Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Use the following steps to migrate the WSUS database (SUSDB) from a Windows Internal Database instance to a Local or Remote instance of SQL Server.
Prerequisites
- SQL Instance. This can be the default MSSQLServer or a custom Instance.
- SQL Server Management Studio
- WSUS with WID role installed
- IIS (This is normally included when you install WSUS through Server Manager). It is not already installed, it will need to be.
Migrating the WSUS database
Stop the IIS and WSUS services on the WSUS server
From PowerShell (elevated), run:
Stop-Service IISADMIN
Stop-Service WsusService
Detach SUSDB from the Windows Internal Database
Using SQL Management Studio
- Right-click SUSDB -> Tasks -> click Detach:
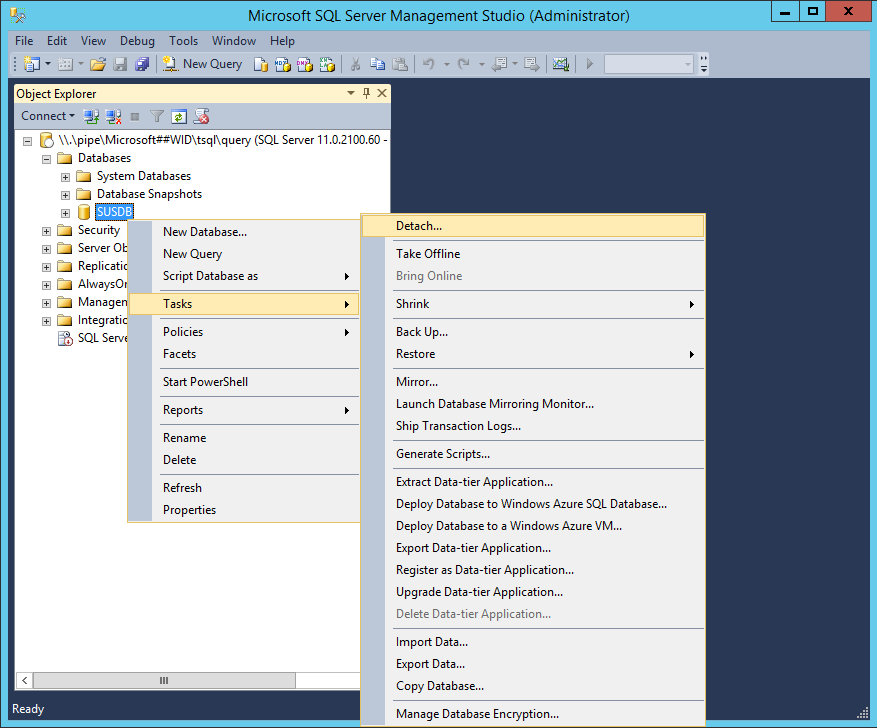
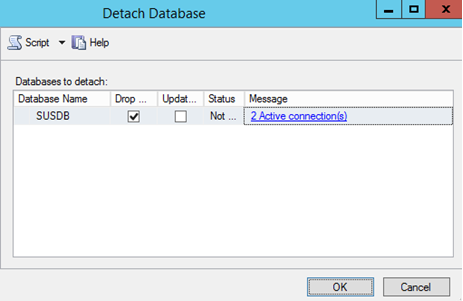
- Check Drop Existing Connections and click OK (optional, if active connections exist).
Using Command Prompt
Important
These steps show how to detach the WSUS database (SUSDB) from the Windows Internal Database instance by using the sqlcmd utility. For more information about the sqlcmd utility, see sqlcmd Utility.
- Open an elevated command prompt
- Run the following SQL command to detach the WSUS database (SUSDB) from the Windows Internal Database instance by using the sqlcmd utility:
sqlcmd -S \\.\pipe\Microsoft##WID\tsql\query
use master
GO
alter database SUSDB set single_user with rollback immediate
GO
sp_detach_db SUSDB
GO
Copy the SUSDB files to the SQL Server
- Copy SUSDB.mdf and SUSDB_log.ldf from the WID Data Folder (%SystemDrive%\Windows\WID\Data) to the SQL Instance Data Folder.
