Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Visual Studio provides support for configuring the interactive development environment (IDE) for Python development. You can set options according to your preference and to meet specific development environment needs. This article describes options available for general layout and behavior, debugging, diagnostics, and advanced Python language features.
Location of Python options
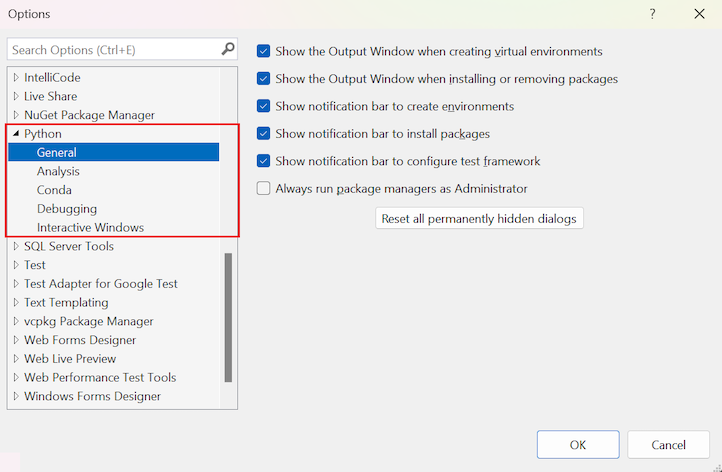
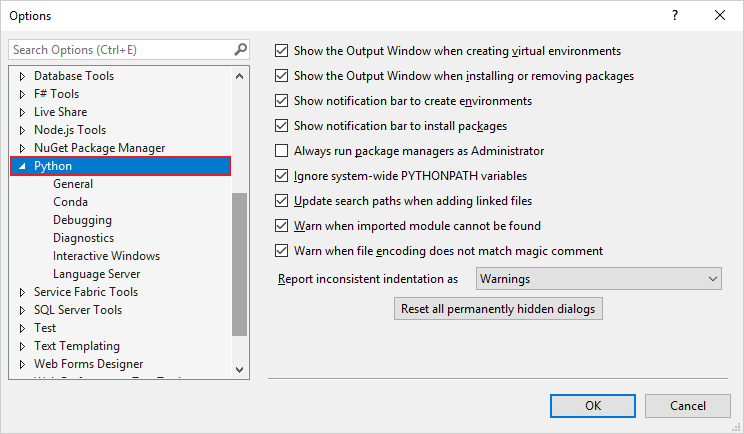
Python configuration settings are available from the Visual Studio toolbar under Tools > Options. The Options dialog lists most settings for Python on the Python tab:
You can configure preferences for debugging, Pylance language server analysis, conda environments, the general environment, and Interactive Windows.
You can configure preferences for debugging, the language server, diagnostics, and Interactive Windows. Options are also available for the general environment and conda environments.
The Options dialog lists other Python settings under Text Editor > Python. There are options for scroll bars, tabs, and formatting, along with general and advanced settings. Other settings are available under Environment > Fonts and Colors for the Text Editor settings group.
In earlier versions of Visual Studio, you might need to select Show All Settings on the Options dialog to see all available options for Python.
Note
The Options dialog might include an Experimental tab or group for features under development that aren't described in this article. You can find more information in posts on the Python engineering at Microsoft blog.
Specific options for Python
Under Tools > Options > Python, you can set Python-specific options for the general environment including Interactive Windows, conda environments, debugging, and more.
