Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
SMB over QUIC introduces an alternative to the TCP network transport, providing secure, reliable connectivity to edge file servers over untrusted networks like the Internet. QUIC is an IETF-standardized protocol with many benefits when compared with TCP:
- All packets are always encrypted and handshake is authenticated with TLS 1.3
- Parallel streams of reliable and unreliable application data
- Exchanges application data in the first round trip (0-RTT)
- Improved congestion control and loss recovery
- Survives a change in the clients IP address or port
SMB over QUIC offers an "SMB VPN" for telecommuters, mobile device users, and high security organizations. The server certificate creates a TLS 1.3-encrypted tunnel over the internet-friendly UDP port 443 instead of the legacy TCP port 445. All SMB traffic, including authentication and authorization within the tunnel is never exposed to the underlying network. SMB behaves normally within the QUIC tunnel, meaning the user experience doesn't change. SMB features like multichannel, signing, compression, continuous availability, directory leasing, and so on, work normally.
A file server administrator must opt in to enabling SMB over QUIC. It isn't on by default and a client can't force a file server to enable SMB over QUIC. Windows SMB clients still use TCP by default and will only attempt SMB over QUIC if the TCP attempt first fails or if intentionally requiring QUIC using NET USE /TRANSPORT:QUIC or New-SmbMapping -TransportType QUIC.
Note
It's not recommended to define particular names for DFS namespaces in scenarios involving SMB and QUIC connections with external endpoints. This is because the internal DFS namespace names are going to be referenced, and these references are usually not reachable for an external client in current releases of Windows.
Prerequisites
To use SMB over QUIC, you need the following things:
An SMB server running on one of the following operating systems.
Windows Server 2022 Datacenter: Azure Edition (Microsoft Server Operating Systems) or later
Any edition of Windows Server 2025 or later
A Windows 11 device (Windows for business)
The SMB server and client must be joined to an Active Directory domain or the client must have a local user account on the SMB server. The SMB server must have access to at least one domain controller for authentication, but no domain controller requires any internet access. We recommended using SMB over QUIC with Active Directory domains however it isn't required. You can also use SMB over QUIC on a workgroup-joined server with local user credentials and NTLM.
Your server must be accessible to clients on its public interface by adding a firewall allow rule to allow SMB over QUIC. By default SMB over QUIC uses UDP/443 inbound. Do not allow TCP/445 inbound to the file server. To learn about how to change the default port, see Configure alternative SMB ports.
The file server must have access to at least one domain controller for authentication, but no domain controller requires any internet access.
Windows Admin Center (WAC) (Homepage)
A Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to issue certificates like Active Directory Certificate Server or access to a trusted third party certificate issuer like Verisign, Digicert, Let's Encrypt, etc.
Administrative privileges or equivalent for the SMB server you're configuring.
Deploy SMB over QUIC
Step 1: Install a server certificate
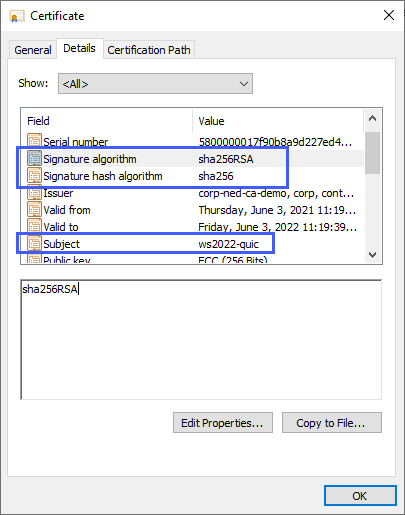
Create a Certificate Authority-issued certificate with the following properties:
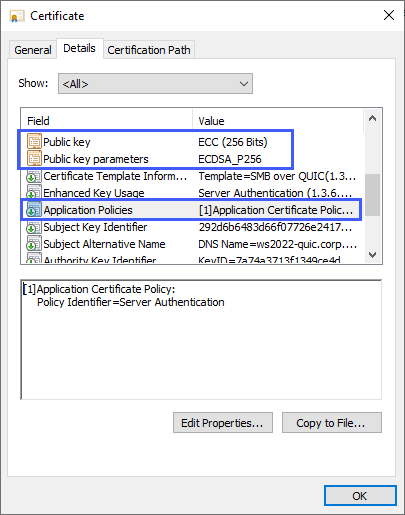
- Key usage: digital signature
- Purpose: Server Authentication (EKU 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1)
- Signature algorithm: SHA256RSA (or greater)
- Signature hash: SHA256 (or greater)
- Public key algorithm: ECDSA_P256 (or greater. Can also use RSA with at least 2048 length)
- Subject Alternative Name (SAN): (A DNS name entry for each fully qualified DNS name used to reach the SMB server)
- Subject: (CN= anything, but must exist)
- Private key included: yes

If using a Microsoft Enterprise Certificate Authority, you can create a certificate template and allow the file server administrator to supply the DNS names when requesting it. For more information on creating a certificate template, review Designing and Implementing a PKI: Part III Certificate Templates. For a demonstration of creating a certificate for SMB over QUIC using a Microsoft Enterprise Certificate Authority, watch this video:
For requesting a third-party certificate, consult your vendor documentation.
