Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The diffuse and specular lighting components of the global illumination equation contain terms that describe light attenuation and the spotlight cone. These terms are described below.
Attenuation
The attenuation of a light depends on the type of light and the distance between the light and the vertex position. To calculate attenuation, use one of the following equations.
Atten = 1/( att0i + att1i * d + att2i * d²)
Where:
| Parameter | Default value | Type | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| att0i | 0.0 | Floating point | Constant attenuation factor | 0 to +infinity |
| att1i | 0.0 | Floating point | Linear attenuation factor | 0 to +infinity |
| att2i | 0.0 | Floating point | Quadratic attenuation factor | 0 to +infinity |
| d | N/A | Floating point | Distance from vertex position to light position | N/A |
- Atten = 1, if the light is a directional light.
- Atten = 0, if the distance between the light and the vertex exceeds the light's range.
The distance between the light and the vertex position is always positive.
d = | Ldir |
Where:
| Parameter | Default value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ldir | N/A | 3D vector with x, y, and z floating-point values | Direction vector from vertex position to the light position |
If d is greater than the light's range, Direct3D makes no further attenuation calculations and applies no effects from the light to the vertex.
The attenuation constants act as coefficients in the formula - you can produce a variety of attenuation curves by making simple adjustments to them. You can set Attenuation1 to 1.0 to create a light that doesn't attenuate but is still limited by range, or you can experiment with different values to achieve various attenuation effects.
The attenuation at the maximum range of the light is not 0.0. To prevent lights from suddenly appearing when they are at the light range, an application can increase the light range. Or, the application can set up attenuation constants so that the attenuation factor is close to 0.0 at the light range. The attenuation value is multiplied by the red, green, and blue components of the light's color to scale the light's intensity as a factor of the distance light travels to a vertex.
Spotlight Factor
The following equation specifies the spotlight factor.
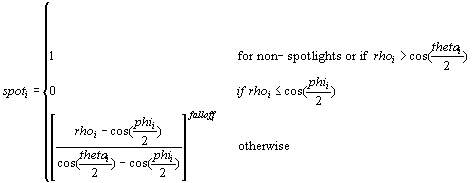
| Parameter | Default value | Type | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rhoi | N/A | Floating point | cosine(angle) for spotlight i | N/A |
| phii | 0.0 | Floating point | Penumbra angle of spotlight i in radians | [thetai, pi) |
| thetai | 0.0 | Floating point | Umbra angle of spotlight i in radians | [0, pi) |
| falloff | 0.0 | Floating point | Falloff factor | (-infinity, +infinity) |
Where:
rho = norm(Ldcs).norm(Ldir)
and:
| Parameter | Default value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ldcs | N/A | 3D vector with x, y, and z floating-point values | The negative of the light direction in camera space |
| Ldir | N/A | 3D vector with x, y, and z floating-point values | Direction vector from vertex position to the light position |
After computing the light attenuation, to calculate the diffuse and specular components for the vertex, Direct3D also considers spotlight effects if applicable, the angle that the light reflects from a surface, and the reflectance of the current material. In Light types, see "Spotlight".
Related topics