General Python options
The following options are available under Tools > Options > Python> General:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Show the Output Window when creating virtual environments | On | Clear to prevent the Output window from appearing. |
| Show the Output Window when installing or removing packages | On | Clear to prevent the Output window from appearing. |
| Show notifications bar to create environments | On | When set and you open a project with a requirements.txt or environment.yml file, Visual Studio displays an information bar with suggestions to create a virtual environment or conda environment, respectively, instead of using the default global environment. |
| Show notifications bar to install packages | On | When set and you open a project with a requirements.txt file that doesn't use the default global environment), Visual Studio compares those requirements with packages installed in the current environment. If any packages are missing, Visual Studio displays a prompt to install those dependencies. |
| Show notifications bar to configure test framework | On | When set, if Visual Studio detects files in your Python project that might contain tests but no test framework is enabled, Visual Studio prompts you to enable pytest or unittest. |
| Always run package managers as administrator | Off | Always elevates pip install and similar package manager operations for all environments. When you install packages, Visual Studio prompts for administrator privileges if the environment is located in a protected area of the file system such as c:\Program Files. In that prompt you can choose to always elevate the install command for just that one environment. For more information, see Packages tab. |
| Option | Default | Description | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Show the Output Window when creating virtual environments | On | Clear to prevent the Output window from appearing. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Show the Output Window when installing or removing packages | On | Clear to prevent the Output window from appearing. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Show notifications bar to create environments | On | When set and you open a project with a requirements.txt or environment.yml file, Visual Studio displays an information bar with suggestions. You can create a virtual environment or conda environment rather than use the default global environment. | Visual Studio 2019 and later |
| Show notifications bar to install packages | On | When set and you open a project with a requirements.txt file that doesn't use the default global environment, Visual Studio compares those requirements with packages installed in the current environment. If any packages are missing, Visual Studio displays a prompt to install those dependencies. | Visual Studio 2019 and later |
| Always run package managers as administrator | Off | Always elevates pip install and similar package manager operations for all environments. When you install packages, Visual Studio prompts for administrator privileges if the environment is located in a protected area of the file system such as c:\Program Files. In that prompt you can choose to always elevate the install command for just that one environment. For more information, see Packages tab. |
Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Automatically generate completion DB on first use | On | Prioritizes completion of the database for a library when you write code that uses it. For more information, see Intellisense tab. | - Visual Studio 2017 version 15.5 and earlier - Later versions of Visual Studio when used with an IntelliSense database |
| Ignore system-wide PYTHONPATH variables | On | PYTHONPATH is ignored by default because Visual Studio provides a more direct means to specify search paths in environments and projects. For more information, see Use Python folders in Visual Studio search paths. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Update search paths when adding linked files | On | When set, adding a linked file to a project updates Search paths so that IntelliSense can include the contents of the linked file's folder in its completion database. Clear this option to exclude such content from the completion database. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Warn when imported module cannot be found | On | Clear this option to suppress warnings when you know an imported module isn't presently available but doesn't otherwise affect code operation. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Report inconsistent indentation as | Warnings | Because the Python interpreter depends heavily on proper indentation to determine scope, Visual Studio by default issues warnings when it detects inconsistent indentations that might indicate coding errors. Set to Errors to be even more strict, which causes the program to exit in such cases. To disable this behavior altogether, select Don't. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Check for survey/news | Once a week | Sets the frequency at which you allow Visual Studio to open a window containing a web page with Python-related surveys and news items, if available. Options are Never, Once a day, Once a week, and Once a month. | Visual Studio 2017 and earlier |
| Reset all permanently hidden dialogs | n/a | Different dialog boxes provide options such as Don't show me this again. Use this button to clear those options and cause the dialogs to reappear. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
Conda environment options
The following options are available under Tools > Options > Python> Conda:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Conda executable path | (blank) | Specifies an exact path to the conda.exe executable rather than relying on the default Miniconda installation included with the Python workload. If another path is given here, it takes precedence over the default installation and any other conda.exe executables specified in the registry. You might change this setting if you manually install a newer version of Anaconda or Miniconda, or want to use a 32-bit distro rather than the default 64-bit distro. |