If using a Microsoft Enterprise Certificate Authority:
- Start MMC.EXE on the file server.
- Add the Certificates snap-in, and select the Computer account.
- Expand Certificates (Local Computer), Personal, then right-click Certificates and select Request New Certificate.
- Select Next
- Select Active Directory Enrollment Policy
- Select Next
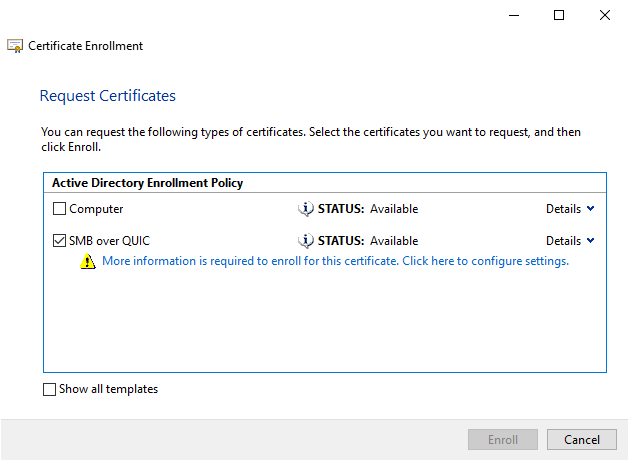
- Select the certificate template for SMB over QUIC that was published in Active Directory.
- Select More information is required to enroll for this certificate. Click here to configure settings.
- So users can use to locate the file server, fill in the value Subject with a common name and Subject Alternative Name with one or more DNS names.
- Select Ok and then select Enroll.

Note
Don't use IP addresses for SMB over QUIC server Subject Alternative Names.
- IP addresses will require the use of NTLM, even if Kerberos is available from a domain controller or through KDC Proxy.
- Azure IaaS VMs running SMB over QUIC use NAT for a public interface back to a private interface. SMB over QUIC does not support using the IP address for the server name through a NAT, you must use a fully qualified DNS name that resolves to the public interface IP address only in this case.
Note
If you're using a certificate file issued by a third party certificate authority, you can use the Certificates snap-in or WAC to import it.
Step 2: Configure SMB over QUIC
To configure SMB over QUIC, select your preferred method and follow the steps.
Important
If you're using Windows Server 2025, you need to use the PowerShell method to configure SMB over QUIC. The Windows Admin Center method is not currently supported for Windows Server 2025.
For a demonstration of configuring and using SMB over QUIC, watch this video:
Sign in to your file server as an administrator.
Install the latest version of WAC on a management PC or the file server. You need the latest version of the Files & File Sharing extension. It's installed automatically by WAC if Automatically update extensions is enabled in Settings > Extensions.
Connect to the server with WAC and select the Settings icon in the lower left. In the File shares (SMB server) section, under File sharing across the internet with SMB over QUIC, select Configure.
Select a certificate under Select a computer certificate for this file server, select the server addresses clients can connect to or select Select all, and select Enable.
