Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The CryptoAPI system architecture is composed of five major functional areas:
- Base Cryptographic Functions
- Certificate Encode/Decode Functions
- Certificate Store Functions
- Simplified Message Functions
- Low-level Message Functions
Base Cryptographic Functions
- Context functions used to connect to a CSP. These functions enable applications to choose a specific CSP by name or to choose a specific CSP that can provide a needed class of functionality.
- Key generation functions used to generate and store cryptographic keys. Full support is included for changing chaining modes, initialization vectors, and other encryption features. For more information, see Key Generation and Exchange Functions.
- Key exchange functions used to exchange or transmit keys. For more information, see Cryptographic Key Storage and Exchange and Key Generation and Exchange Functions.
Certificate Encode/Decode Functions
- Functions used to encrypt or decrypt data. Support is also included for hashing data. For more information, see Data Encryption and Decryption Functions and Data Encryption and Decryption.
Certificate Store Functions
- Functions used to manage collections of digital certificates. For more information, see Digital Certificates and Certificate Store Functions.
Simplified Message Functions
- Functions used to encrypt and decrypt messages and data.
- Functions used to sign messages and data.
- Functions used to verify the authenticity of signatures on received messages and related data.
For more information, see Simplified Messages and Simplified Message Functions.
Low-level Message Functions
- Functions used to perform all of the tasks performed by the simplified message functions. The low-level message functions provide more flexibility than the simplified message functions but require more function calls. For more information, see Low-level Messages and Low-level Message Functions.
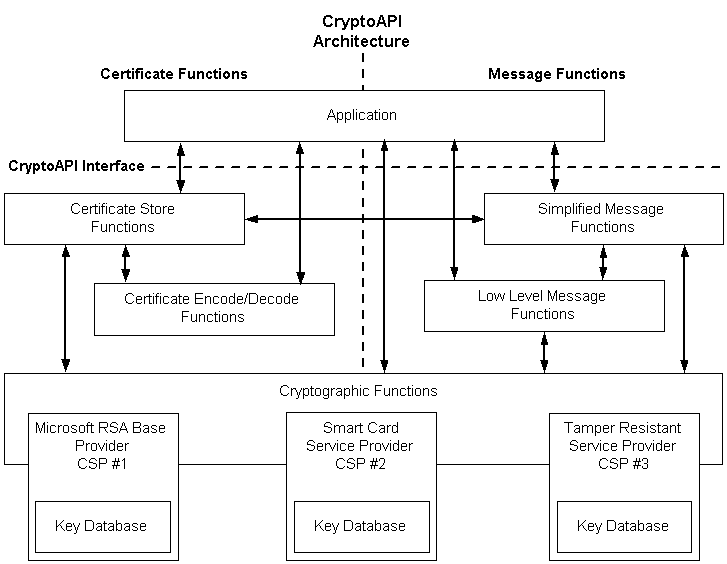
Each of the functional areas has a key word in its function name that indicates its functional area.
| Functional area | Function name convention |
|---|---|
| Base cryptographic functions | Crypt |
| Encoding/decoding functions | Crypt |
| Certificate store functions | Store |
| Simplified message functions | Message |
| Low-level message functions | Msg |
Applications use functions in all of these areas. These functions, taken together, make up CryptoAPI. The base cryptographic functions use the CSPs for the necessary cryptographic algorithms and for the generation and secure storage of cryptographic keys.
Two different kinds of cryptographic keys are used: session keys, which are used for a single encryption/decryption, and public/private key pairs, which are used on a more permanent basis.
Note
Although an application can communicate directly with any of the five functional areas, it cannot communicate directly with a CSP. All application-to-CSP communications occur through the base cryptographic functions. Base cryptographic functions have a parameter that specifies which CSP to use. This parameter can be set to NULL to select a default CSP.