have a distinct shape for the half form and does not form any ligature, it will be displayed with an explicit Virama (same shape as the halant form).
Note - the result of listing a consonant in the half feature (whether it has a true half form or not) will affect the re-ordering (and positioning) of the reph and pre-pended matras. See illustration in the Introduction section of this document.
This feature is applied to all consonants preceding the 'main' consonant.
Half feature substitutes half form of Ka:
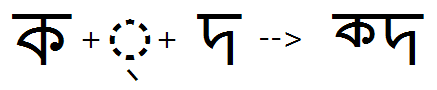
Half feature applied to multiple consonants:
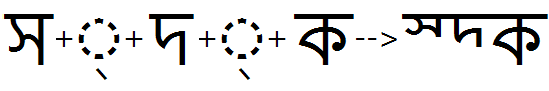
Post-base form of consonant
Feature Tag: "pstf"
Applying this feature substitutes post-base forms, such as the 'Bengali Ya'.
The post-base form of the Ya is substituted, when it is the last consonant in a syllable:
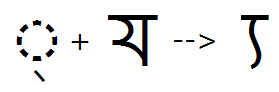
Vattu variants
Feature Tag: "vatu"
The 'vatu' feature can be used to substitute a ligature of a full (or half) form consonant plus a below-base vattu (Bengali ra-phala). The 'blws' can also be used for these ligature substitutions.
The input context for the 'vatu' feature consists of a consonant (in full or half form) + vattu glyph.
The 'vatu' feature used to substitute a ligature of Ka + below-base Ra:
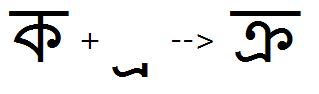
The 'vatu' feature used to substitute a ligature of Tta + below-base Ra:
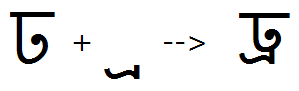
Conjunct forms
Feature Tag: "cjct"
Apply feature 'cjct' to substitute conjunct forms where the first consonant in the consonant-cluster pair does not have a half form. This feature allows for control over re-ordering 'Žof reph and pre-pended matras in case of consonants that do not take half forms yet do form 'Žconjunct ligatures in combination with certain following consonants.
The 'cjct' feature used to substitute a ligature for Gha + Na:
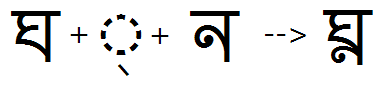
Presentation forms
After the glyphs have been reordered, the presentation lookups are applied to provide the best typographic rendering of the text. The features of the presentation forms are applied to the entire cluster simultaneously, executing lookups within each feature in the order that they are specified in the font.
The pres, abvs, blws, psts and haln features are all mandatory for software implementations: they are required for correct script behaviour and none should ever be treated as discretionary. Because of this and because they are all applied simultaneously over entire clusters, they are not functionally different: a set of lookups could be divided between these features or grouped together under one of them with no difference in effect. These multiple features are provided, however, as an aid to the font developer for organizing lookups based on the combinations of glyphs they apply to. There are no specific requirements on how each should be used; the examples provided below illustrate typical usage, however.
Initial form
Feature Tag: "init"
This feature is used to substitute initial forms of the vowels E and Ai, in Bengali scripts. The initial form is a glyph variant that does not have a connecting bar on the leading side of the glyph.
All initial forms must be based on an input context consisting of the full form of consonants.
Initial feature applied:
Pre-base substitutions
Feature Tag: "pres"
This feature is used to substitute pre-base consonant conjuncts made with half forms, the type most common in Bengali. The resulting conjunct can be in full or half form.
This feature is also used to select typographically correct forms of the I-Matra. For example, a font can have several versions of the I-Matra to be used in context with different consonant bases or clusters. In addition the 'pres' feature can contain pre-composed ligatures of the I-matra with certain bases.
