Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This tutorial guides you through creating an overlay port for a library hosted on a private Azure DevOps repository, covering authentication setup and packaging into an overlay.
Prerequisites:
- Basic understanding of Git and vcpkg.
- Access to Azure DevOps with permissions to create projects and manage SSH keys.
vcpkginstalled on your system.- Git installed on your system.
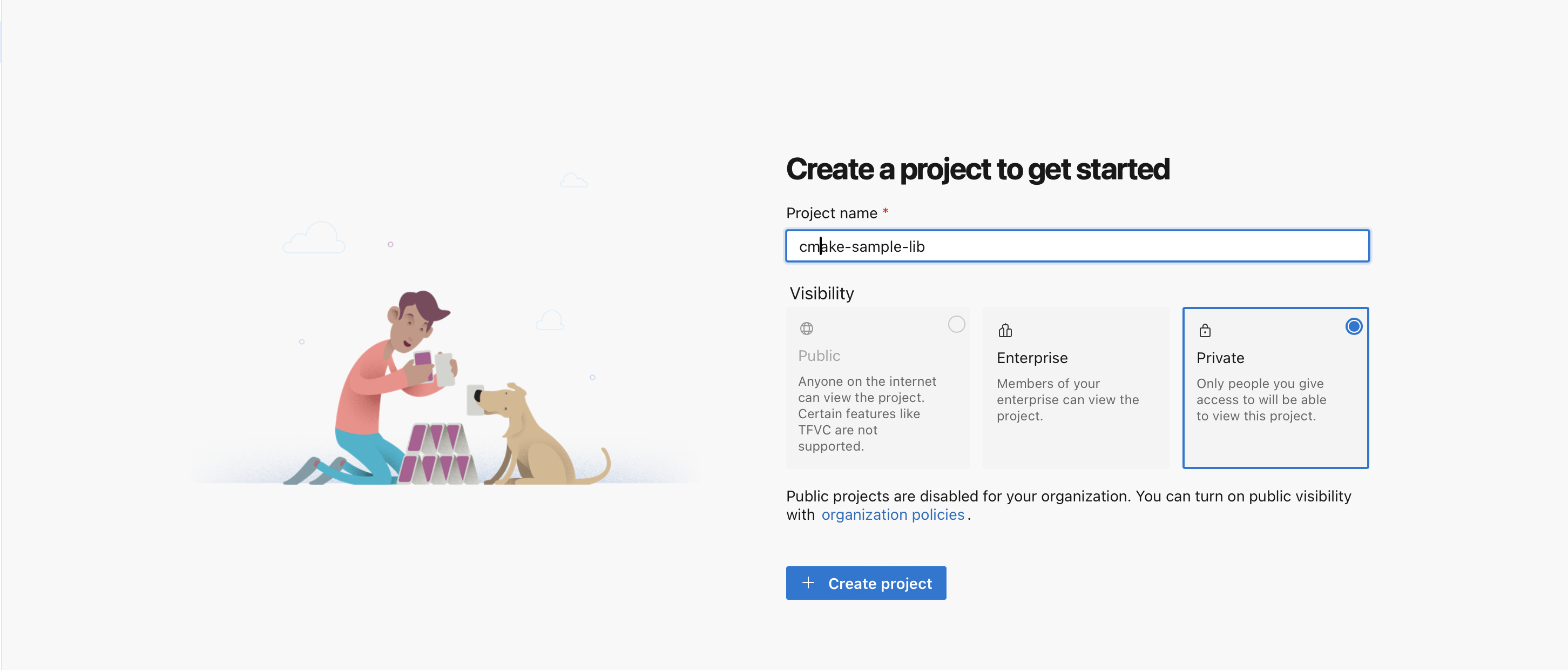
1 - Create a private project
- Log into your Azure DevOps account
- Create a new private project. If you don't have an organization, you'll be prompted to create one during the project creation process.
Name your project: Choose a meaningful name that reflects your library or its purpose.
Visibility: Ensure the project is set to "Private" to control access.
2 - Set Up Authentication in Azure DevOps
Secure access to your repository with SSH keys.
Generate an SSH Key Pair
Open a terminal or command prompt.
