Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Use the following procedure to raise the value of the relative ID (RID) pools that the RID operations master will allocate after that DC is restored. By raising the value of the available RID pools, you can ensure that no DC allocates a RID for a security principal that was created after the backup that was used to restore the domain.
Active Directory RID Pools and rIDAvailablePool
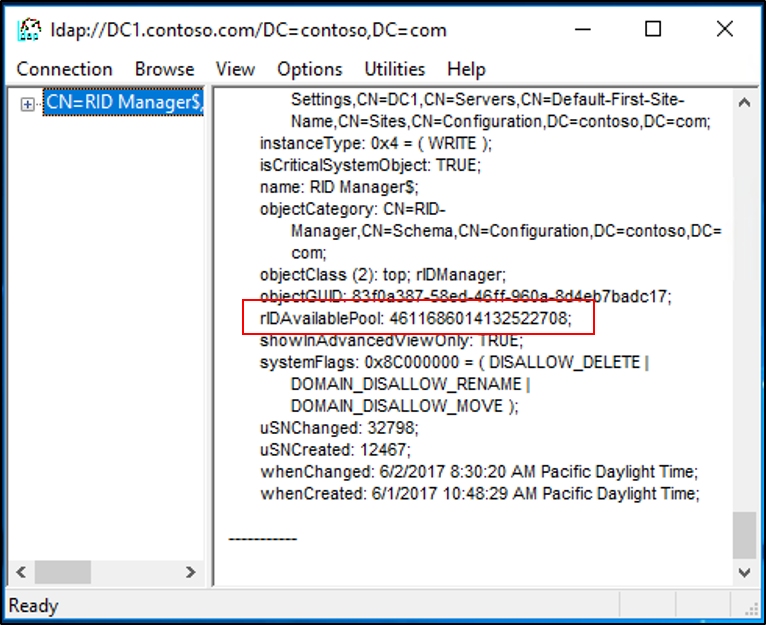
Each domain has an object CN=RID Manager$,CN=System,DC=<domain_name>. This object has an attribute named rIDAvailablePool. This attribute value maintains the global RID space for an entire domain. The value is a large integer with upper and lower parts. The upper part defines the number of security principals that can be allocated for each domain (0x3FFFFFFF or just over 1 billion). The lower part is the number of RIDs that have been allocated in the domain.
Note
In Windows Server 2016 and 2012, the number of security principals that can be allocated is increased to just over 2 billion. For more information, see Managing RID issuance.
- Sample Value: 4611686014132422708
- Low Part: 2100 (beginning of the next RID pool to be allocated)
- Upper Part: 1073741823 (total number of RIDs that can be created in a domain)
When you increase the value of the large integer, you increase the value of the low part. For example, if you add 100,000 to the sample value of 4611686014132422708 for a sum of 4611686014132522708, the new low part is 102100. This indicates that the next RID pool that will be allocated by the RID master will begin with 102100 instead of 2100.
Raise the value of available RID pools using adsiedit and the calculator
- Open Server Manager, select Tools and select ADSI Edit.
- Right-click, select Connect to and connect do the Default Naming Context and select OK.
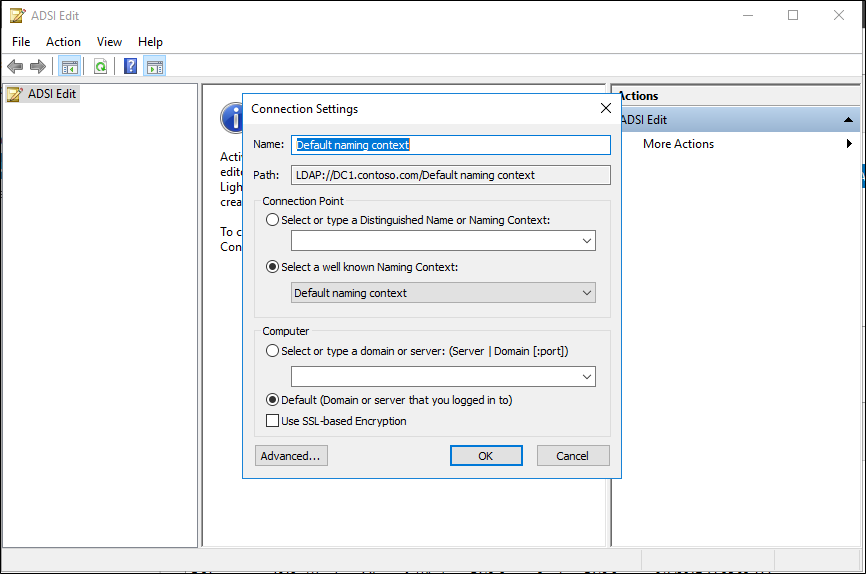
- Browse to the following distinguished name path: CN=RID Manager$,CN=System,DC=<domain name>.