Example 1 - half Ka + full Ka is substituted by the KaKa conjunct:
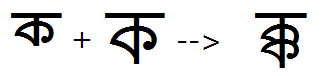
Example 2 - half Ka + full Ma is substituted by the KaMa conjunct:
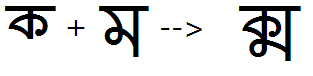
Example 3 - half La + full Ka is substituted by the LaKa conjunct:
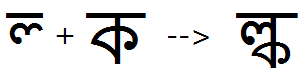
Example 4 - half Ka + half Ssa + full Nna is substituted by the KaSsaNna ligature:
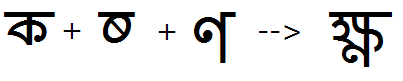
Example 5 - The 'pres' feature is also used to substitute ligatures with the I-Matra:
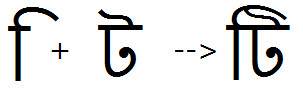
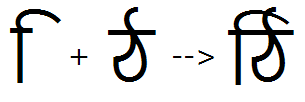
Above-base substitutions
Feature Tag: "abvs"
This feature is used for substitutions involving above-base marks. Such substitutions might be used to select contextual forms of marks, to create mark-mark ligatures, or to create mark-base ligatures. Specific context-dependent forms or below-base consonants are handled by this lookup as well.
The 'abvs' feature used to substitute a ligature for the reph + matre I combination:
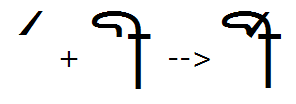
The 'abvs' feature used to substitute a ligature for the reph + candrabindu glyphs:
Below-base substitutions
Feature Tag: "blws"
This feature is used for glyph substitutions involving below-base marks or consonants. Such substitutions can be used to create conjuncts of base glyphs with below-base consonants, below mark ligatures or below mark-base ligatures. Specific context-dependent forms are handled by this lookup as well.
Example 1- 'blws' substitution for base + below-base conjuncts:
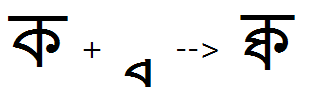
Example 2- In the presence of below-base consonants, the below-base matra can change shape in the ligature:

Example 3- 'blws' substitution when conjunct base + matra form a new ligature:

Post-base substitutions
Feature Tag: "psts"
This feature is used to substitute post-base consonants or matras. Such substitutions can be used to create conjuncts of base glyphs with post-base consonants or post-base matra ligatures. It can also be used to specify contextual alternates of post-base forms.
Example 1- 'psts' used to substitute conjunct of base and post-base matra:
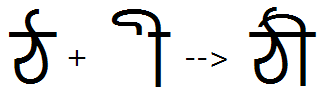
Example 2- 'psts' used to substitute conjunct of base and post-base matra:
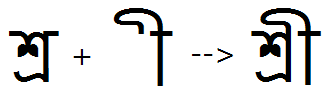
Halant form of consonants
Feature Tag: "haln"
This feature is used to substitute a pre-composed halant form of a base (or conjunct base) glyph in syllables ending with a halant. (Rather than using substitution, halant forms can also be created by positioning the halant as a below-base mark on the base glyph using the 'blwm' positioning feature.)
This feature is applied only on the base glyph if the syllable ends with a halant, or in the case of non-final consonants that do not take a half form and do not form a conjunct ligature with the following consonant.
Example 1 - 'haln' feature used to substitute halant form of base glyph:
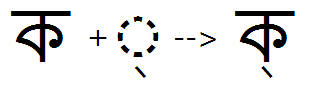
Example 2 - 'haln' feature used to substitute halant form of conjunct base glyph:
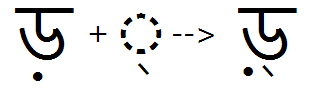
Contextual Alternates
Feature Tag: "calt"
Unlike the previous presentation lookups, the 'calt' feature is optional and is used to substitute discretionary contextual alternates. It is important to note that an application may allow users to turn off this feature, therefore should not be used for any obligatory Bengali typography.
Positioning features
Distances
Feature Tag: "dist"
This feature covers positioning lookups that adjust distances between glyphs, such as kerning between pre- and post-base elements and the base glyph. Note; the feature 'dist' can be used in the same way as the 'kern' feature. The advantage of using the 'dist' feature is that it does not rely on the application to enable kerning.
