Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The following documentation provides information on how to disable and enable certain TLS/SSL protocols and cipher suites that Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) uses.
TLS/SSL, Schannel, and cipher suites in AD FS
The Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol provides for encrypted secure communications over the network. The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol encrypts sensitive data exchanges transmitted between a web server and a web browser similar to TLS. Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) uses these protocols for communications. Today, several versions of these protocols exist.
Security Channel (Schannel) is a Security Support Provider (SSP) that implements the SSL, TLS, and DTLS internet standard authentication protocols. The Security Support Provider Interface (SSPI) is an API used by Windows systems to perform security-related functions including authentication. The SSPI functions as a common interface to several SSPs, including the Schannel SSP.
A cipher suite is a set of cryptographic algorithms. The Schannel SSP implementation of the TLS/SSL protocols uses algorithms from a cipher suite to create keys and encrypt information. A cipher suite specifies one algorithm for each of the following tasks:
- Key exchange
- Bulk encryption
- Message authentication
AD FS uses Schannel.dll to perform its secure communications interactions. Currently AD FS supports all of the protocols and cipher suites that Schannel.dll supports.
Manage the TLS/SSL protocols and cipher suites
Important
This section contains steps that tell you how to modify the registry. However, serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully.
Be aware that changing the default security settings for SCHANNEL could break or prevent communications between certain clients and servers. This occurs if secure communication is required and they don't have a protocol to negotiate communications with.
If you're applying these changes, they must be applied to all of your AD FS servers in your farm. After applying these changes, a reboot is required.
In today's day and age, hardening your servers and removing older or weak cipher suites is becoming a major priority for many organizations. Software suites are available that test your servers and provide detailed information on these protocols and suites. In order to remain compliant or achieve secure ratings, removing or disabling weaker protocols or cipher suites has become a must. The remainder of this document provides guidance on how to enable or disable certain protocols and cipher suites.
The following registry keys are located in the same location: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols. Use the Registry Editor or PowerShell to enable or disable these protocols and cipher suites.

Enable and disable SSL 3.0
Use the following registry keys and their values to enable and disable SSL 3.0.
Enable SSL 3.0
| Path | Value Name | Value Data |
|---|---|---|
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Server | Enabled | 00000001 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Server | DisabledByDefault | 00000000 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Client | Enabled | 00000001 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Client | DisabledByDefault | 00000000 |
Disable SSL 3.0
| Path | Value Name | Value Data |
|---|---|---|
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Server | Enabled | 00000000 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Server | DisabledByDefault | 00000001 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Client | Enabled | 00000000 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Client | DisabledByDefault | 00000001 |
Use PowerShell to disable SSL 3.0
New-Item 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Server' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Server' -name 'Enabled' -value '0' -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Server' -name 'DisabledByDefault' -value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-Item 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Client' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Client' -name 'Enabled' -value '0' -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\SSL 3.0\Client' -name 'DisabledByDefault' -value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
Write-Host 'SSL 3.0 has been disabled.'
Enable and disable TLS 1.0
Use the following registry keys and their values to enable and disable TLS 1.0.
Important
Disabling TLS 1.0 breaks the WAP to AD FS trust. If you disable TLS 1.0, you should enable strong authentication for your applications. For more information, see Enable strong authentication for .NET applications
Enable TLS 1.0
| Path | Value Name | Value Data |
|---|---|---|
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server | Enabled | 00000001 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server | DisabledByDefault | 00000000 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client | Enabled | 00000001 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client | DisabledByDefault | 00000000 |
Disable TLS 1.0
| Path | Value Name | Value Data |
|---|---|---|
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server | Enabled"=00000000 | |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server | DisabledByDefault | 00000001 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client | Enabled | 00000000 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client | DisabledByDefault | 00000001 |
Use PowerShell to disable TLS 1.0
New-Item 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server' -name 'Enabled' -value '0' -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server' -name 'DisabledByDefault' -value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-Item 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client' -name 'Enabled' -value '0' -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client' -name 'DisabledByDefault' -value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
Write-Host 'TLS 1.0 has been disabled.'
Enable and disable TLS 1.1
Use the following registry keys and their values to enable and disable TLS 1.1.
Enable TLS 1.1
| Path | Value Name | Value Data |
|---|---|---|
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server | Enabled | 00000001 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server | DisabledByDefault | 00000000 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client | Enabled | 00000001 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client | DisabledByDefault | 00000000 |
Disable TLS 1.1
| Path | Value Name | Value Data |
|---|---|---|
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server | Enabled | 00000000 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server | DisabledByDefault | 00000001 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client | Enabled | 00000000 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client | DisabledByDefault | 00000001 |
Use PowerShell to disable TLS 1.1
New-Item 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server' -name 'Enabled' -value '0' -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server' -name 'DisabledByDefault' -value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-Item 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client' -name 'Enabled' -value '0' -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client' -name 'DisabledByDefault' -value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
Write-Host 'TLS 1.1 has been disabled.'
Disable TLS 1.2
TLS 1.2 is enabled by default starting with Windows Server 2012. You can use the following registry keys and their values to disable TLS 1.2.
Warning
Disabling TLS 1.2 is not recommended, as it may disrupt the functionality of other components on the server that rely on this protocol. For instance, services such as Microsoft Azure AD Connect (Azure AD Sync) require TLS 1.2 to operate correctly. Disabling it could result in service failures or degraded functionality.
| Path | Value Name | Value Data |
|---|---|---|
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Server | Enabled | 00000000 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Server | DisabledByDefault | 00000001 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client | Enabled | 00000000 |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client | DisabledByDefault | 00000001 |
Use PowerShell to disable TLS 1.2
New-Item 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Server' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Server' -name 'Enabled' -value '0' -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Server' -name 'DisabledByDefault' -value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-Item 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client' -name 'Enabled' -value '0' -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client' -name 'DisabledByDefault' -value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
Write-Host 'TLS 1.2 has been disabled.'
