Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Example Test Environments
The following diagrams show some of the possible test setups. These topologies could be used to test a single HMD, two HMDs, or an HMD with servo controlled motion.
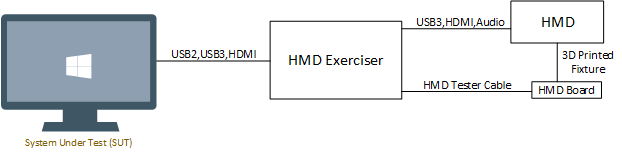
High-level connectivity diagram with one HMD
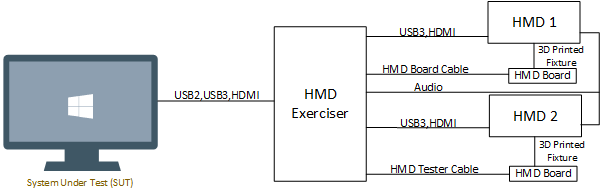
High-level connectivity diagram with two HMDs

High-level connectivity diagram with one HMD and servo
Hardware Requirements
In addition to the HMD Exerciser Kit, the test environment must include the following hardware components:
System Under Test (SUT)
- The SUT must meet the minimum requirements to support Windows Mixed Reality
- The SUT must have the version of Windows installed with which to test interoperability (Windows 10 Fall Creator Update or newer)
- The SUT must have the following ports available:
- 1 USB 3.0 port for connection to the HMD
- 1 USB 2.0/3.0 port for connection to the HMD Exerciser
- 1 HDMI port for connection to the HMD
HMD
The HMD Exerciser Kit is compatible with all HMDs that support Windows Mixed Reality.
Example Test Setup
Test setup should resemble the image below:
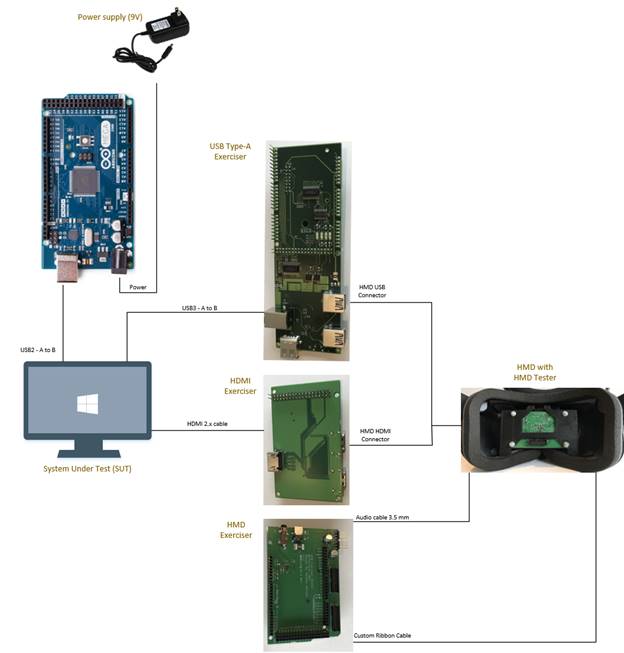
Hardware Setup Instructions
Ensure that the HMD Exerciser Main Board's shields are all present and are firmly attached.
Connect HDMI cable from HDMI port J1 to the System Under Test.
Connect USB 3.0 cable from USB port J1 to a USB 3.0 port on the System Under Test.
Connect USB 2.0 cable from the Arduino USB port to the System Under Test.
Connect the power supply for the HMD Exerciser to the lower barrel jack on the HMD Exerciser Main Board.
Connect the HMD Board cable to the P1 port on the HMD Shield.
Connect the other side of the HMD Board cable to the HMD Board.
Ensure the HMD Board is firmly attached to the appropriate mount.
Clip the HMD Board into the HMD. Ensure it is centered on the displays. If present, adjust the mechanical IPD dial as needed.
Attach the audio cable between the audio jack on the HMD Exerciser Main Board to the HMD headphone jack (if present).
Connect the HMD's USB and HDMI connection to the HMD Exerciser Main Board, noting which port they are plugged into.
Ensure the HMD Exerciser Main Board is recognized by Device Manager on the proxy controller.
- Right-click the Start button in the task bar and select Device Manager.
- Expand the Ports (COM & LPT) node and note the COM port that is used by the microcontroller. In this example, it is connected to COM4.

Run ConnExUtil /SetPort <USB Port> where <USB Port> is the port where the HMD is connected to the HMD Exerciser USB Shield. This will be J2 or J3.
Run ConnExUtil /SetHDMIPort <HDMI Port> where <HDMI Port> is the port where the HMD is connected to the HMD Exerciser's HDMI Shield. This will be J2 or J3.
Ensure that your HMD enumerates in Device Manager.
Additional resources
Confirming USB current and power
The onboard LCD on the HMD Exerciser's USB Shield displays power (volts, amps, and direction). Confirm that it matches expectations from power sources plugged in and actively enabled. Power draw from port J2 or J3 will show as negative.

Confirming device addition on desktops
Identify the USB host controller to which the device is connected.
Ensure that the new device appears under the correct node in Device Manager.
For USB 3.0 hubs connected to a USB 3.0 port, Device Manager shows two hub devices: one enumerated at SuperSpeed and another at high speed.
Confirm device removal on desktops
Identify the device in Device Manager.
Perform the test step to remove the device from the system.
Confirm that the device is no longer present in Device Manager.
For a USB 3.0 hub, check that both devices (SuperSpeed and companion hubs) are removed. Failure to remove a device in this case may be a device failure and should be investigated by all components involved to triage the appropriate root cause.
Using ETW to log issues
To enable ETW for USB 2.0 ports, see Overview of USB Event Tracing for Windows.
To enable USB 3.0 logging, run the following commands (or see How to capture a USB event trace with Logman):
logman start usbtrace -ets -o usbtrace.etl -nb 128 640 -bs 128 logman update usbtrace -ets -p Microsoft-Windows-USB-UCX Default logman update usbtrace -ets -p Microsoft-Windows-USB-USBHUB3 Default
After these are logs are captured, run the test scenario.
Stop the trace by using this command:
logman stop usbtrace -ets