Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Active Directory Domain Services contains numerous built-in accounts and groups that are granted elevated privileges to perform administrative tasks. These privileged accounts are granted powerful rights, privileges, and permissions that allow them to perform nearly any action in Active Directory and on domain-joined systems.
This appendix provides essential information about:
- Rights, privileges, and permissions.
- Highest privilege groups.
- Built-in and default accounts.
Understanding these privileged accounts and groups is crucial for implementing effective security controls and monitoring strategies. The information in this appendix serves as the foundation for the specific security recommendations and implementation guidance provided in the accompanying appendices.
Important
The accounts and groups described in this appendix have extensive privileges that can affect your entire Active Directory forest. Proper security of these accounts is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your directory environment.
Rights, privileges, and permissions in Active Directory
The differences between rights, permissions, and privileges can be confusing. This section describes some of the characteristics of each as they're used in this document. These descriptions shouldn't be considered authoritative for other Microsoft documentation, because it might use these terms differently.
Rights and privileges
Rights and privileges are effectively the same system-wide capabilities that are granted to security principals such as users, services, computers, or groups. In interfaces typically used by IT professionals, it's referred to as rights or user rights, and they're often assigned by Group Policy Objects. The following screenshot shows some of the most common user rights that can be assigned to security principals (it represents the Default Domain Controllers GPO in a Windows Server 2012 domain). Some of these rights apply to Active Directory, such as the Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation user right, while other rights apply to the Windows operating system, such as Change the system time.
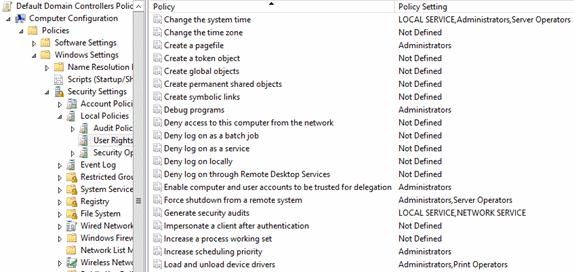
In interfaces such as the Group Policy Object Editor, all of these assignable capabilities are referred to broadly as user rights. In reality however, some user rights are programmatically referred to as rights, while others are programmatically referred to as privileges. Although Group Policy and other interfaces refer to all of these as user rights, some are programmatically identified as rights, while others are defined as privileges.
For more information about each of the user rights listed in the following table, see Threats and Countermeasures Guide: User Rights in the Threats and Vulnerabilities Mitigation guide for Windows Server
Note
For the purposes of this document, the terms rights and user rights are used to identify rights and privileges unless otherwise specified.
Permissions
Permissions are access controls that are applied to securable objects such as the file system, registry, service, and Active Directory objects. Each securable object has an associated access control list (ACL), which contains access control entries (ACEs) that grant or deny security principals (users, services, computers, or groups) the ability to perform various operations on the object. For example, the ACLs for many objects in Active Directory contain ACEs that allow Authenticated Users to read general information about the objects, but don't grant them the ability to read sensitive information or to change the objects. Except for each domain's built-in Guest account, every security principal that logs on and is authenticated by a domain controller in an Active Directory forest or a trusted forest has the Authenticated Users Security Identifier (SID) added to its access token by default. Therefore, whether a user, service, or computer account attempts to read general properties on user objects in a domain, the read operation is successful.
If a security principal attempts to access an object for which no ACEs are defined and that contain a SID that is present in the principal's access token, the principal can't access the object. Moreover, if an ACE in an object's ACL contains a deny entry for a SID that matches the user's access token, the deny ACE generally overrides a conflicting allow ACE. For more information about access control in Windows, see Access Control on the MSDN website.
Within this document, permissions refers to capabilities that are granted or denied to security principals on securable objects. Whenever there's a conflict between a user right and a permission, the user right generally takes precedence. For example, if an object in Active Directory is configured with an ACL that denies Administrators all read and write access to an object, a user who is a member of the domain's Administrators group is unable to view much information about the object. However, because the Administrators group is granted the user right Take ownership of files or other objects, the user can simply take ownership of the object in question, then rewrite the object's ACL to grant Administrators full control of the object.
It's for this reason that this document encourages you to avoid using powerful accounts and groups for day-to-day administration, rather than trying to restrict the capabilities of the accounts and groups. It isn't effectively possible to stop a determined user who has access to powerful credentials from using those credentials to gain access to any securable resource.