Tip
For example, if your SQL Instance Folder is C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL, and the WID Data folder is C:\Windows\WID\Data, copy the SUSDB files from C:\Windows\WID\Data to C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Data
Attach SUSDB to the SQL Instance
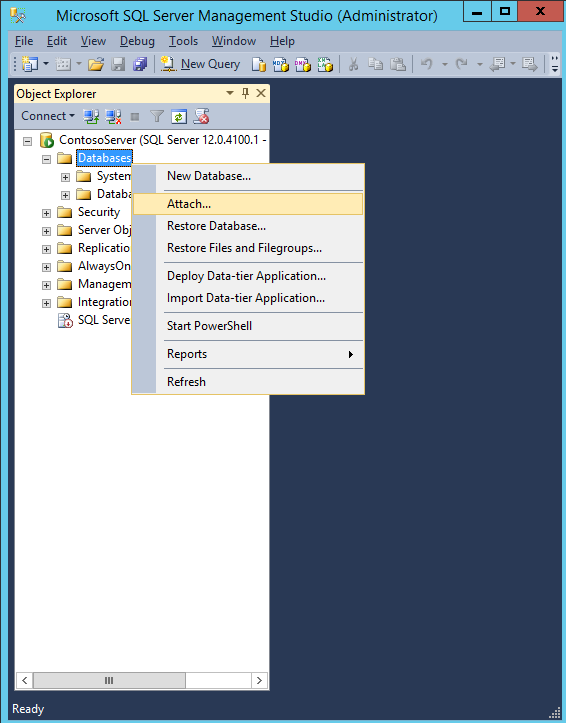
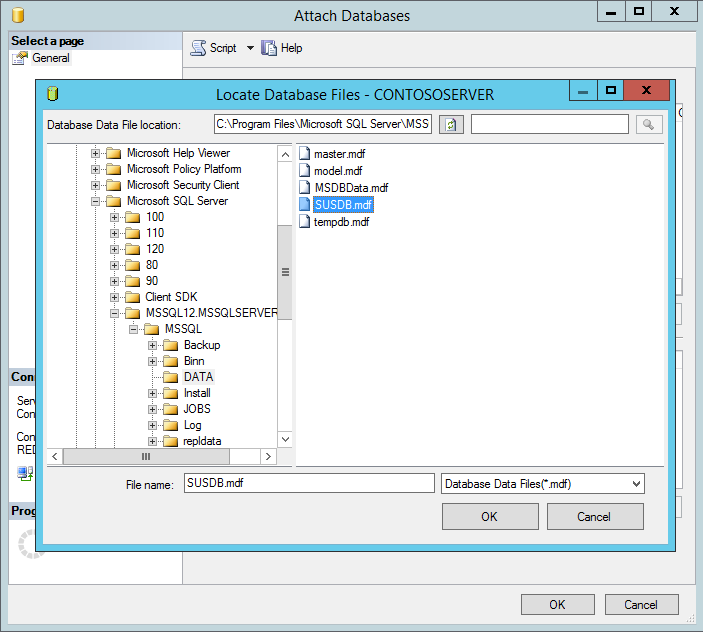
- In SQL Server Management Studio, under the Instance node, right-click Databases, and then click Attach.
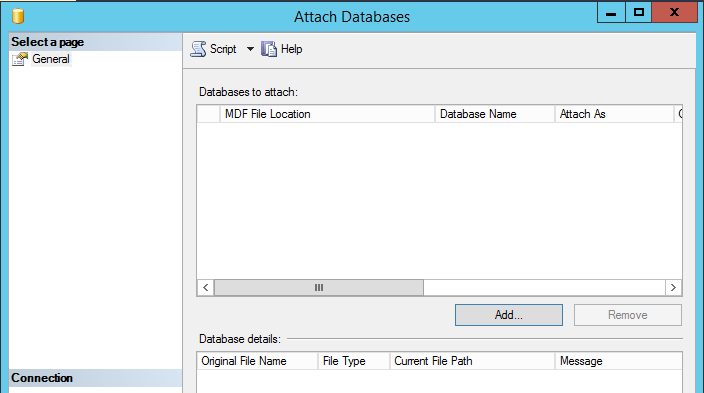
- In the Attach Databases box, under Databases to attach, click the Add button and locate the SUSDB.mdf file (copied from the WID Folder), and then click OK.
Tip
This is also able to be done using Transact-Sql. Please see the SQL documentation for attaching a database for its instructions.
