Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
You can configure Storage Replica in Windows Server for cluster-to-cluster replication of cross-region applications in Azure. In the article example, we use a two-node cluster, but you can use Storage Replica if you have more than two nodes in your clusters.
For a complete walkthrough of the process, see the following video:
The diagram that follows depicts a two-node Storage Space Direct cluster that can communicate with each other, are in the same domain, and are cross-region.
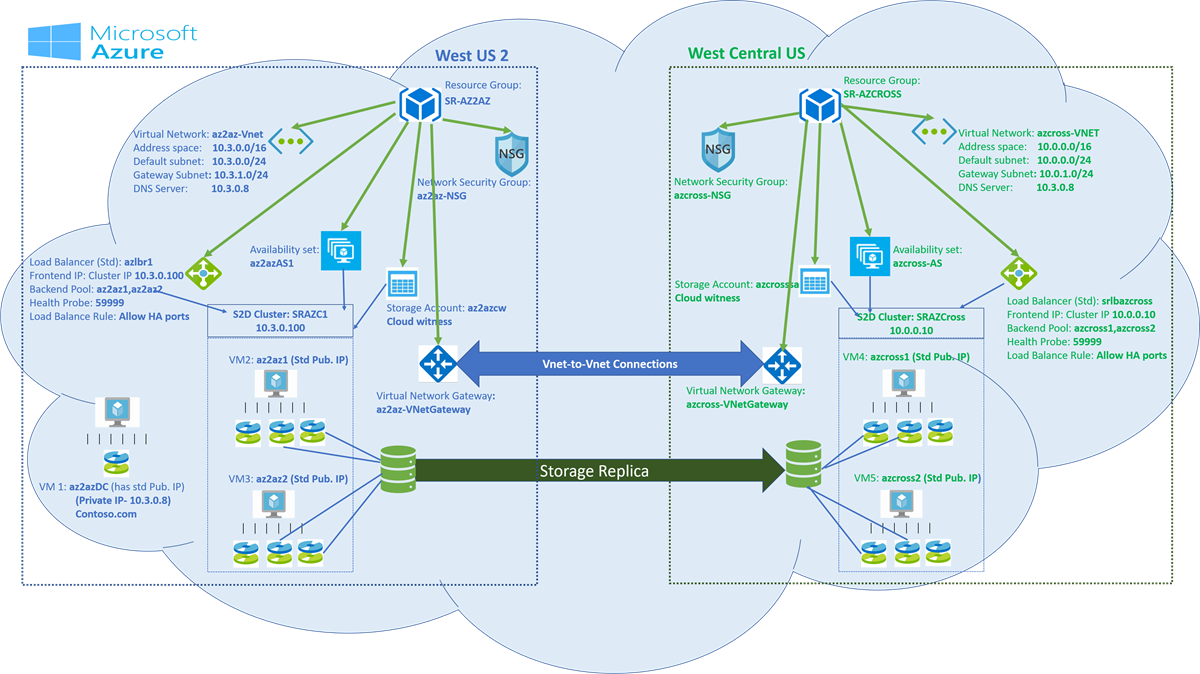
The figure and the videos refer to the article examples.
In the Azure portal, create resource groups in two different regions.
For example:
- Create SR-AZ2AZ in West US 2.
- Create SR-AZCROSS in West Central US.
Create two availability sets, one in each resource group for each cluster.
For example:
- Create availability set az2azAS1 in resource group SR-AZ2AZ.
- Create availability set azcross-AS in resource group SR-AZCROSS.
Create two virtual networks.
For example:
- Create virtual network az2az-VNet in resource group SR-AZ2AZ. The virtual network should have one subnet and one gateway subnet.
- Create virtual network azcross-VNet in resource group SR-AZCROSS. The virtual network should have one subnet and one gateway subnet.
Create two network security groups. Add an inbound security rule for Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) port 3389 to each network security group. You can choose to remove this rule after you finish setup.