Built-in privileged accounts and groups
Active Directory is intended to facilitate delegation of administration and the principle of least privilege in assigning rights and permissions. Regular users who have accounts in an Active Directory domain are, by default, able to read much of what is stored in the directory, but are able to change only a limited set of data in the directory. Users who require extra privilege can be granted membership in various privileged groups that are built into the directory so that they might perform specific tasks related to their roles, but can't perform tasks that aren't relevant to their duties.
Within Active Directory, there are three built-in groups that comprise the highest privilege groups in the directory, plus a fourth group, the Schema Admins (SA) group:
The Schema Admins (SA) group, has privileges that, if abused, can damage or destroy an entire Active Directory forest, but this group is more restricted in its capabilities than the EA, DA, and BA groups.
In addition to these four groups, there are many extra built-in and default accounts and groups in Active Directory, each of which is granted rights and permissions that allow specific administrative tasks to be performed. Although this appendix doesn't provide a thorough discussion of every built-in or default group in Active Directory, it does provide a table of the groups and accounts that you're most likely to see in your installations.
For example, if you install Microsoft Exchange Server into an Active Directory forest, extra accounts and groups might be created in the Built-in and Users containers in your domains. This appendix describes only the groups and accounts that are created in the Built-in and Users containers in Active Directory, based on native roles and features. Accounts and groups that are created by the installation of enterprise software aren't included.
Enterprise Admins
The Enterprise Admins (EA) group is located in the forest root domain, and by default, it's a member of the built-in Administrators group in every domain in the forest. The Built-in Administrator account in the forest root domain is the only default member of the EA group. EAs are granted rights and permissions that allow them to affect forest-wide changes. These are changes that affect all domains in the forest, such as adding or removing domains, establishing forest trusts, or raising forest functional levels. In a properly designed and implemented delegation model, EA membership is required only when first constructing the forest or when making certain forest-wide changes such as establishing an outbound forest trust.
The EA group is located by default in the Users container in the forest root domain, and it's a universal security group, unless the forest root domain is running in Windows 2000 Server mixed mode, in which case the group is a global security group. Although some rights are granted directly to the EA group, many of this group's rights are inherited by the EA group because it's a member of the Administrators group in each domain in the forest. Enterprise Admins have no default rights on workstations or member servers.
Domain Admins
Each domain in a forest has its own Domain Admins (DA) group, which is a member of that domain's built-in Administrators (BA) group in addition to a member of the local Administrators group on every computer that is joined to the domain. The only default member of the DA group for a domain is the Built-in Administrator account for that domain.
DAs are all-powerful within their domains, while EAs have forest-wide privilege. In a properly designed and implemented delegation model, DA membership should be required only in break glass scenarios, which are situations in which an account with high levels of privilege on every computer in the domain is needed, or when certain domain wide changes must be made. Although native Active Directory delegation mechanisms do allow delegation to the extent that it's possible to use DA accounts only in emergency scenarios, constructing an effective delegation model can be time consuming, and many organizations use third-party applications to expedite the process.
The DA group is a global security group located in the Users container for the domain. There's one DA group for each domain in the forest, and the only default member of a DA group is the domain's Built-in Administrator account. Because a domain's DA group is nested in the domain's BA group and every domain-joined system's local Administrators group, DAs not only have permissions that are granted to Domain Admins, but they also inherit all rights and permissions granted to the domain's Administrators group and the local Administrators group on all systems joined to the domain.
Administrators
The built-in Administrators (BA) group is a domain local group in a domain's Built-in container into which DAs and EAs are nested, and it's this group that is granted many of the direct rights and permissions in the directory and on domain controllers. However, the Administrators group for a domain doesn't have any privileges on member servers or on workstations. Membership in domain-joined computers' local Administrators group is where local privilege is granted; and of the groups discussed, only DAs are members of all domain-joined computers' local Administrators groups by default.
The Administrators group is a domain-local group in the domain's Built-in container. By default, every domain's BA group contains the local domain's Built-in Administrator account, the local domain's DA group, and the forest root domain's EA group. Many user rights in Active Directory and on domain controllers are granted specifically to the Administrators group, not to EAs or DAs. A domain's BA group is granted full control permissions on most directory objects, and can take ownership of directory objects. Although EA and DA groups are granted certain object-specific permissions in the forest and domains, much of the power of groups is inherited from their membership in BA groups.