Example (using paths from previous example):
USE master;
GO
CREATE DATABASE SUSDB
ON
(FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Data\SUSDB.mdf'),
(FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Log\SUSDB_Log.ldf')
FOR ATTACH;
GO
Verify SQL Server and Database Logins and Permissions
SQL Server Login Permissions
After attaching the SUSDB, verify that NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE has login permissions to the instance of SQL Server by doing the following:
- Go into SQL Server Management Studio
- Opening the Instance
- Click Security
- Click Logins
The NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE account should be listed. If it is not, you need to add it by adding New Login Name.
Important
If the SQL Instance is on a different machine from WSUS, the WSUS Server's computer account should be listed in the format [FQDN]\[WSUSComputerName]$. If not, the steps below can be used to add it, replacing NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE with the WSUS Server's computer account ([FQDN]\[WSUSComputerName]$) This would be in addition to granting rights to NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE
Adding NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE and granting it rights
- Right Click Logins and click New Login…
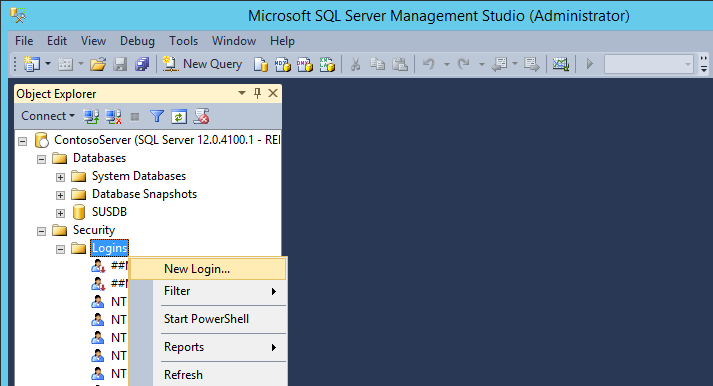
- On the General page, fill out the Login name (NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE), and set the Default database to SUSDB.
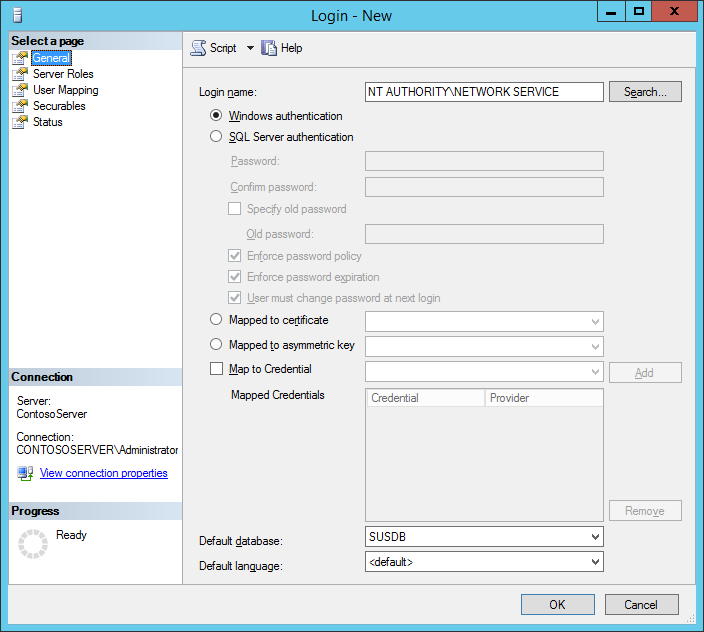
- On the Server Roles page, ensure public and sysadmin are selected.