Enable or disable hashes, ciphers, and cipher suites
Controlling ciphers, hashes and key exchange algorithms, other than Key size, via the registry isn't supported. Hashes, ciphers and key exchange algorithms are controlled via PowerShell, MDM or Cipher Suite Ordering.
For a full list of supported cipher suites, see Cipher Suites in TLS/SSL (Schannel SSP). This article provides a table of suites that are enabled by default, and it shows which suites are supported but not enabled by default. To prioritize the cipher suites, see Prioritizing Schannel Cipher Suites.
Enable strong authentication for .NET applications
The .NET Framework 3.5/4.0/4.5.x applications can switch the default protocol to TLS 1.2 by enabling the SchUseStrongCrypto registry key. These registry keys force .NET applications to use TLS 1.2.
Important
For AD FS on Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2012 R2, you need to use the .NET Framework 4.0/4.5.x key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319
For the .NET Framework 3.5, use the following registry key:
| Path | Value Name | Value Data |
|---|---|---|
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727 | SchUseStrongCrypto | 00000001 |
For the .NET Framework 4.0/4.5.x, use the following registry key:
| Path | Value Name | Value Data |
|---|---|---|
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319 | SchUseStrongCrypto | 00000001 |
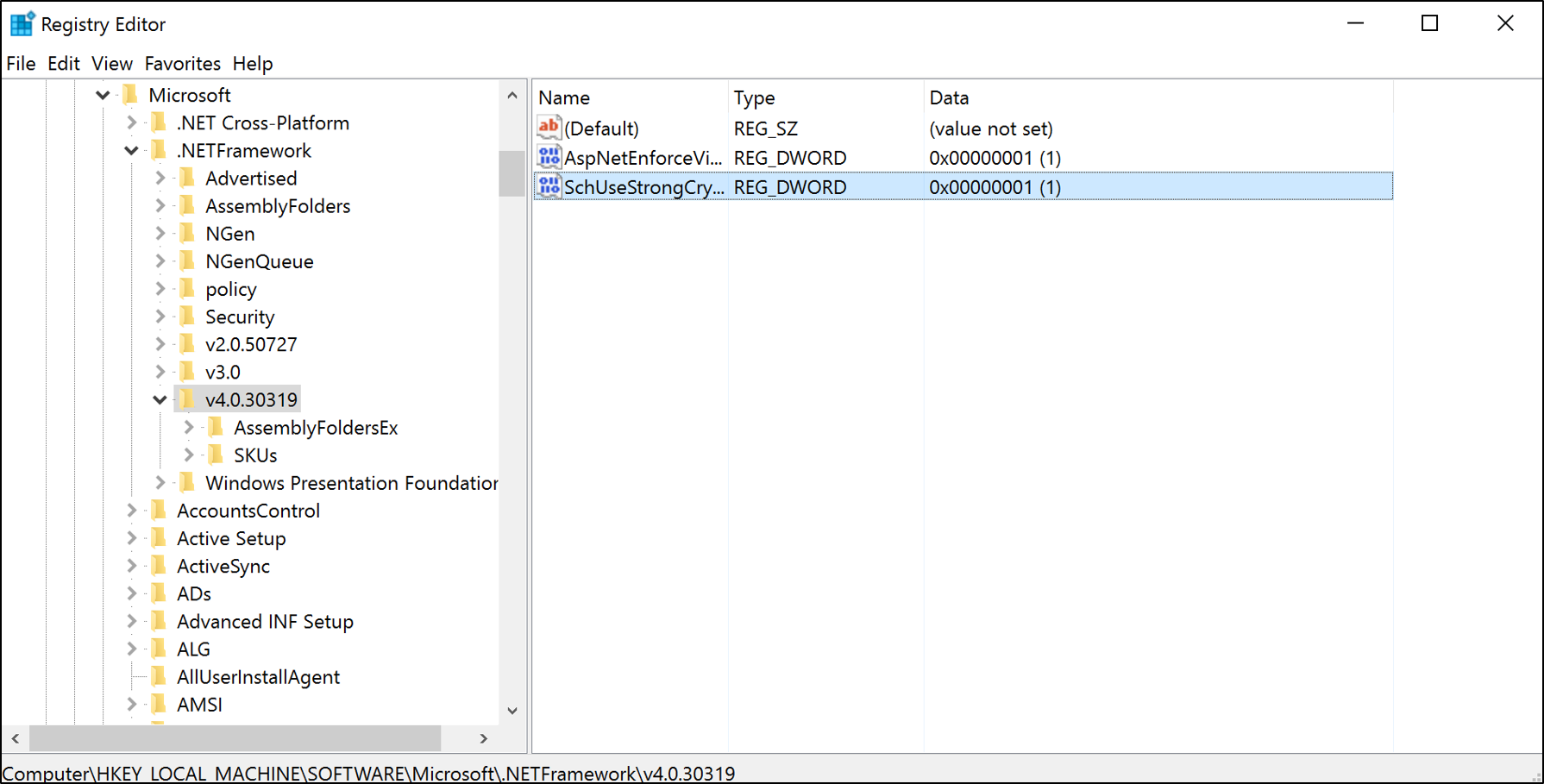
New-ItemProperty -path 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NetFramework\v4.0.30319' -name 'SchUseStrongCrypto' -value '1' -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null