Note
Although these are the default configurations of these privileged groups, a member of any one of the three groups can manipulate the directory to gain membership in any of the other groups. In some cases, it's trivial to achieve, while in others it's more difficult, but from the perspective of potential privilege, all three groups should be considered effectively equivalent.
Schema Admins
The Schema Admins (SA) group is a universal group in the forest root domain and has only that domain's Built-in Administrator account as a default member, similar to the EA group. Although membership in the SA group can allow an attacker to compromise the Active Directory schema, which is the framework for the entire Active Directory forest, SAs have few default rights and permissions beyond the schema.
You should carefully manage and monitor membership in the SA group, but in some respects, this group is less privileged than the three highest privileged groups described earlier because the scope of its privilege is narrow; that is, SAs have no administrative rights anywhere other than the schema.
Additional built-in and default groups in Active Directory
To facilitate delegating administration in the directory, Active Directory ships with various built-in and default groups that have been granted specific rights and permissions. These groups are described briefly in the following table.
The following sections list the built-in and default groups in Active Directory. Both sets of groups exist by default; however, built-in groups are located (by default) in the Built-in container in Active Directory, while default groups are located (by default) in the Users container in Active Directory. Groups in the Built-in container are all Domain Local groups, while groups in the Users container are a mixture of Domain Local, Global, and Universal groups, in addition to three individual user accounts (Administrator, Guest, and Krbtgt).
In addition to the highest privileged groups described earlier in this appendix, some built-in and default accounts and groups are granted elevated privileges and should also be protected and used only on secure administrative hosts. Because some of these groups and accounts are granted rights and permissions that can be misused to compromise Active Directory or domain controllers, they're afforded more protections as described in Appendix C: Protected Accounts and Groups in Active Directory.
Access Control Assistance Operators
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group can remotely query authorization attributes and permissions for resources on this computer.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
- Notes: Active Directory in Windows Server 2012 and later.
Account Operators
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members can administer domain user and group accounts.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Administrator account
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Not a group
- Description and Default User Rights: Built-in account for administering the domain.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Adjust memory quotas for a process
- Allow log on locally
- Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services
- Back up files and directories
- Bypass traverse checking
- Change the system time
- Change the time zone
- Create a pagefile
- Create global objects
- Create symbolic links
- Debug programs
- Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation
- Force shutdown from a remote system
- Impersonate a client after authentication
- Increase a process working set
- Increase scheduling priority
- Load and unload device drivers
- Log on as a batch job
- Manage auditing and security log
- Modify firmware environment values
- Perform volume maintenance tasks
- Profile single process
- Profile system performance
- Remove computer from docking station
- Restore files and directories
- Shut down the system
- Take ownership of files or other objects
Administrators group
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Administrators have complete and unrestricted access to the domain.
- Direct user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Adjust memory quotas for a process
- Allow log on locally
- Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services
- Back up files and directories
- Bypass traverse checking
- Change the system time
- Change the time zone
- Create a pagefile
- Create global objects
- Create symbolic links
- Debug programs
- Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation
- Force shutdown from a remote system
- Impersonate a client after authentication
- Increase scheduling priority
- Load and unload device drivers
- Log on as a batch job
- Manage auditing and security log
- Modify firmware environment values
- Perform volume maintenance tasks
- Profile single process
- Profile system performance
- Remove computer from docking station
- Restore files and directories
- Shut down the system
- Take ownership of files or other objects
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Allowed RODC Password Replication Group
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members in this group can have their passwords replicated to all read-only domain controllers in the domain.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Backup Operators
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Backup Operators can override security restrictions for the sole purpose of backing up or restoring files.
- Direct user rights:
- Allow log on locally
- Back up files and directories
- Log on as a batch job
- Restore files and directories
- Shut down the system
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Cert Publishers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group are permitted to publish certificates to the directory.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Certificate Service DCOM Access
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: If Certificate Services is installed on a domain controller (not recommended), this group grants DCOM enrollment access to Domain Users and Domain Computers.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Cloneable Domain Controllers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Global security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group that are domain controllers may be cloned.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
- Notes: Active Directory in Windows Server 2012 and later.
