Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Add existing folders of music, pictures, or videos to the corresponding libraries. You can also remove folders from libraries, get the list of folders in a library, and discover stored photos, music, and videos.
A library is a virtual collection of folders, which includes a known folder by default plus any other folders the user has added to the library by using your app or one of the built-in apps. For example, the Pictures library includes the Pictures known folder by default. The user can add folders to, or remove them from, the Pictures library by using your app or the built-in Photos app.
Prerequisites
Understand async programming for Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps
You can learn how to write asynchronous apps in C# or Visual Basic, see Call asynchronous APIs in C# or Visual Basic. To learn how to write asynchronous apps in C++, see Asynchronous programming in C++.
Access permissions to the location
In Visual Studio, open the app manifest file in Manifest Designer. On the Capabilities page, select the libraries that your app manages.
- Music Library
- Pictures Library
- Videos Library
To learn more, see File access permissions.
Get a reference to a library
Note
Remember to declare the appropriate capability. See App capability declarations for more information.
To get a reference to the user's Music, Pictures, or Video library, call the StorageLibrary.GetLibraryAsync method. Provide the corresponding value from the KnownLibraryId enumeration.
var myPictures = await Windows.Storage.StorageLibrary.GetLibraryAsync(Windows.Storage.KnownLibraryId.Pictures);
Get the list of folders in a library
To get the list of folders in a library, get the value of the StorageLibrary.Folders property.
using Windows.Foundation.Collections;
IObservableVector<Windows.Storage.StorageFolder> myPictureFolders = myPictures.Folders;
Get the folder in a library where new files are saved by default
To get the folder in a library where new files are saved by default, get the value of the StorageLibrary.SaveFolder property.
Windows.Storage.StorageFolder savePicturesFolder = myPictures.SaveFolder;
Add an existing folder to a library
To add a folder to a library, you call the StorageLibrary.RequestAddFolderAsync. Taking the Pictures Library as an example, calling this method causes a folder picker to be shown to the user with an Add this folder to Pictures button. If the user picks a folder then the folder remains in its original location on disk and it becomes an item in the StorageLibrary.Folders property (and in the built-in Photos app), but the folder does not appear as a child of the Pictures folder in File Explorer.
Windows.Storage.StorageFolder newFolder = await myPictures.RequestAddFolderAsync();
Remove a folder from a library
To remove a folder from a library, call the StorageLibrary.RequestRemoveFolderAsync method and specify the folder to be removed. You could use StorageLibrary.Folders and a ListView control (or similar) for the user to select a folder to remove.
When you call StorageLibrary.RequestRemoveFolderAsync, the user sees a confirmation dialog saying that the folder "won't appear in Pictures anymore, but won't be deleted." What this means is that the folder remains in its original location on disk, is removed from the StorageLibrary.Folders property, and will no longer included in the built-in Photos app.
The following example assumes that the user has selected the folder to remove from a ListView control named lvPictureFolders.
bool result = await myPictures.RequestRemoveFolderAsync(folder);
Get notified of changes to the list of folders in a library
To get notified about changes to the list of folders in a library, register a handler for the StorageLibrary.DefinitionChanged event of the library.
myPictures.DefinitionChanged += MyPictures_DefinitionChanged;
void HandleDefinitionChanged(Windows.Storage.StorageLibrary sender, object args)
{
// ...
}
Media library folders
A device provides five predefined locations for users and apps to store media files. Built-in apps store both user-created media and downloaded media in these locations.
The locations are:
Pictures folder. Contains pictures.
Camera Roll folder. Contains photos and video from the built-in camera.
Saved Pictures folder. Contains pictures that the user has saved from other apps.
Music folder. Contains songs, podcasts, and audio books.
Video folder. Contains videos.
Users or apps may also store media files outside the media library folders on the SD card. To find a media file reliably on the SD card, scan the contents of the SD card, or ask the user to locate the file by using a file picker. For more info, see Access the SD card.
