Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This test leverages SNMP-controlled, programmable power strips to validate that the driver, controller, and underlying device honor the appropriate flush command by persisting data to the device.
It includes the following steps:
Write a known pattern directly to disk (by-passing the file system) and wait for writes to complete.
Send Flush command and wait for completion.
Immediately trigger sudden power loss.
On reboot, read back and verify that all data that was written to disk before the flush command.
Repeat cycle with a different write scenario (different size, pattern, location, etc.).
Test details
| Specifications |
|
| Platforms |
|
| Supported Releases |
|
| Expected run time (in minutes) | 480 |
| Category | Compatibility |
| Timeout (in minutes) | 480 |
| Requires reboot | false |
| Requires special configuration | false |
| Type | automatic |
Additional documentation
Tests in this feature area might have additional documentation, including prerequisites, setup, and troubleshooting information, that can be found in the following topic(s):
Running the test
Before you run the test, complete the test setup as described in the test requirements for the type of storage controller that you are testing. See Storage Adapter or Controller Testing Overview for more information.
This test runs both on boot and non-boot controller compared to the older test which could only run on non-boot controller. This enables testing of both boot disks and data disks. For boot disk, the multithreaded scenarios are skipped, whereas for a data disk, all the scenarios are executed.
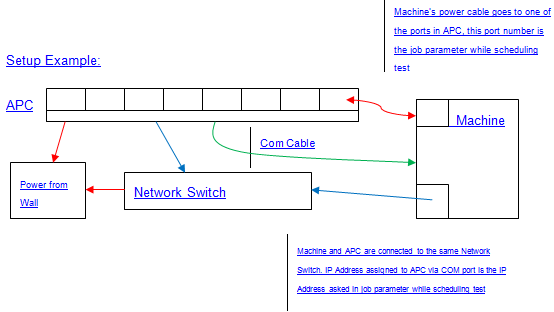
Setup required for the test: Connect a power distribution unit (PDU), controllable via SNMP, to the HLK test machine.
Power strip should have a valid IP address associated as the test uses both the IP address and the port to initiate sudden power loss.
Power strip can be connected locally/remotely to machine, please see power strip manual for configuration details.
Troubleshooting
For generic troubleshooting of HLK test failures, see Troubleshooting Windows HLK Test Failures.
For troubleshooting information, see Troubleshooting Device.Storage Testing.
Power-strip
The test supports providing OID value for SNMP connections for a PDU. The default OID is set as .1.3.6.1.4.1.318.1.1.12.3.3.1.1.4 as it is the one that is used by APC and it can be changed when providing parameters to the test based on the OID of the PDU. The only limit as of now is the ASN value as mentioned below. Other PDU models should have the same ASN value.
ImmediatePowerOn = 1
ImmediatePowerOff = 2
ImmediateReboot = 3
The test is known to support the APC and CPS PDUs with these ASN values and can be tested out with other PDUs as well that supports configuration mentioned as above. To run the test, you will need the IP address of the power-strip. Please refer to the power-strip user manual for information on how to discover the IP address.
Sudden Power Loss and BIOS setting
Test runs about 21 scenarios initiating sudden power loss each time. When power-strip port is programmed for power off and delayed power on, systems may not power ON automatically as this is a BIOS setting and is usually available on desktop machines. Example: On HP Compaq DC7800 machine, In BIOS under Advanced->Power-On Options, there is a field called "After Power Loss", set it to ON.
For uninterrupted and automated way of running flush test, set the BIOS setting to power ON machine automatically when power is plugged in.
Battery/Non-battery powered systems
Flush runs only on non-battery powered systems. If you are using a desktop machine, flush is applicable. If you are using a laptop machine (we assume battery is plugged in), flush is not applicable. Below are the options available for certifying devices against systems.
Certifying devices on desktop machines
- See options for BIOS power setting above
Certifying devices on laptop machines
Select a laptop which has a BIOS power setting, remove battery and follow steps for running tests
Or, Put laptop motherboard in a desktop casing (i.e., just like a desktop machine) and follow steps for running tests
More information
These scenarios send a flush command to the device as soon as all outstanding I/O complete for a given scenario. Power loss occurs immediately after the flush command completes. If any data from the scenario did not persist to disk, the test will fail. The logo test will run each of these 21 scenarios.
Flush and Reboot after 512MB of Syncronous Sequential Writes
Small writes (512B - 4KB)
Large writes (768KB - 1MB)
Pseudorandom-sized writes (512B - 1MB)
Flush and Reboot after 512MB of Syncronous Random Writes
Small writes (512B - 4KB)
Large writes (768KB - 1MB)
Pseudorandom-sized writes (512B - 1MB)
Flush and Reboot after 512MB of Syncronous Striding Writes
Small writes (512B - 4KB)
Large writes (768KB - 1MB)
Pseudorandom-sized writes (512B - 1MB)
Flush and Reboot after 1GB of Asyncronous Sequential Writes via 4 threads
Small writes (512B - 4KB)
Large writes (768KB - 1MB)
Pseudorandom-sized writes (512B - 1MB)
Flush and Reboot after 1GB of Asyncronous Random Writes via 4 threads
Small writes (512B - 4KB)
Large writes (768KB - 1MB)
Pseudorandom-sized writes (512B - 1MB)
Flush and Reboot after 1GB of Asyncronous Striding Writes via 4 threads
Small writes (512B - 4KB)
Large writes (768KB - 1MB)
Pseudorandom-sized writes (512B - 1MB)
Flush and Reboot after 1.5GB of Asyncronous Random, Sequential, and Striding Writes via 6 threads
Small writes (512B - 4KB)
Large writes (768KB - 1MB)
Pseudorandom-sized writes (512B - 1MB)
Parameters
| Parameter name | Parameter description |
|---|---|
| WDKDeviceID | Device to test |
| StorageDriveLetter | Assigned by Create Storage Parameters |
| IP | IP Address of Remote PDU |
| OID | OID of Remote PDU outlet |
| Outlet | Port of Remote PDU outlet |
| Community | Community of Remote PDU (e.g. private) |
| DiskDeviceObjLink | Assigned by Create Storage Parameters |