Cryptographic Operators
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members are authorized to perform cryptographic operations.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Debugger Users
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: This is neither a default nor a built-in group, but when present in AD DS, is cause for further investigation.
- Description and Default User Rights: The presence of a Debugger Users group indicates that debugging tools have been installed on the system at some point, whether via Visual Studio, SQL, Office, or other applications that require and support a debugging environment. This group allows remote debugging access to computers. When this group exists at the domain level, it indicates that a debugger or an application that contains a debugger has been installed on a domain controller.
Denied RODC Password Replication Group
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members in this group cannot have their passwords replicated to any read-only domain controllers in the domain.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
DHCP Administrators
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group have administrative access to the DHCP Server service.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
DHCP Users
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group have view-only access to the DHCP Server service.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Distributed COM Users
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group are allowed to launch, activate, and use distributed COM objects on this computer.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
DnsAdmins
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group have administrative access to the DNS Server service.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
DnsUpdateProxy
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Global security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group are DNS clients who are permitted to perform dynamic updates on behalf of clients that cannot themselves perform dynamic updates. Members of this group are typically DHCP servers.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Domain Admins
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Global security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Designated administrators of the domain; Domain Admins is a member of every domain-joined computer's local Administrators group and receives rights and permissions granted to the local Administrators group, in addition to the domain's Administrators group.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Adjust memory quotas for a process
- Allow log on locally
- Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services
- Back up files and directories
- Bypass traverse checking
- Change the system time
- Change the time zone
- Create a pagefile
- Create global objects
- Create symbolic links
- Debug programs
- Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation
- Force shutdown from a remote system
- Impersonate a client after authentication
- Increase a process working set
- Increase scheduling priority
- Load and unload device drivers
- Log on as a batch job
- Manage auditing and security log
- Modify firmware environment values
- Perform volume maintenance tasks
- Profile single process
- Profile system performance
- Remove computer from docking station
- Restore files and directories
- Shut down the system
- Take ownership of files or other objects
Domain Computers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Global security group
- Description and Default User Rights: All workstations and servers that are joined to the domain are by default members of this group.
- Default direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Domain Controllers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Global security group
- Description and Default User Rights: All domain controllers in the domain. Note: Domain controllers are not a member of the Domain Computers group.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Domain Guests
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Global security group
- Description and Default User Rights: All guests in the domain
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Domain Users
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Global security group
- Description and Default User Rights: All users in the domain
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Enterprise Admins
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Universal security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Enterprise Admins have permissions to change forest-wide configuration settings; Enterprise Admins is a member of every domain's Administrators group and receives rights and permissions granted to that group.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Adjust memory quotas for a process
- Allow log on locally
- Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services
- Back up files and directories
- Bypass traverse checking
- Change the system time
- Change the time zone
- Create a pagefile
- Create global objects
- Create symbolic links
- Debug programs
- Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation
- Force shutdown from a remote system
- Impersonate a client after authentication
- Increase a process working set
- Increase scheduling priority
- Load and unload device drivers
- Log on as a batch job
- Manage auditing and security log
- Modify firmware environment values
- Perform volume maintenance tasks
- Profile single process
- Profile system performance
- Remove computer from docking station
- Restore files and directories
- Shut down the system
- Take ownership of files or other objects
- Notes: exists only in forest root domain.
Enterprise Read-only Domain Controllers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Universal security group
- Description and Default User Rights: This group contains the accounts for all read-only domain controllers in the forest.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Event Log Readers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group in can read the event logs on domain controllers.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Group Policy Creator Owners
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Global security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group can create and modify Group Policy Objects in the domain.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Guest
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Not a group
- Description and Default User Rights: This is the only account in an AD DS domain that does not have the Authenticated Users SID added to its access token. Therefore, any resources that are configured to grant access to the Authenticated Users group will not be accessible to this account. This behavior is not true of members of the Domain Guests and Guests groups, however- members of those groups do have the Authenticated Users SID added to their access tokens.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Guests
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Guests have the same access as members of the Users group by default, except for the Guest account, which is further restricted as described earlier.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Hyper-V Administrators
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group have complete and unrestricted access to all features of Hyper-V.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
- Notes: Windows Server 2012 and later.