Querying the media libraries
To get a collection of files, specify the library and the type of files that you want.
using Windows.Storage;
using Windows.Storage.Search;
private async void getSongs()
{
QueryOptions queryOption = new QueryOptions
(CommonFileQuery.OrderByTitle, new string[] { ".mp3", ".mp4", ".wma" });
queryOption.FolderDepth = FolderDepth.Deep;
Queue<IStorageFolder> folders = new Queue<IStorageFolder>();
var files = await KnownFolders.MusicLibrary.CreateFileQueryWithOptions
(queryOption).GetFilesAsync();
foreach (var file in files)
{
// do something with the music files
}
}
Query results include both internal and removable storage
Users can choose to store files by default on the optional SD card. Apps, however, can opt out of allowing files to be stored on the SD card. As a result, the media libraries can be split across the device's internal storage and the SD card.
You don't have to write additional code to handle this possibility. The methods in the Windows.Storage namespace that query known folders transparently combine the query results from both locations. You don't have to specify the removableStorage capability in the app manifest file to get these combined results, either.
Consider the state of the device's storage shown in the following image:
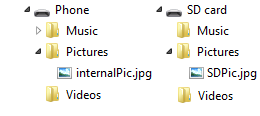
If you query the contents of the Pictures Library by calling await KnownFolders.PicturesLibrary.GetFilesAsync(), the results include both internalPic.jpg and SDPic.jpg.
Working with photos
On devices where the camera saves both a low-resolution image and a high-resolution image of every picture, the deep queries return only the low-resolution image.
The Camera Roll and the Saved Pictures folder do not support the deep queries.
Opening a photo in the app that captured it
If you want to let the user open a photo again later in the app that captured it, you can save the CreatorAppId with the photo's metadata by using code similar to the following example. In this example, testPhoto is a StorageFile.
IDictionary<string, object> propertiesToSave = new Dictionary<string, object>();
propertiesToSave.Add("System.CreatorOpenWithUIOptions", 1);
propertiesToSave.Add("System.CreatorAppId", appId);
testPhoto.Properties.SavePropertiesAsync(propertiesToSave).AsyncWait();
Using stream methods to add a file to a media library
When you access a media library by using a known folder such as KnownFolders.PictureLibrary, and you use stream methods to add a file to the media library, you have to make sure to close all the streams that your code opens. Otherwise these methods fail to add the file to the media library as expected because at least one stream still has a handle to the file.
For example, when you run the following code, the file is not added to the media library. In the line of code, using (var destinationStream = (await destinationFile.OpenAsync(FileAccessMode.ReadWrite)).GetOutputStreamAt(0)), both the OpenAsync method and the GetOutputStreamAt method open a stream. However only the stream opened by the GetOutputStreamAt method is disposed as a result of the using statement. The other stream remains open and prevents saving the file.
StorageFolder testFolder = await StorageFolder.GetFolderFromPathAsync(@"C:\test");
StorageFile sourceFile = await testFolder.GetFileAsync("TestImage.jpg");
StorageFile destinationFile = await KnownFolders.CameraRoll.CreateFileAsync("MyTestImage.jpg");
using (var sourceStream = (await sourceFile.OpenReadAsync()).GetInputStreamAt(0))
{
using (var destinationStream = (await destinationFile.OpenAsync(FileAccessMode.ReadWrite)).GetOutputStreamAt(0))
{
await RandomAccessStream.CopyAndCloseAsync(sourceStream, destinationStream);
}
}
To use stream methods successfully to add a file to the media library, make sure to close all the streams that your code opens, as shown in the following example.
StorageFolder testFolder = await StorageFolder.GetFolderFromPathAsync(@"C:\test");
StorageFile sourceFile = await testFolder.GetFileAsync("TestImage.jpg");
StorageFile destinationFile = await KnownFolders.CameraRoll.CreateFileAsync("MyTestImage.jpg");
using (var sourceStream = await sourceFile.OpenReadAsync())
{
using (var sourceInputStream = sourceStream.GetInputStreamAt(0))
{
using (var destinationStream = await destinationFile.OpenAsync(FileAccessMode.ReadWrite))
{
using (var destinationOutputStream = destinationStream.GetOutputStreamAt(0))
{
await RandomAccessStream.CopyAndCloseAsync(sourceInputStream, destinationStream);
}
}
}
}