Above-base marks
Feature Tag: "abvm"
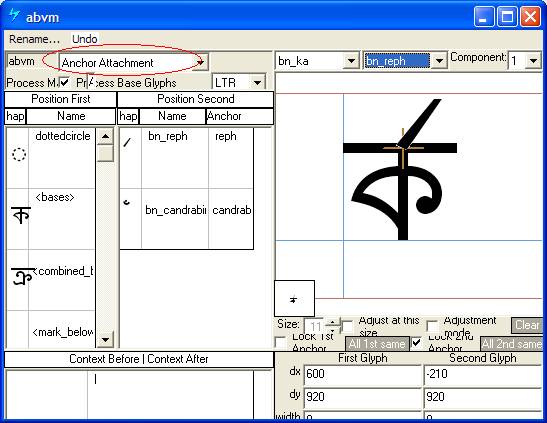
This feature positions all above-base marks on the base glyph or the post-base matra. The best method for encoding this feature in an OpenType font is to use a chaining context positioning lookup that triggers mark-to-base and mark-to-mark attachments for above-base marks.
The 'abvm' lookup in MS Volt using 'Anchor Attachment' for adjusting positions of above-marks over bases:
A contextual 'abvm' lookup in MS Volt using 'Single Adjustment' for positioning candrabindu over certain bases:
Below-base marks
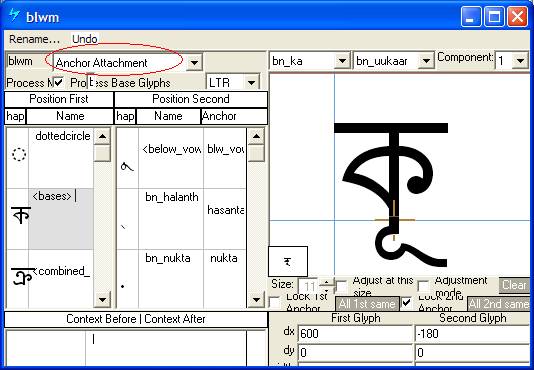
Feature Tag: "blwm"
This feature positions all below-base marks on the base glyph. The best method for encoding this feature in an OpenType font is to use a chaining context positioning lookup that triggers mark-to-base and mark-to-mark attachments for below-base marks.
The 'blwm' lookup in MS Volt using 'Anchor Attachment' for adjusting positions of below-marks with bases:
Examples of Bengali syllables
Complex Bengali syllable formation is possible using the wide range of features available in OpenType. The following examples show how the shaping engine applies the OpenType features, one at a time to the input string. These combinations do not necessarily represent actual syllables or words, but are meant to illustrate the various OpenType features in a Bengali font.
Example #1:

Example #2:

Appendices
Appendix A: Writing System Tags
Features are encoded according to both a designated script and language system. There are different language systems defined for the Assamese, Bengali and Manipuri languages, although they all use the Bengali script.
Currently most shaping engine implementations only support the "default" language system for each script. However, font developers may want to build language specific features which are supported in other applications and will be supported in future Microsoft OpenType implementations.
NOTE: It is strongly recommended to include the "dflt" language tag in all OpenType fonts because it defines the basic script handling for a font. The "dflt" language system is used as the default if no other language specific features are defined, or if the application does not support that particular language. If the "dflt" tag is not present for the script being used, the font may not work in some applications.
The following table lists the registered tag names for script and language systems. Note for new Indic shaping implementation 'bng2' is used (old-behavior implementations used 'beng').
| Registered tags for the Bengali script | Registered tags for Bengali language systems | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Script tag |
Script |
Language system tag |
Language |
|
"bng2" |
Bengali |
"dflt" |
*default script handling |
|
"ASM " |
Assamese |
||
|
"BEN " |
Bangla |
||
|
"MNI " |
Manipuri |
||
Note: both the script and language tags are case sensitive (script tags should be lowercase, language tags are all caps) and must contain four characters (ie. you must add a space to the three character language tags).
Script development specifications