For example:
- Create network security group az2az-NSG in resource group SR-AZ2AZ.
- Create an inbound security rule for RDP:3389 to the az2az-NSG network security group.
- Create network security group azcross-NSG in resource group SR-AZCROSS.
- Create an inbound security rule for RDP:3389 to the azcross-NSG network security group.
Create Windows Server virtual machines (VMs) in the resource groups.
For example:
- Create domain controller az2azDC. You can choose to create a third availability set for your domain controller or add the domain controller in one of the two availability sets. If you add the domain controller to the availability set you created for the two clusters, assign it a standard public IP address when you create the VM.
To create the domain controller:
- Install Active Directory Domain Service.
- Create a domain (for example,
contoso.com). - Create a user who has administrator permissions (for example, contosoadmin).
Create VMs az2az1 and az2az2 in the resource group SR-AZ2AZ by using virtual network az2az-VNet and network security group az2az-NSG in availability set az2azAS1. Configure the VMs:
- Assign a standard public IP address to each VM when you create the VMs.
- Add at least two managed disks to each VM.
- Install Failover Clustering and the Storage Replica feature to each VM.
Create VMs azcross1 and azcross2 in the resource group SR-AZCROSS by using virtual network azcross-VNet and network security group azcross-NSG in availability set azcross-AS. Configure the VMs:
- Assign a standard public IP address to each VM when you create the VMs.
- Add at least two managed disks to each VM.
- Install Failover Clustering and the Storage Replica feature to each VM.
Connect all the nodes to the domain and provide administrator permissions to the user you created.
Change the DNS server of the virtual network to the domain controller private IP address. In the example, the domain controller az2azDC has a private IP address (10.3.0.8). In the virtual networks (az2az-VNet and azcross-VNet), change DNS Server to 10.3.0.8.
In the example, connect all the nodes to
contoso.comand provide administrator permissions to the user contosoadmin.Log in as contosoadmin from all the nodes.
Create two clusters: SRAZC1 and SRAZCross.
For the example, use the following PowerShell commands:
New-Cluster -Name SRAZC1 -Node az2az1,az2az2 -StaticAddress 10.3.0.100New-Cluster -Name SRAZCross -Node azcross1,azcross2 -StaticAddress 10.0.0.10Enable Storage Spaces Direct:
Enable-clusterS2DNote
For each cluster, create a virtual disk volume. One volume is for the data, and one is for the log.
Create an internal Standard SKU load balancer for each cluster (azlbr1, azlbazcross).
Provide the cluster IP address as a static private IP address for the load balancer azlbr1:
- Front-end IP: 10.3.0.100 (pick up an unused IP address from the virtual network az2az-VNet subnet).
- Create a back-end pool for each load balancer. Add the associated cluster nodes.
- Create a health probe on port 59999.
- Create a load-balance rule. Allow high-availability ports, with floating IP enabled.
Provide the cluster IP address as a static private IP address for the load balancer azlbazcross:
- Front-end IP: 10.0.0.10 (pick up an unused IP address from the virtual network azcross-VNet subnet).
- Create a back-end pool for each load balancer. Add the associated cluster nodes.
- Create a health probe on port 59999.
- Create a load-balance rule. Allow high-availability ports, with floating IP enabled.
Create a virtual network gateway for network-to-network connectivity.
- Create the first virtual network gateway (az2az-VNetGateway) in the first resource group (SR-AZ2AZ). For Gateway Type, select VPN. For VPN type, select Route-based.
- Create the second Virtual network gateway (azcross-VNetGateway) in the second resource group (SR-AZCROSS). For Gateway Type, select VPN. For VPN type, select Route-based.
- Create a network-to-network connection from the first virtual network gateway to the second virtual network gateway. Provide a shared key.
- Create a network-to-network connection from the second virtual network gateway to the first virtual network gateway. Provide the same shared key that you used in the preceding step.
On each cluster node, open port 59999 (the health probe).
