Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Gaze input in mixed reality apps is all about finding out what your users are looking at. When the eye tracking cameras on your device match up with rays in Unreal's world space, your user's line of sight data becomes available. Gaze can be used in both blueprints and C++, and is a core feature for mechanics like object interaction, way finding, and camera controls.
Enabling eye tracking
- In Project Settings > HoloLens, enable the Gaze Input capability:
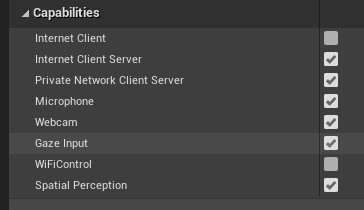
- Create a new actor and add it to your scene
Note
HoloLens eye tracking in Unreal only has a single gaze ray for both eyes. Stereoscopic tracking, which requires two rays, isn't supported.
Using eye tracking
First, check that your device supports eye tracking with the IsEyeTrackerConnected function. If the function returns true, call GetGazeData to find where the user’s eyes are looking at in the current frame:
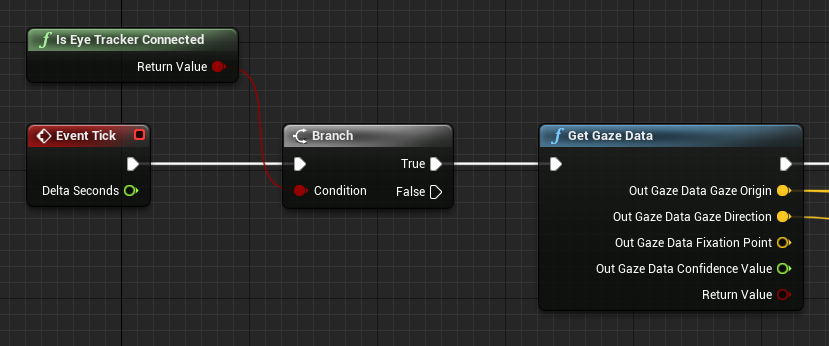
Note
The fixation point and the confidence value are not available on HoloLens.
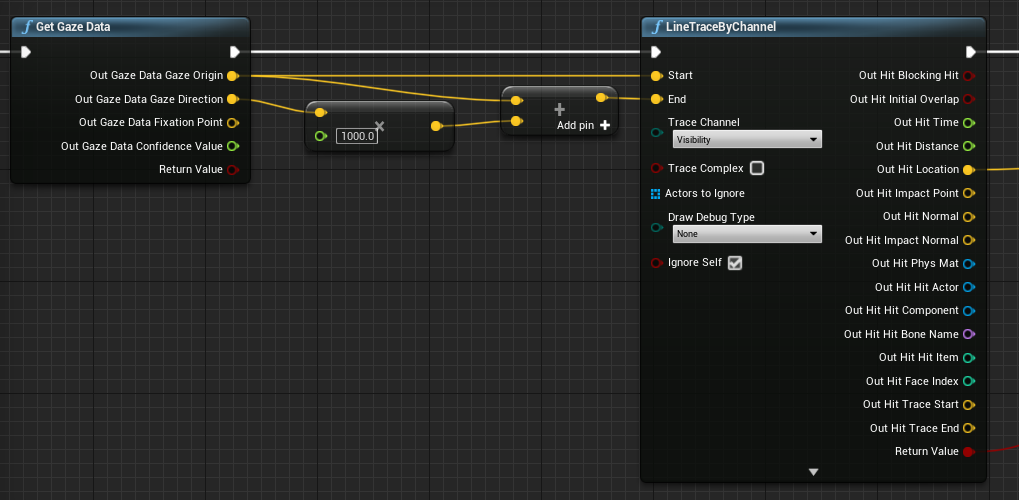
Use the gaze origin and direction in a line trace to find out exactly where your users are looking. The gaze value is a vector, starting at the gaze origin and ending at the origin plus the gaze direction multiplied by the line trace distance:
Getting head orientation
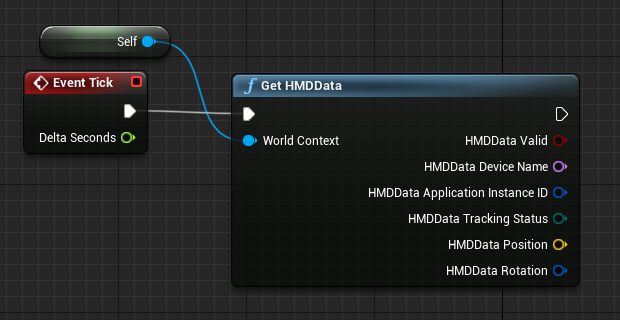
You can also use the rotation of the Head Mounted Display (HMD) to represent the direction of the user’s head. You can get the users head direction without enabling the Gaze Input capability, but you won't get you any eye tracking information. Add a reference to the blueprint as the world context to get the correct output data:
Note
Getting HMD Data is only available in Unreal 4.26 and onwards.
Using C++
- In your game’s build.cs file, add EyeTracker to the PublicDependencyModuleNames list:
PublicDependencyModuleNames.AddRange(
new string[] {
"Core",
"CoreUObject",
"Engine",
"InputCore",
"EyeTracker"
});
- In File/ New C++ Class, create a new C++ actor called EyeTracker
- A Visual Studio solution will open up the new EyeTracker class. Build and run to open the Unreal game with the new EyeTracker actor. Search for “EyeTracker” in the Place Actors window and drag and drop the class into the game window to add it to the project:
- In EyeTracker.cpp, add includes for EyeTrackerFunctionLibrary, and DrawDebugHelpers:
#include "EyeTrackerFunctionLibrary.h"
#include "DrawDebugHelpers.h"
Check that your device supports eye tracking with UEyeTrackerFunctionLibrary::IsEyeTrackerConnected before trying to get any gaze data. If eye tracking is supported, find the start and end of a ray for a line trace from UEyeTrackerFunctionLibrary::GetGazeData. From there, you can construct a gaze vector and pass its contents to LineTraceSingleByChannel to debug any ray hit results:
void AEyeTracker::Tick(float DeltaTime)
{
Super::Tick(DeltaTime);
if(UEyeTrackerFunctionLibrary::IsEyeTrackerConnected())
{
FEyeTrackerGazeData GazeData;
if(UEyeTrackerFunctionLibrary::GetGazeData(GazeData))
{
FVector Start = GazeData.GazeOrigin;
FVector End = GazeData.GazeOrigin + GazeData.GazeDirection * 100;
FHitResult Hit Result;
if (GWorld->LineTraceSingleByChannel(HitResult, Start, End, ECollisionChannel::ECC_Visiblity))
{
DrawDebugCoordinateSystem(GWorld, HitResult.Location, FQuat::Identity.Rotator(), 10);
}
}
}
}
Next Development Checkpoint
If you're following the Unreal development journey we've laid out, you're in the midst of exploring the MRTK core building blocks. From here, you can continue to the next building block:
Or jump to Mixed Reality platform capabilities and APIs:
You can always go back to the Unreal development checkpoints at any time.