Debugging options
The following options are available under Tools > Options > Python> Debugging:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Prompt before running when errors are present | On | When this option is set, Visual Studio prompts you to confirm that you want to run code that has errors. To disable the warning, clear this option. |
| Wait for input when process exits abnormally Wait for input when process exits normally |
On (for both) | A Python program started from Visual Studio runs in its own console window. By default, the window waits for you to press a key before closing it regardless of how the program exits. To remove that prompt and close the window automatically, clear either or both of these options. |
| Tee program output to Debug Output window | On | Displays program output in both a separate console window and the Visual Studio Output window. Clear this option to show output only in the separate console window. |
| Break on SystemExit exception with exit code of zero | Off | If set, stops the debugger on this exception. When clear, the debugger exits without breaking. |
| Enable debugging of the Python standard library | Off | Makes it possible to step into the standard library source code while debugging, but increases the time it takes for the debugger to start. |
| Show function return value | On | Displays function return values in the Locals window then stepping over a function call in the debugger (F10) |
| Show variables | On | Displays four groups of variables to show and how to format the display (Group, Hide, Inline). - Class: Default is "Group" - Protected: Default is Inline" - Function: Default is "Group" - Special: Default is "Group" |
| Option | Default | Description | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prompt before running when errors are present | On | When this option is set, Visual Studio prompts you to confirm that you want to run code that contains errors. To disable the warning, clear this option. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Wait for input when process exits abnormally Wait for input when process exits normally |
On (for both) | A Python program started from Visual Studio runs in its own console window. By default, the window waits for you to press a key before closing it regardless of how the program exits. To remove that prompt and close the window automatically, clear either or both of these options. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Tee program output to Debug Output window | On | Displays program output in both a separate console window and the Visual Studio Output window. Clear this option to show output only in the separate console window. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Break on SystemExit exception with exit code of zero | Off | If set, stops the debugger on this exception. When clear, the debugger exits without breaking. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Enable debugging of the Python standard library | Off | Makes it possible to step into the standard library source code while debugging, but increases the time it takes for the debugger to start. | Visual Studio 2019 and later |
| Show function return value | On | Displays function return values in the Locals window then stepping over a function call in the debugger (F10) | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Use legacy debugger | Off | Instructs Visual Studio to use the legacy debugger by default. For more information, see Debugging - Use the legacy debugger. | Visual Studio 2019 only |
Analysis options
The following options are available under Tools > Options > Python> Analysis:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic mode | Open files only | Specifies what code files the language server analyzes for problems, including Workspace and Open files only. |
| Log level | Information | Specifies the level of logging to perform by the language server. The possible levels of logging, in increasing level of information provided, include Error, Warning, Information, and Trace. |
| Type checking | Off | Specifies the level of type checking analysis to perform: - Off: Produce unresolved imports/variables diagnostics but don't conduct type checking analysis - Basic: Use non-type (all rules on under the Off level) and also basic type checking-related rules - Strict: Use all type checking rules at the highest severity of error, including all rules on under both the Off and Basic levels |
| Import format | Absolute | Defines the default format when auto importing modules, including Absolute or Relative. |
| Stubs path | <Empty> | Specifies a path to a directory that contains custom type stubs. The type stub files for each package are expected to be in their own subdirectory. |
| Search paths | <Empty> | Specifies search paths for import resolution. Accepts paths specified as strings and separated by commas if there are multiple paths, such as ["path 1","path 2"]. |
| Typeshed paths | <Empty> | Specifies paths for Visual Studio to use custom Typeshed files instead of its bundled version. |
| Automatically add common search paths like 'src' | On | Indicates whether to automatically add search paths based on predefined names, such as src. |
| Index installed third party libraries and user files for language features such as auto-import, add import, workspace symbols and etc. | Off | Specifies whether the language server should index user files and installed third-party libraries at start up. The index provides a more complete set of symbols in features, including auto imports, Quick Fixes, auto completions, and so on. - When set, Visual Studio indexes the top-level symbols of installed packages, such as symbols in all under package/__init__.py, along with all symbols from up to 2,000 user files. - When not set, Visual Studio displays symbols referenced or used in files previously opened in or loaded by the editor. |