Run the following command:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "ADO-RSA" -f /path/to/.ssh/id_rsa_ado-t rsa: Specifies the type of key to create, in this case, RSA.-b 4096: Sets the number of bits in the key, in this case, 4096, which is considered strong and secure.-C "ADO-RSA": Adds a label to the key for identification, which can be particularly useful when you have multiple keys.-f /path/to/.ssh/id_rsa_ado: Specifies the filename for the new key. This command saves the private key toid_rsa_adoand the public key toid_rsa_ado.pub.
You'll be prompted to enter a passphrase for additional security. You can either enter a passphrase or press Enter to proceed without one. A passphrase adds an extra layer of security by requiring the passphrase to be entered whenever the key is used.
After the key generation, confirm the new key is created by listing the contents of your
/.ssh/directory again:ls /path/to/.ssh
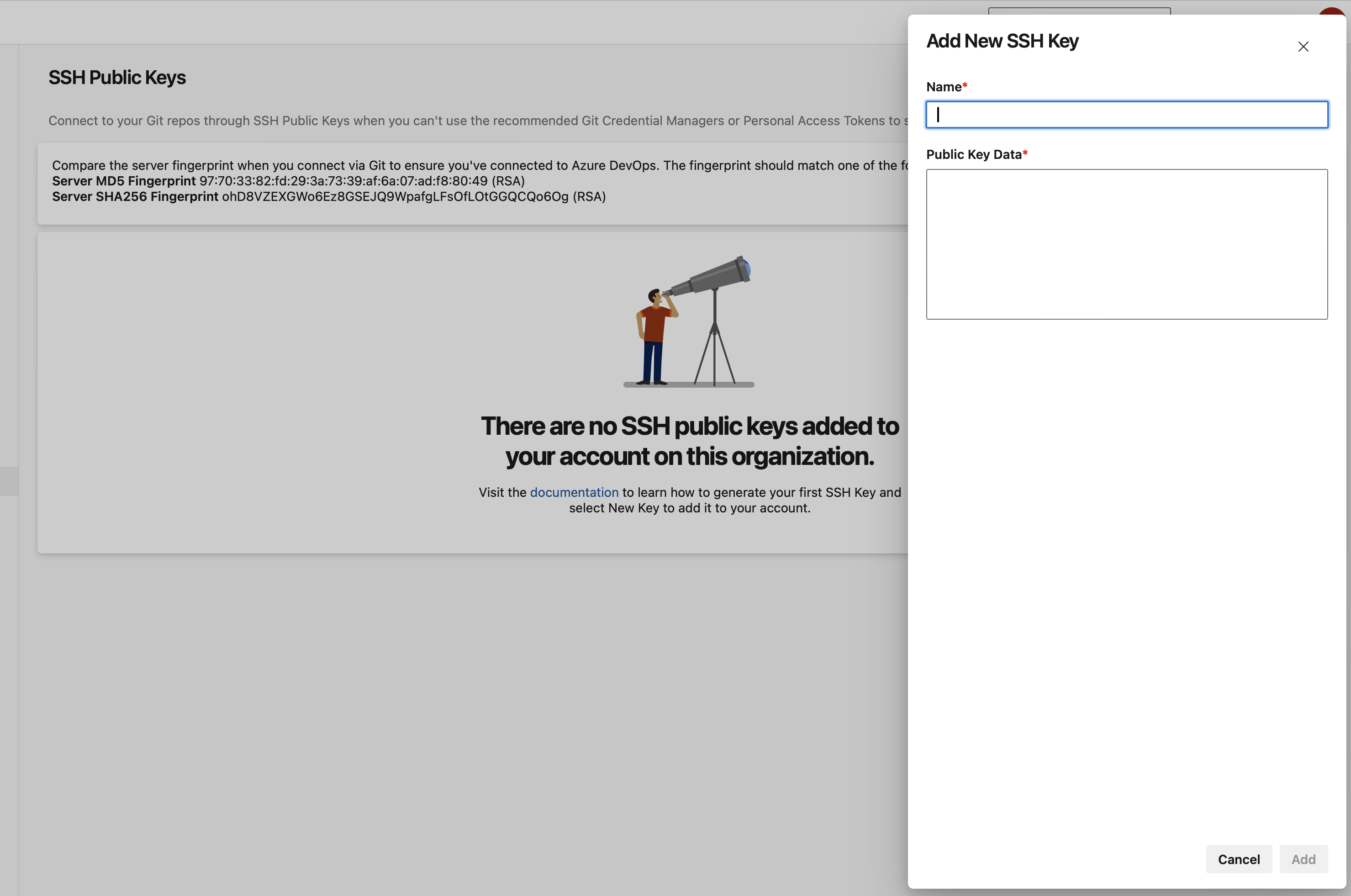
Add your SSH key to Azure DevOps
Open the
id_rsa_ado.pubfile with a text editor to view the public key.Copy the entire content of the file.