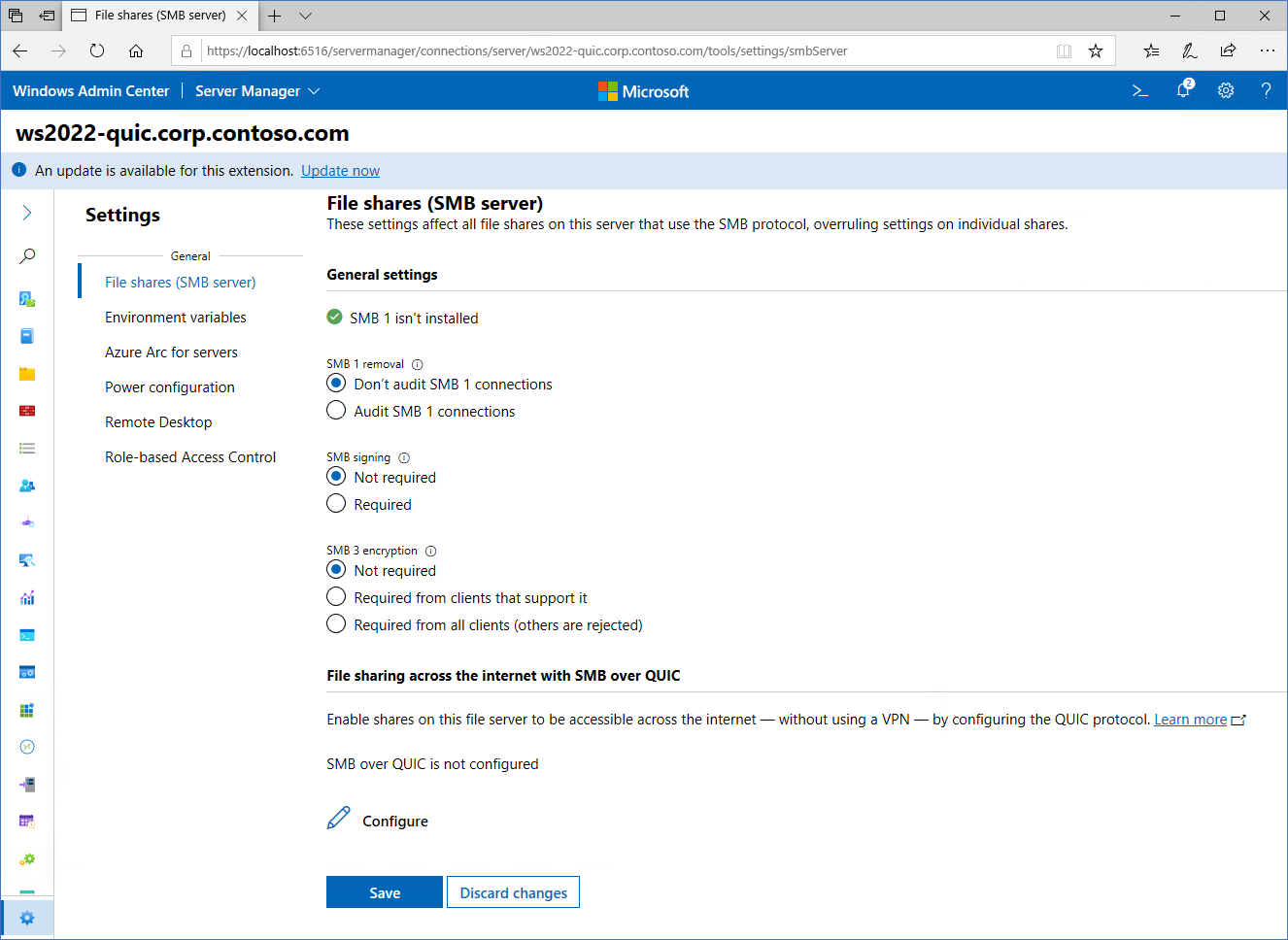
Ensure that the certificate and SMB over QUIC report are healthy.

Select the Files and File Sharing menu option. Note your existing SMB shares or create a new one.
If you want to apply control to SMB over client, you can use Client Access Control. To learn more how to restrict which clients can access SMB over QUIC servers, see Configure SMB over QUIC client access control.
Step 3: Connect to SMB shares
Join your Windows client device to your domain. Be certain the names of the SMB over QUIC file server's certificate subject alternative names are published to DNS and are fully qualified or added to the HOST files for your Windows client. Ensure that the server's certificate subject alternative names are published to DNS or added to the HOSTS files for your Windows client.
Move your Windows client device to an external network where it no longer has any network access to domain controllers or the file server's internal IP addresses.
In Windows File Explorer, in the Address Bar, type the UNC path to a share on the file server and confirm you can access data in the share. Alternatively, you can use
NET USE /TRANSPORT:QUICorNew-SmbMapping -TransportType QUICwith a UNC path. Examples:REM Automatically tries TCP then QUIC NET USE * \\fsedge1.contoso.com\sales REM Tries only QUIC NET USE * \\fsedge1.contoso.com\sales /TRANSPORT:QUIC#Tries only QUIC New-SmbMapping -LocalPath 'Z:' -RemotePath '\\fsedge1.contoso.com\sales' -TransportType QUIC
Manage SMB over QUIC
Admins can disable SMB over QUIC for a server by running the following command:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMBQUIC $false
To disable SMB over QUIC for a client device, run the following command:
Set-SmbClientConfiguration -EnableSMBQUIC $false
SMB over QUIC can be enabled on either the server or client by setting $false to $true.