IIS_IUSRS
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Built-in group used by Internet Information Services.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Incoming Forest Trust Builders
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group can create incoming, one-way trusts to this forest. (Creation of outbound forest trusts is reserved for Enterprise Admins.) Members of this group can create incoming trusts that allow TGT delegation which can lead to compromise of your forest. To learn more about TGT delegation across incoming trust, Updates to TGT delegation across incoming trusts in Windows Server.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
- Notes: exists only in forest root domain.
Krbtgt
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Not a group
- Description and Default User Rights: The Krbtgt account is the service account for the Kerberos Key Distribution Center in the domain. This account has access to all accounts' credentials stored in Active Directory. This account is disabled by default and should never be enabled
- User rights: N/A
Network Configuration Operators
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group are granted privileges that allow them to manage configuration of networking features.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Performance Log Users
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group can schedule logging of performance counters, enable trace providers, and collect event traces locally and via remote access to the computer.
- Direct user rights:
- Log on as a batch job
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Performance Monitor Users
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group can access performance counter data locally and remotely.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Pre-Windows 2000 Compatible Access
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: This group exists for backward compatibility with operating systems prior to Windows 2000 Server, and it provides the ability for members to read user and group information in the domain.
- Direct user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Bypass traverse checking
- Inherited user rights:
- Add workstations to domain
- Increase a process working set
Print Operators
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group can administer domain printers.
- Direct user rights:
- Allow log on locally
- Load and unload device drivers
- Shut down the system
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
RAS and IAS Servers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Servers in this group can read remote access properties on user accounts in the domain.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
RDS Endpoint Servers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Servers in this group run virtual machines and host sessions where users RemoteApp programs and personal virtual desktops run. This group needs to be populated on servers running RD Connection Broker. RD Session Host servers and RD Virtualization Host servers used in the deployment need to be in this group.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
- Notes: Windows Server 2012 and later.
RDS Management Servers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Servers in this group can perform routine administrative actions on servers running Remote Desktop Services. This group needs to be populated on all servers in a Remote Desktop Services deployment. The servers running the RDS Central Management service must be included in this group.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
- Notes: Windows Server 2012 and later.
RDS Remote Access Servers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Servers in this group enable users of RemoteApp programs and personal virtual desktops access to these resources. In Internet-facing deployments, these servers are typically deployed in an edge network. This group needs to be populated on servers running RD Connection Broker. RD Gateway servers and RD Web Access servers used in the deployment need to be in this group.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
- Notes: Windows Server 2012 and later.
Read-only Domain Controllers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Global security group
- Description and Default User Rights: This group contains all read-only domain controllers in the domain.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Remote Desktop Users
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group are granted the right to log on remotely using RDP.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Remote Management Users
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group can access WMI resources over management protocols (such as WS-Management via the Windows Remote Management service). This applies only to WMI namespaces that grant access to the user.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
- Notes: Windows Server 2012 and later.
Replicator
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Supports legacy file replication in a domain.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Schema Admins
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Universal security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Schema admins are the only users who can make modifications to the Active Directory schema, and only if the schema is write-enabled.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
- Notes: exists only in forest root domain.
Server Operators
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group can administer domain controllers.
- Direct user rights:
- Allow log on locally
- Back up files and directories
- Change the system time
- Change the time zone
- Force shutdown from a remote system
- Restore files and directories
- Shut down the system
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Terminal Server License Servers
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group can update user accounts in Active Directory with information about license issuance, for the purpose of tracking and reporting TS Per User CAL usage
- Default direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
Users
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Users have permissions that allow them to read many objects and attributes in Active Directory, although they cannot change most. Users are prevented from making accidental or intentional system-wide changes and can run most applications.
- Direct user rights:
- Increase a process working set
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
Windows Authorization Access Group
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Built-in container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group have access to the computed tokenGroupsGlobalAndUniversal attribute on User objects
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
WinRMRemoteWMIUsers_
- Default Container, Group Scope and Type: Users container, Domain-local security group
- Description and Default User Rights: Members of this group can access WMI resources over management protocols (such as WS-Management via the Windows Remote Management service). This applies only to WMI namespaces that grant access to the user.
- Direct user rights: None
- Inherited user rights:
- Access this computer from the network
- Add workstations to domain
- Bypass traverse checking
- Increase a process working set
- Notes: Windows Server 2012 and later.