- On the User Mapping page:
- Under Users mapped to this login: select SUSDB
- Under Database role membership for: SUSDB, ensure the following are checked:
- public
- webService
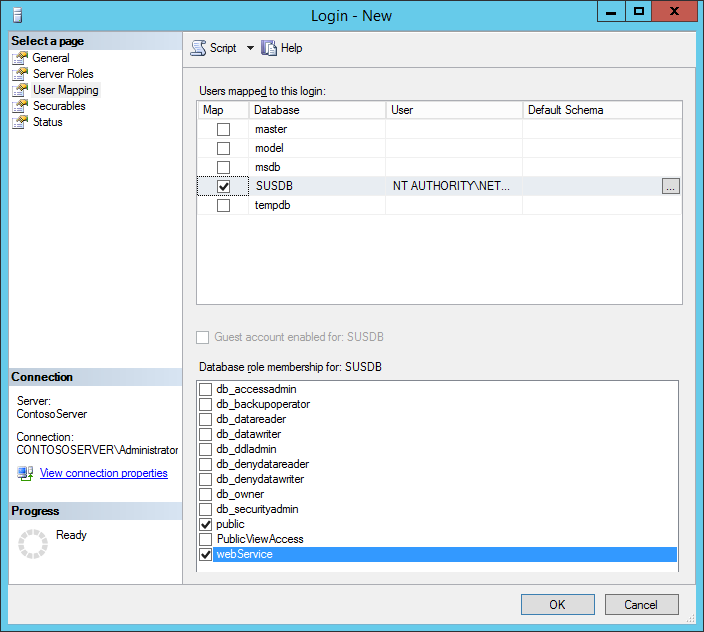
- Click OK
You should now see NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE under Logins.
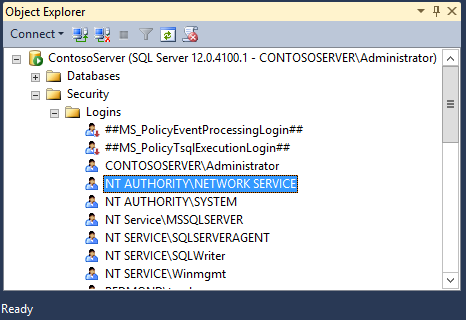
Database Permissions
- Right-click the SUSDB
- Select Properties
- Click Permissions
The NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE account should be listed.
If it is not, add the account.
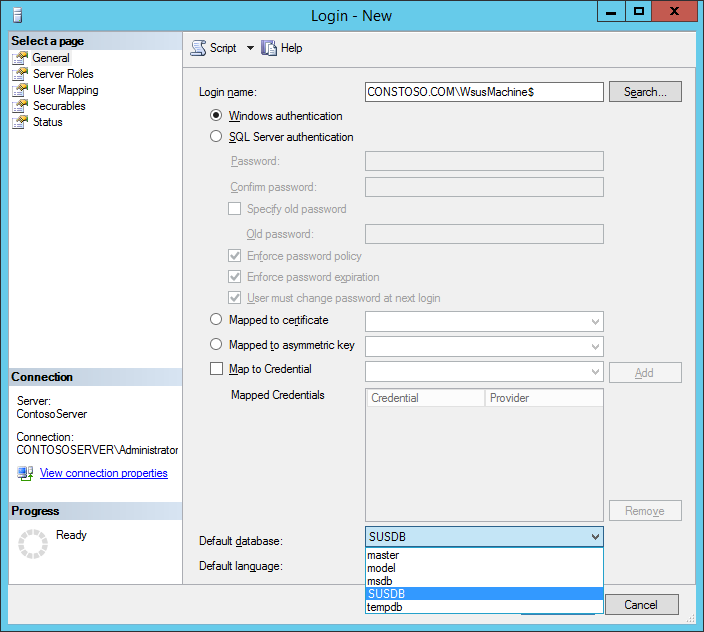
On the Login name textbox, enter the WSUS machine in the following format:
[FQDN]\[WSUSComputerName]$
Verify that the Default database is set to SUSDB.
Tip
In the following example, the FQDN is Contosto.com and the WSUS machine name is WsusMachine:
On the User Mapping page, select the SUSDB Database under Users mapped to this login
Check webservice under the Database role membership for: SUSDB:
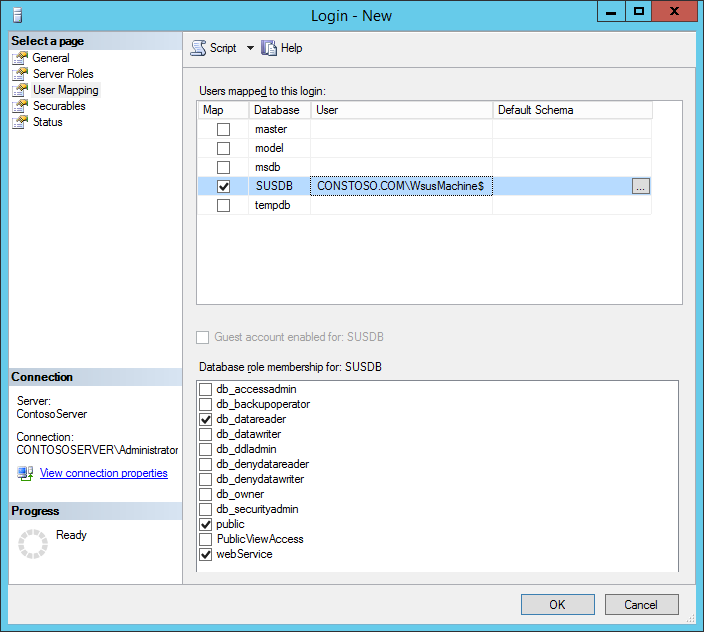
Click OK to save settings.