Note
If a client attempts to connect to a server over QUIC and SMB over QUIC is disabled, the client attempts to connect to the server over TCP. This is assuming the server is not in the exception list.
Admins can now specify an SMB over QUIC server exception list on the client. A client can connect to a server when SMB over QUIC is disabled on the client as long as the server IP address, NetBIOS name or FQDN is in the exception list. To learn more, see Enable exceptions to NTLM blocking. A server exception list can be created by running the following command:
Set-SmbClientConfiguration -DisabledSMBQUICServerExceptionList "<Server01>, <Server02>, <Server03>"
SMB over QUIC client auditing
Auditing is used to track client connections for SMB over QUIC, with events being written to an event log. The Event Viewer captures this information for the QUIC transport protocol. This feature is available to SMB Client starting with Windows 11, version 24H2 To view these logs, follow these steps:
- Open the Event Viewer.
- Navigate to Applications and Services Logs\Microsoft\Windows\SMBClient\Connectivity.
- Monitor event ID 30832.
Configure the KDC Proxy (optional, but recommended)
By default, a Windows client device won't have access to an Active Directory domain controller when connecting to an SMB over QUIC file server. This means authentication uses NTLMv2, where the file server authenticates on behalf of the client. No NTLMv2 authentication or authorization occurs outside the TLS 1.3-encrypted QUIC tunnel. However, we still recommend using Kerberos as a general security best practice and don't recommend creating new NTLMv2 dependencies in deployments. To allow this, you can configure the KDC proxy to forward ticket requests on the user's behalf, all while using an internet-friendly HTTPS encrypted communication channel. The KDC Proxy is supported by SMB over QUIC and highly recommended.
Note
You cannot configure the WAC in gateway mode using TCP port 443 on a file server where you are configuring KDC Proxy. When configuring WAC on the file server, change the port to one that is not in use and is not 443. If you have already configured WAC on port 443, re-run the WAC setup MSI and choose a different port when prompted.
Ensure you're using WAC version 2110 or later.
Configure SMB over QUIC normally. Starting in WAC 2110, the option to configure KDC proxy in SMB over QUIC is automatically enabled and you don't need to perform extra steps on the file servers. The default KDC proxy port is 443 and assigned automatically by WAC.
Note
You cannot configure an SMB over QUIC server joined to a Workgroup using WAC. You must join the server to an Active Directory domain or follow the steps in configuring the KDC proxy either in PowerShell or Group Policy.
Note
Automatic configuration of the KDC Proxy will come later in the SMB over QUIC and these server steps will not be necessary.
Certificate expiration and renewal
An expired SMB over QUIC certificate that you replace with a new certificate from the issuer will contain a new thumbprint. While you can automatically renew SMB over QUIC certificates when they expire using Active Directory Certificate Services, a renewed certificate gets a new thumbprint as well. This effectively means that SMB over QUIC must be reconfigured when the certificate expires, as a new thumbprint must be mapped. Select your new certificate in WAC for the existing SMB over QUIC configuration or use the Set-SMBServerCertificateMapping PowerShell command to update the mapping for the new certificate. You can use Azure Automanage for Windows Server to detect impending certificate expiration and prevent an outage. For more information, review Azure Automanage for Windows Server.
Notes
- For customers not using Azure public cloud, Windows Server 2022 Datacenter: Azure Edition is available on Azure Local beginning with version 22H2.
- We recommended using SMB over QUIC with Active Directory domains but isn't a requirement. You can also use SMB over QUIC on a workgroup-joined server with local user credentials and NTLM, or Azure IaaS with Microsoft Entra joined Windows Servers. Microsoft Entra joined Windows Servers for non-Azure IaaS based machines isn't supported. Microsoft Entra joined Windows Servers don't support credentials for remote Windows security operations because Microsoft Entra ID doesn't contain user or group SIDs. Microsoft Entra joined Windows Servers must use either a domain-based or local user account to access the SMB over QUIC share.
- You can't configure SMB over QUIC using WAC when the SMB server is in a workgroup (that is, not AD domain joined). Per this scenario, you must use the New-SMBServerCertificateMapping cmdlet.
- We recommend read-only domain controllers configured only with passwords of mobile users be made available to the file server.
- Users should have strong passwords or, ideally, be configured using a passwordless strategy with Windows Hello for Business MFA or smart cards. Configure an account lockout policy for mobile users through fine-grained password policy and you should deploy intrusion protection software to detect brute force or password spray attacks.