Diagnostics options
The following options are available under Tools > Options > Python> Diagnostics:
| Option | Default | Description | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Include analysis logs | On | Includes detailed logs relating to analysis of installed Python environments when saving diagnostics to a file or copying them to the clipboard using the buttons. This option can significantly increase the size of the generated file, but is often required to diagnose IntelliSense issues. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Save diagnostics to file | n/a | This option prompts for a filename and saves the log to a text file. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Copy diagnostics to clipboard button | n/a | Select this option to place the entire log file on the clipboard. This operation might take some time depending on the size of the log. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
Language server options
The following options are available under Tools > Options > Python> Language server:
| Option | Default | Description | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disable completions from Typeshed | Off | Visual Studio IntelliSense normally uses a bundled version of Typeshed (a set of .pyi files) to find type hints for standard library and third-party libraries for both Python 2 and Python 3. Setting this option disables the bundled TypeShed behavior. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
| Custom Typeshed path | (blank) | If set, Visual Studio uses the Typeshed files at this path instead of its bundled version. Ignore if Disable completions from Typeshed is set. | Visual Studio 2019 and earlier |
Interactive Windows options
The following options are available under Tools > Options > Python> Interactive Windows:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Scripts | n/a | Specifies a general folder for startup scripts to apply to Interactive Windows for all environments. For more information, see Startup scripts. Note: This feature might not work in your version of Visual Studio. |
| Up/down arrows navigate history | On | Uses the arrow keys to navigate through history in the Interactive window. Clear this setting to use the arrow keys to navigate within the Interactive window's output instead. |
| Completion mode | Only evaluate expressions without function calls | The process of determining the available members on an expression in the Interactive window might require evaluating the current unfinished expression, which can result in side-effects or functions being called multiple times. The default setting, Only evaluate expressions without function calls excludes expressions that appear to call a function, but evaluates other expressions. For example, it evaluates the statement a.b but not the a().b statement. Never evaluate expressions prevents all side-effects, using only the normal IntelliSense engine for suggestions. Evaluate all expressions evaluates the complete expression to obtain suggestions, regardless of side effects. |
| Hide static analysis suggestions | Off | When set, displays only suggestions that are obtained by evaluating the expression. If combined with the Completion mode value Never evaluate expressions, no useful completions appear in the Interactive window. |
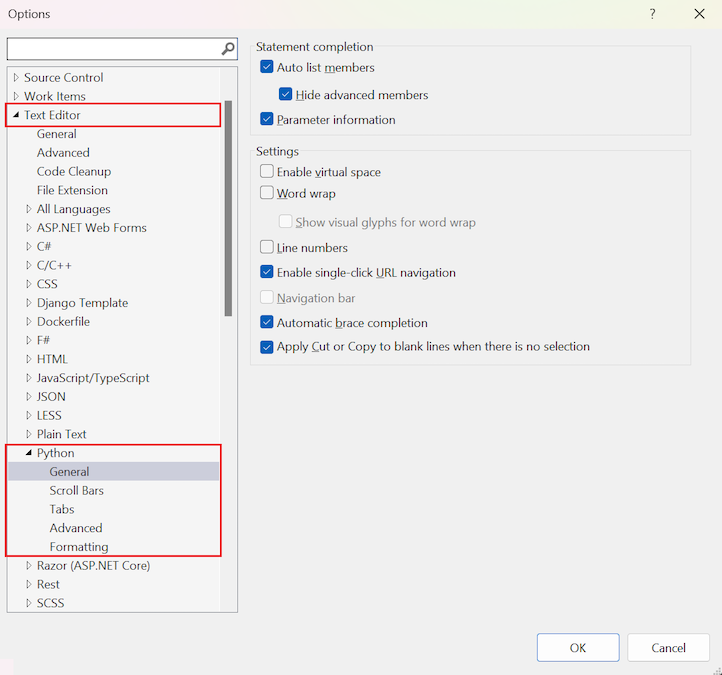
Text editor options for Python
Under Text Editor > Python, there are options for scroll bars, tabs, and formatting, along with general and advanced settings:
General Python editor options
The following options are available under Tools > Options > Text Editor > Python > General:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Auto list members | On | Set this option to automatically list members for completion of code statements. |
| Hide advanced members | On | When the Auto list members option is enabled, set this option to hide advanced members from the completion suggestions. Advanced members are members that are used less frequently than others. |
| Parameter information | On | When set, hovering over parameters shows detailed information, such as the item definition and links to documentation. |
| Enable virtual space | On | When set, inserts spaces at the end of each line of code. Select this option to position comments at a consistent point next to your code. The Virtual Space mode is enabled in Column Selection mode. When Virtual Space mode isn't enabled, the insertion point moves from the end of one line directly to the first character of the next line. Note: This option is influenced by the Text Editor > All Languages > General > Enable virtual space global setting. If the global setting isn't enabled, this option can't be enabled at the language level. |
| Word wrap | Off | Set this option to allow long lines of code to wrap based on the editors viewport width. |
| Show visual glyphs for word wrap | Off | When the Word wrap option is enabled, set this option to show visual glyphs. |
| Line numbers | Off | Set this option to show line numbers in the left margin of the editor for each line of code. |
| Enable single-click URL navigation | On | When set, you can single-click a URL to browse to the target location. |
| Navigation bar | Off | Set this option to enable the dropdown boxes at the top of the code window. These fields help you navigate to code in a codebase where you can choose a type or member to go directly to. Note: This option is influenced by the Text Editor > All Languages > General > Enable navigation bar global setting. For more information, see Navigate code> Navigation bar. |
| Automatic brace completion | On | When set, Visual Studio automatically adds the closing brace for any open brace as you enter code. |
| Apply Cut or Copy to blank lines when there is no selection | On | By default, Visual Studio cuts or copies the entire line of code when there's no explicit selection. Use this option to enable or disable this Cut or Copy behavior when invoked on blank lines. |
For more information, see Options dialog box: Text Editor > General.
