Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Here are some example designs for USB Type-C systems.
A typical USB Type-C system has these components:
- USB Dual-Role controller is capable of operating either in host role or in function/device/peripheral role. This component is integrated into SoC.
- Battery Charging 1.2 detection might be integrated in certain SoCs. Some SoC vendors provide a PMIC module that implements detection logic, others implement in software. Windows 10 Mobile supports all those options. Contact your SoC vendor to get details about this component.
- Type-C -PD Port controller manages CC pins on the USB Type-C connector. Supports BMC encoding/decoding of power delivery messages. This component isn't integrated in most SoCs.
- Mux SuperSpeed USB pairs to a port on the controller depending on the orientation detected by Type-C port controller. Mux SuperSpeed pairs and possibly SBU lines elsewhere (usually the Display module) when entering an alternate mode.
- VBus/VConn source is required. Most PMICs implement VBus/VConn control. Contact your SoC/PMIC vendor for details.
USB Type-C system design with an embedded controller
In addition to the components in the preceding list, a USB Type-C system can have an embedded controller. This intelligent microcontroller that acts as the Type-C and Power Delivery policy manager for the system.
Here's an example of a USB Type-C system with an embedded controller:
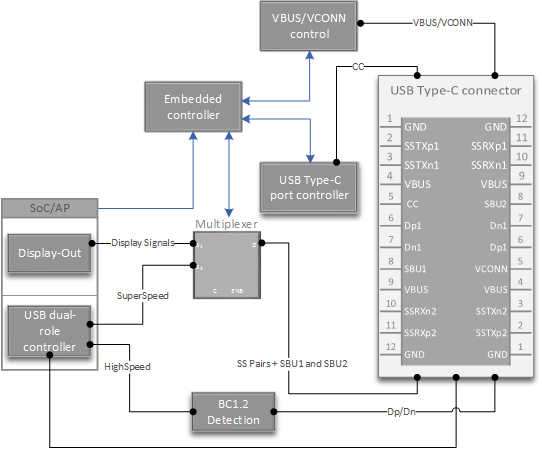
Here's another view:
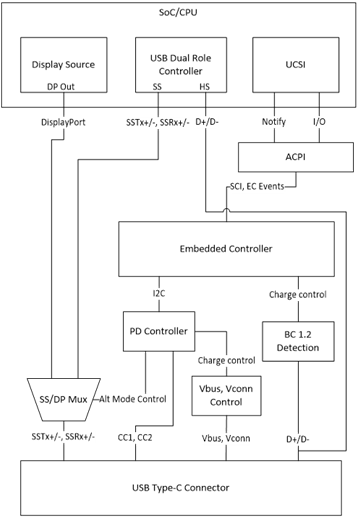
For a system that has an embedded controller, load the Microsoft provided in-box driver. UcmUcsi.sys implements USB Type-C Connector System Software Interface (UCSI) Specification.
UCSI driver. For information about the device stacks loaded for the driver, see Drivers for supporting USB Type-C components for systems with embedded controllers.
For a system that has an embedded controller that uses non-ACPI transport.
USB Type-C system design
Here's an example of a USB Type-C system for a mobile device that doesn't have an embedded controller:
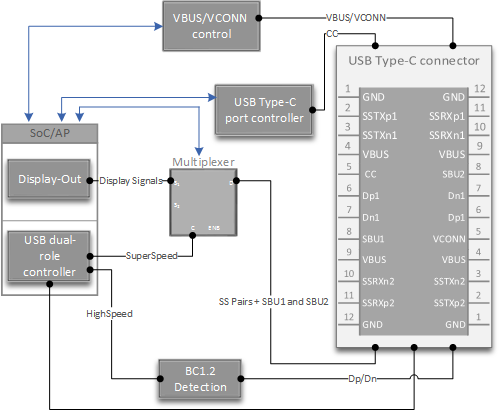
Here's another view:
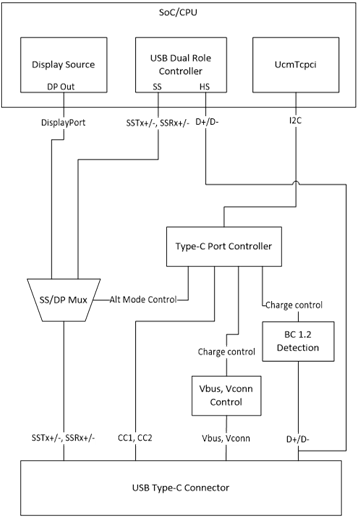
For the preceding design, implement a driver that communicates with the connector and keeps the operating system informed about USB Type-C events on the connector.
Write a USB Type-C connector driver