Note
You may need to restart the SQL Service for the changes to take effect.
Edit the registry to point WSUS to the SQL Server Instance
Important
Follow the steps in this section carefully. Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Before you modify it, back up the registry for restoration in case problems occur.
Click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
Locate the following key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\UpdateServices\Server\Setup\SqlServerName
In the Value text box, type [ServerName]\[InstanceName], and then click OK. If the instance name is the default instance, type [ServerName].
Locate the following key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Update Services\Server\Setup\Installed Role Services\UpdateServices-WidDatabase
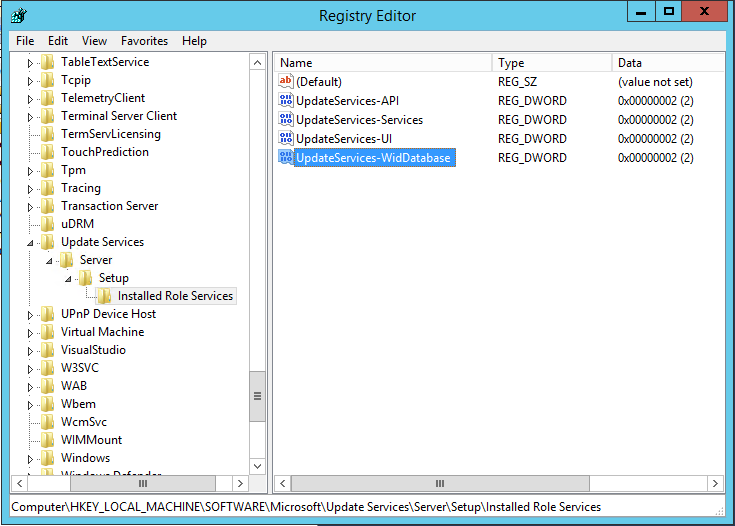
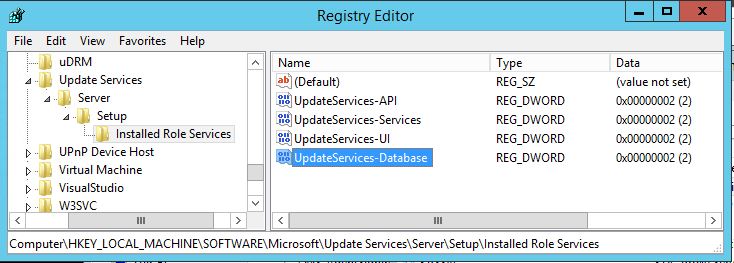
Rename the Key to UpdateServices-Database
Note
If you do not update this key, then WsusUtil will attempt to service the WID rather than the SQL Instance to which you have migrated.
Start the IIS and WSUS services on the WSUS server
From PowerShell (elevated), run:
Start-Service IISADMIN
Start-Service WsusService
Note
If you are using the WSUS Console, close and restart it.
Uninstalling the WID role (not recommended)
Warning
Removing the WID role also removes a database folder (%SystemDrive%\Program Files\Update Services\Database) that contains scripts required by WSUSUtil.exe for post-installation tasks. If you choose to uninstall the WID role, make sure you back up the %SystemDrive%\Program Files\Update Services\Database folder beforehand.
Using PowerShell:
Uninstall-WindowsFeature -Name 'Windows-Internal-Database'
After the WID role is removed, verify that the following registry key is present: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Update Services\Server\Setup\Installed Role Services\UpdateServices-Database