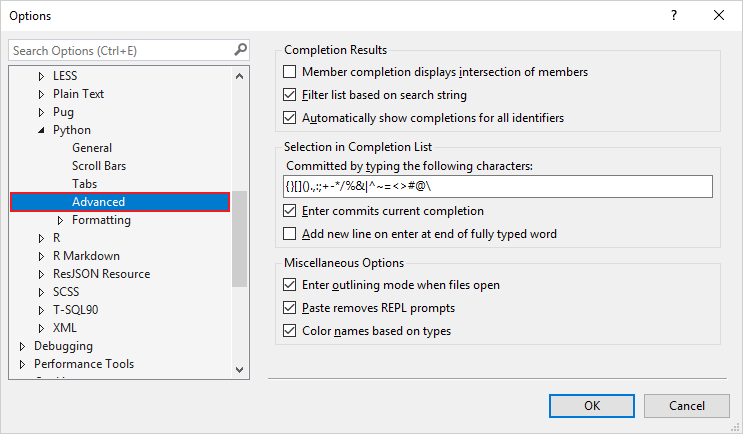
Advanced Python editor options
The following options are available under Tools > Options > Text Editor > Python > Advanced:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Offer auto-import completions | On | When set, Visual Studio offers auto imports in completions. |
| Automatically add brackets for functions | Off | When set, Visual Studio automatically adds brackets for functions as you enter code in the editor. |
Completion Results
The Completion Results group includes the following options:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Member completion displays intersection of members | Off | When this option is set, Visual Studio shows only completions supported by all possible types. |
| Filter list based on search string | On | Applies filtering of completion suggestions as you enter input. |
| Automatically show completions for all identifiers | On | To disable completions in both the editor and Interactive Windows, clear this option. |
Selection in Completion List
The Selection in Completion List group includes the following options:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Committed by typing the following characters | {}[]().,:;+-*/%&|^~=<>#@\ | These characters typically follow an identifier that one might select from a completion list, so it's convenient to commit the completion simply by typing a character. You can remove or add specific characters to the list as desired. |
| Enter commits current completion | On | When set, the Enter key chooses and applies the currently selected completion. See the first entry in this table for the list of recognized characters. |
| Add new line on enter at end of fully typed word | Off | By default, if you type the entire word that appears in the completion popup and press Enter, you commit that completion. By setting this option, you effectively commit completions when you finish typing the identifier, such that Enter inserts a new line. |
Miscellaneous Options
The Miscellaneous Options group includes the following settings:
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enter outlining mode when files open | On | Automatically turn on Visual Studio's outlining feature in the editor when opening a Python code file. |
| Paste removed REPL prompts | On | Removes the REPL Python command prompt and continuation prompt (>>> and ...) from pasted text, which allows for easy transfer of code from the Interactive window to the editor. Clear this option if you need to retain those characters when pasting from other sources. |
| Color names based on types | On | Enables syntax coloring in Python code. |
Fonts and Colors options
Other Python options are available under Environment > Fonts and Colors when the Text Editor group is set to Python:
The names of the Python options are all prefixed with "Python" and are self-explanatory. The default font for all Visual Studio color themes is 10 pt Consolas regular (not bold). The default colors vary by theme. Typically, you change a font or color to make it easier to read text.