Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Source Reader is an alternative to using the Media Session and the Microsoft Media Foundation pipeline to process media data.
Why Use the Source Reader?
Media Foundation provides a pipeline that is optimized for playback. The pipeline is end-to-end, meaning it handles data flow from the source (such as a video file) all the way to the destination (such as the graphics display). However, if you want to read or modify the data as it goes through the pipeline, you must write a custom plug-in. That requires a fairly deep knowledge of the Media Foundation pipeline. For certain tasks, creating a new plug-in is too much overhead. The source reader is designed for this type of situation, when you want to get the raw data from a source without the overhead of the entire pipeline.
Internally, the source reader holds a pointer to a media source. A media source is a Media Foundation object that generates media data from an external source, such as a media file or video capture device. The source reader manages all of the method calls to the media source. (For more information about media sources, see Media Sources.)
If the media source delivers compressed data, you can use the source reader to decode the data. In that case, the source reader will load the correct decoder and manage the data flow between the media source and the decoder. The source reader can also perform some limited video processing: color conversion from YUV to RGB-32, and software deinterlacing, although these operations are not recommended for real-time video rendering. The following image illustrates this process.
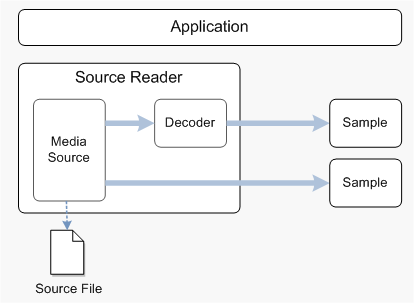
The source reader does not send the data to a destination; it is up to the application to consume the data. For example, the source reader can read a video file, but it will not render the video to the screen. Also, the source reader does not manage a presentation clock, handle timing issues, or synchronize video with audio.
Consider using the source reader when:
- You want to get data from a media file without worrying about the underlying file structure.
- You want to get data from an audio or video capture device.
- Your data-processing tasks are not time sensitive, or you do not require a presentation clock.
- You already have a media pipeline that is not based on Media Foundation, and you want to incorporate the Media Foundation media sources into your own pipeline.
The source reader is not recommended in the following situations:
- For protected content. The source reader does not support digital rights management (DRM).
- If you care about the details of the underlying file structure. The source reader hides that type of detail.
In this section
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Using the Source Reader to Process Media Data |
This topic describes how to use the Source Reader to process media data. |
| Using the Source Reader in Asynchronous Mode |
This topic describes how to use the Source Reader in asynchronous mode. |
| Tutorial: Decoding Audio |
This tutorial shows how to use the Source Reader to decode audio from a media file and write the audio to a WAVE file. |
Related topics