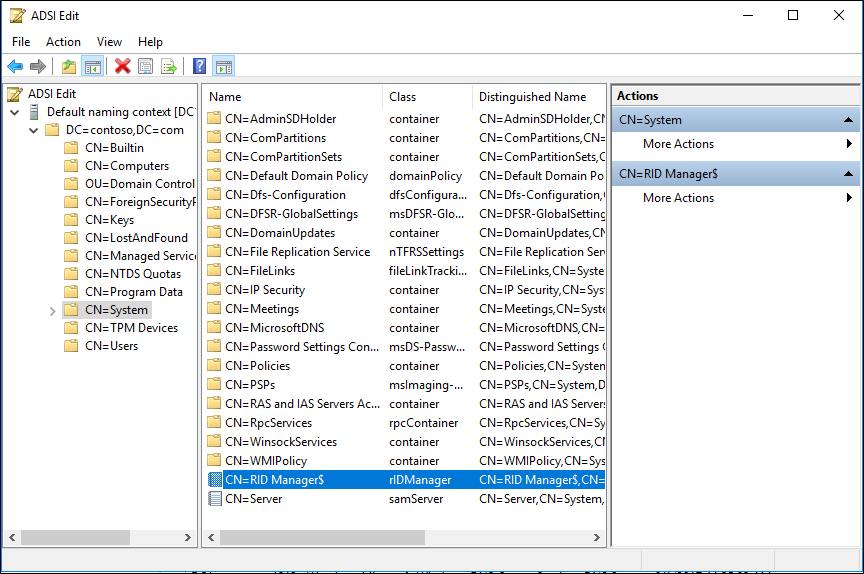
- Right-click and select the properties of CN=RID Manager$.
- Select the attribute rIDAvailablePool, select Edit, and then copy the large integer value to the clipboard.
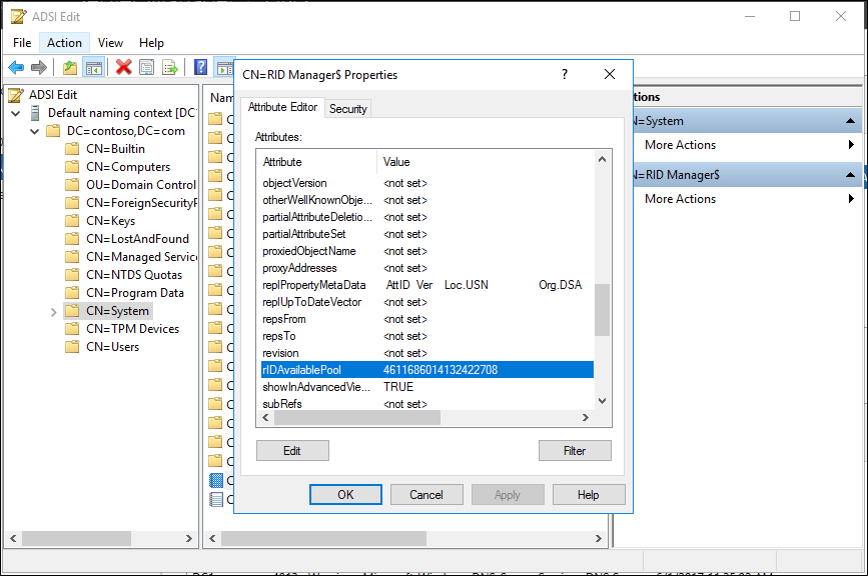
- Start calculator, and from the View menu, select Scientific Mode.
- Add 100,000 to the current value.
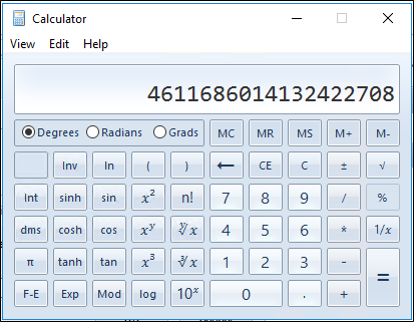
- Using ctrl-c, or the Copy command from the Edit menu, copy the value to the clipboard.
- In the edit dialog of adsiedit, paste this new value.
