A Wave Sink for Kernel-Mode Software Synthesizers
As explained in Synthesizers and Wave Sinks, the DMus port driver implements the wave sink for a software synthesizer that operates in kernel mode. The miniport driver for the synthesizer exposes an ISynthSinkDMus interface to the port driver. The port driver's wave sink uses this interface to read the wave data that is produced by the synthesizer.
To make use of the DMus port driver's wave sink, a DMus miniport driver should define a DirectMusic filter with two types of pin:
A DirectMusic input pin or MIDI input pin. This pin is a sink for a render stream containing MIDI messages.
A wave output pin. This pin is a source for a render stream containing PCM samples.
The following figure shows a DirectMusic filter containing a synthesizer node (KSNODETYPE_SYNTHESIZER). This filter meets the preceding requirements for a kernel-mode software synthesizer by providing a DirectMusic input pin and a wave output pin. (In addition, a DMus miniport driver that supports legacy MIDI synthesis can provide a MIDI input pin.)
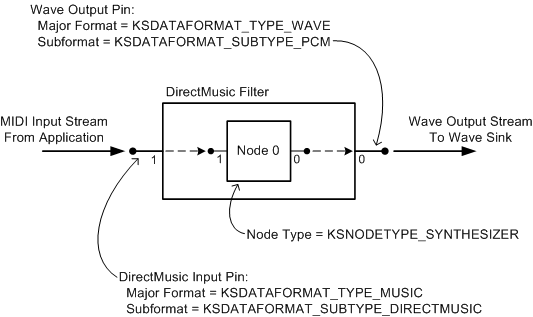
On the left side of the figure, a MIDI stream enters the filter through the DirectMusic input pin. This pin has an IMXF interface that it exposes to the port driver. The port driver obtains this interface by calling the IMiniportDMus::NewStream method. The port driver feeds MIDI messages to the pin by calling the IMXF::PutMessage method.
On the right side of the figure, a wave stream exits the filter through the wave output pin and flows to the port driver's wave sink. The port driver communicates with the pin through its ISynthSinkDMus interface. The port driver obtains this interface by first calling IMiniportDMus::NewStream to obtain a stream object with an IMXF interface, and then querying the object for its ISynthSinkDMus interface. The wave sink pulls wave data from the pin by calling the ISynthSinkDMus::Render method.
Although a hardware synthesizer could, in principle, rely on the port driver's wave sink for rendering, the call to ISynthSinkDMus::Render adds enough latency to the MIDI stream to make it unattractive for many interactive applications. To reduce stream latency, hardware synthesizers are likely to have internal connections to mixing and wave-rendering hardware instead of using the port driver's wave sink. This type of synthesizer replaces the wave output pin on the right side of the preceding figure with a hardwired connection (represented as a bridge pin) to a hardware mixer.
The ISynthSinkDMus interface provides methods to render wave data through a wave sink, convert from reference time to sample time and back, and synchronize to the master clock:
ISynthSinkDMus::RefTimeToSample
ISynthSinkDMus::SampleToRefTime
ISynthSinkDMus inherits from the IMXF interface. For more information, see ISynthSinkDMus.
The DMus miniport driver in the preceding figure identifies its DirectMusic input pin and wave output pin as follows:
To identify its DirectMusic input pin, the miniport driver defines the pin's data range to have a major format of type KSDATAFORMAT_TYPE_MUSIC and a subformat of type KSDATAFORMAT_SUBTYPE_DIRECTMUSIC. This combination indicates that the pin accepts a time-stamped MIDI stream. The data range descriptor is a structure of type KSDATARANGE_MUSIC. (For an example, see DirectMusic Stream Data Range.) The miniport driver defines the pin's data flow direction to be KSPIN_DATAFLOW_IN. (The PCPIN_DESCRIPTOR structure's KsPinDescriptor.DataFlow member indicates the data flow direction.) When calling IMiniportDMus::NewStream to create the stream object for this pin, the port driver sets the StreamType parameter to DMUS_STREAM_MIDI_RENDER.
To identify its wave output pin, the miniport driver defines the pin's data range to have a major format of type KSDATAFORMAT_TYPE_AUDIO and a subformat of type KSDATAFORMAT_SUBTYPE_PCM. This combination indicates that the pin emits a wave audio stream containing PCM samples. The data range descriptor is a structure of type KSDATARANGE_AUDIO. (See the example in PCM Stream Data Range.) The miniport driver defines the pin's data flow direction to be KSPIN_DATAFLOW_OUT. When calling IMiniportDMus::NewStream to create the stream object for this pin, the port driver sets the StreamType parameter to DMUS_STREAM_WAVE_SINK.
In addition, if the driver were to support a MIDI input pin for the synthesizer, its definition would be similar to that of the DirectMusic input pin, but the pin definition would specify a subformat of type KSDATAFORMAT_SUBTYPE_MIDI, and the pin would accept a raw MIDI stream rather than a time-stamped MIDI stream.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for