Navigate to your User Settings > SSH Public Keys.

Add your new key by pasting the copied content and name your key for future reference.
Load your SSH key into the SSH agent.
Ensure your SSH key is available for authentication:
ssh-add /path/to/.ssh/id_rsa_adoTest SSH connection
Verify connectivity to Azure DevOps:
ssh -T git@ssh.dev.azure.comExpect a message indicating successful authentication but noting that shell access is not supported.
ssh -T git@ssh.dev.azure.com remote: Shell access is not supported. shell request failed on channel 0
3 - Upload library to Azure DevOps repo
Initialize a local git repository
Navigate to your library's source code directory and initialize a Git repository:
git initCommit your library Add and commit your library's source code:
git add . git commit -m "Initial commit of the sample library"Link to Your Azure DevOps Repository
Retrieve your repository's SSH URL from Azure DevOps and add it as a remote:

git remote add origin <Your-Repo-SSH-URL>Push Your Library
Upload your library to the Azure DevOps repository:
git push -u origin master:main
4 - Package your library into an overlay port
Overlay ports allow you to use local ports with vcpkg.
Create an overlay ports directory
mkdir vcpkg-overlay-ports cd vcpkg-overlay-portsSet up the port files
vcpkg.json: This manifest file defines your library's metadata and dependencies.Disclaimer: The following examples use placeholders. Replace them with your actual data.
{ "name": "your-library-name", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "Description of your library.", "dependencies": [] }The
vcpkg.jsonfile serves as a manifest that defines metadata and dependencies for a C++ library, providing vcpkg with the necessary information to build, install, and manage the package.name: Specifies the name of the library. This is used as the package identifier.version: Indicates the version number of the library.description: Brief text describing what the library does. This is for documentation and users.dependencies: An array containing the list of dependencies that the library needs.
For more information on how to set up your
vcpkg.json, check out our reference documentation.portfile.cmake: This script tells vcpkg how to build your library.vcpkg_from_git( OUT_SOURCE_PATH SOURCE_PATH URL "git@ssh.dev.azure.com:v3/YourOrg/YourProject/YourRepo" REF "<commit-sha>" ) vcpkg_cmake_configure(SOURCE_PATH "${SOURCE_PATH}") vcpkg_cmake_install() vcpkg_cmake_config_fixup(PACKAGE_NAME your-library-name) file(INSTALL "${SOURCE_PATH}/LICENSE" DESTINATION "${CURRENT_PACKAGES_DIR}/share/your-library-name")This portfile defines how to download, build, install, and package a specific C++ library from GitHub using vcpkg.
vcpkg_from_git: Starts the function to download the source code from a git repository.OUT_SOURCE_PATH SOURCE_PATH: Sets the directory where the source code will be extracted.URL git@ssh.dev.azure.com:v3/YourOrg/YourProject/YourRepo: The SSH URL for the repository containing the source code.REF <commit-sha>: The commit SHA of your library's code in Azure DevOps.vcpkg_cmake_configure: Configures the project using CMake, setting up the build.SOURCE_PATH "${SOURCE_PATH}": The path to the source code downloaded earlier.
vcpkg_cmake_install(): Builds and installs the package using CMake.vcpkg_cmake_config_fixup(PACKAGE_NAME your-library-name): Fixes the CMake package configuration files to be compatible with Vcpkg.file(INSTALL "${SOURCE_PATH}/LICENSE" DESTINATION ...): Installs the LICENSE file to the package's share directory and renames it to copyright.
To obtain the commit SHA:
mkdir temp && cd temp git init git fetch <Your-Repo-SSH-URL> main --depth 1 -n git rev-parse FETCH_HEADFor more information on how to set up your
portfile.cmake, checkout the following articles:
Install your port
Back in your main vcpkg directory, install your library specifying the overlay ports directory:
vcpkg install your-library-name --overlay-ports=/path/to/vcpkg-overlay-ports
Next Steps
You've successfully packaged a private Azure DevOps repository as a vcpkg port. This tutorial is intended as a guideline; please adapt the instructions to fit your specific library and development environment.