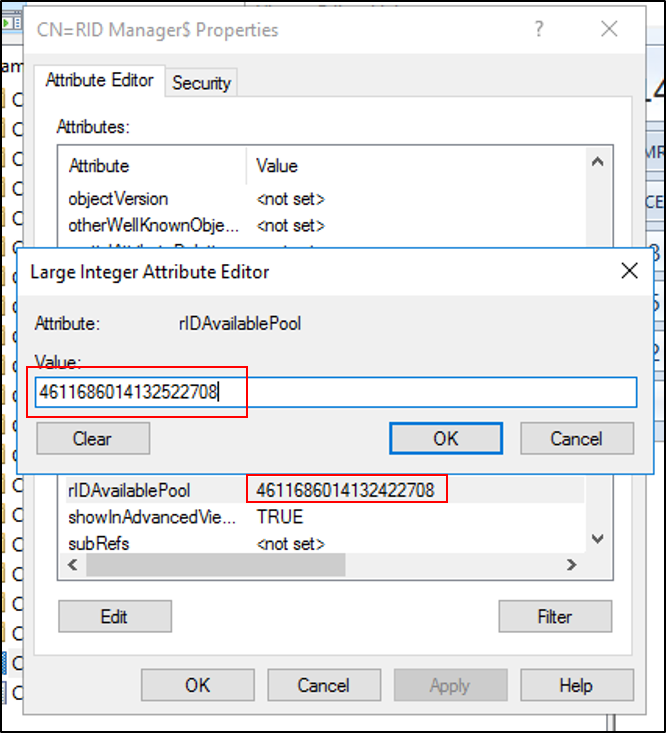
- Select OK in the dialog, and Apply in the property sheet to update the rIDAvailablePool attribute.
Raise the value of available RID pools using LDP
- At the command prompt, type the following command, and then press ENTER: ldp
- Select Connection, select Connect, type the name of RID manager, and then select OK.

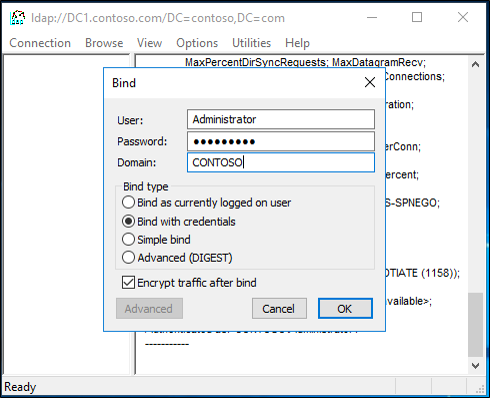
- Select Connection, select Bind, select Bind with credentials and type your administrative credentials, and then select OK.
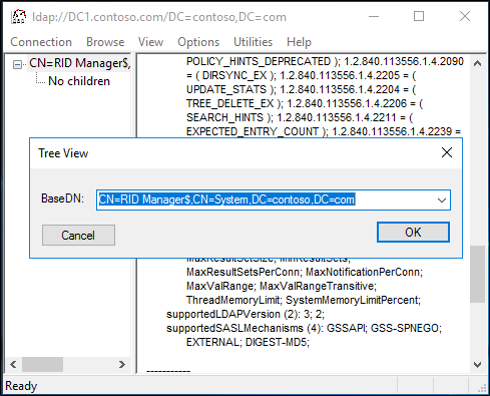
- Select View, select Tree and then type the following distinguished name path: CN=RID Manager$,CN=System,DC=domain name
- Select Browse, and then select Modify.
- Add 100,000 to the current rIDAvailablePool value, and then type the sum into Values.
- In Dn, type
cn=RID Manager$,cn=System,dc=<domain name>. - In Edit Entry Attribute, type
rIDAvailablePool. - Select Replace as the operation, and then select Enter.
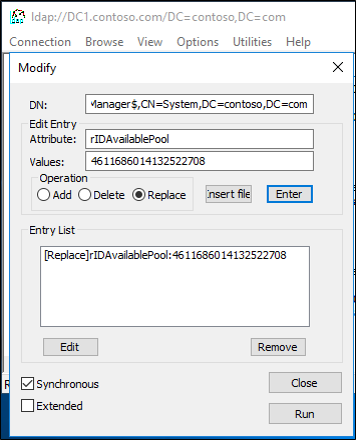
- Select Run to run the operation. Select Close.
- To validate the change, select View, select Tree, and then type the following distinguished name path: CN=RID Manager$,CN=System,DC=domain name. Check the rIDAvailablePool attribute.
Next steps
- AD Forest Recovery - Prerequisites
- AD Forest Recovery - Devise a custom forest recovery plan
- AD Forest Recovery - Steps to restore the forest
- AD Forest Recovery - Identify the problem
- AD Forest Recovery - Determine how to recover
- AD Forest Recovery - Perform initial recovery
- AD Forest Recovery - Procedures
- AD Forest Recovery - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- AD Forest Recovery - Recover a single domain within a multidomain forest
- AD Forest Recovery - Redeploy remaining DCs
- AD Forest Recovery - Virtualization
- AD Forest Recovery - Cleanup