Run the following command on each node:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=PROBEPORT dir=in protocol=tcp action=allow localport=59999 remoteip=any profile=anyInstruct the cluster to listen for health probe messages on port 59999 and respond from the node that currently owns this resource.
For each cluster, run the health probe once from any one node of the cluster.
In the following sample code, make sure that you change the value for
ILBIPper your configuration values. Run the following command from any one node az2az1/az2az2:$ClusterNetworkName = "Cluster network 1" # Cluster network name (Use Get-ClusterNetwork on Windows Server 2012 or higher to find the name. Use Get-ClusterResource to find the IPResourceName.) $IPResourceName = "Cluster IP address" # IP address cluster resource name. $ILBIP = "10.3.0.100" # IP address in Internal Load Balancer (ILB). The static IP address for the load balancer is configured in the Azure portal. [int]$ProbePort = 59999 Get-ClusterResource $IPResourceName | Set-ClusterParameter -Multiple @{"Address"="$ILBIP";"ProbePort"=$ProbePort;"SubnetMask"="255.255.255.255";"Network"="$ClusterNetworkName";"ProbeFailureThreshold"=5;"EnableDhcp"=0}Run the following command from any node on azcross1 and azcross2:
$ClusterNetworkName = "Cluster network 1" # Cluster network name (Use Get-ClusterNetwork on Windows Server 2012 or later to find the name. Use Get-ClusterResource to find the IPResourceName.) $IPResourceName = "Cluster IP address" # IP address cluster resource name. $ILBIP = "10.0.0.10" # IP address in Internal Load Balancer (ILB). The static IP address for the load balancer is configured in the Azure portal. [int]$ProbePort = 59999 Get-ClusterResource $IPResourceName | Set-ClusterParameter -Multiple @{"Address"="$ILBIP";"ProbePort"=$ProbePort;"SubnetMask"="255.255.255.255";"Network"="$ClusterNetworkName";"ProbeFailureThreshold"=5;"EnableDhcp"=0}Verify that both clusters can connect and communicate with each other.
Either use the Connect to Cluster feature in Failover Cluster Manager to connect to the other cluster or verify that the other cluster responds from one of the nodes of the current cluster.
For example:
Get-Cluster -Name SRAZC1 (run from azcross1)Get-Cluster -Name SRAZCross (run from az2az1)Create a cloud witness for both clusters.
Create two storage accounts (az2azcw, azcrosssa) in Azure, one for each cluster in each resource group (SR-AZ2AZ, SR-AZCROSS).
- Copy the storage account name and key from the Access keys section.
- In Failover Cluster Manager, create the cloud witness. Use the copied account name and key to create it.
Run cluster validation tests before you go to the next step.
Start Windows PowerShell and use the
Test-SRTopologycmdlet to determine if you meet all the Storage Replica requirements. You can use the cmdlet in a requirements-only mode for a quick test and in long-running performance evaluation mode.Configure cluster-to-cluster storage replication.
Grant access from one cluster to another cluster in both directions:
From our example:
Grant-SRAccess -ComputerName az2az1 -Cluster SRAZCrossIf you're using Windows Server 2016, run this command also:
Grant-SRAccess -ComputerName azcross1 -Cluster SRAZC1Create a Storage Replica partnership for the two clusters:
Cluster SRAZC1: For volume location, use
C:\ClusterStorage\DataDisk1. For log location, useG:\*.Cluster SRAZCross: For volume location, use
C:\ClusterStorage\DataDiskCross. For log location, useG:\*.
Then run the following command:
New-SRPartnership -SourceComputerName SRAZC1 -SourceRGName rg01 -SourceVolumeName c:\ClusterStorage\DataDisk1 -SourceLogVolumeName g: -DestinationComputerName SRAZCross -DestinationRGName rg02 -DestinationVolumeName c:\ClusterStorage\DataDiskCross -DestinationLogVolumeName g: -LogType Raw