Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) format is a publicly-available image format specification that allows encapsulation of the hard disk into an individual file for use by the operating system as a virtual disk in all the same ways physical hard disks are used. These virtual disks are capable of hosting native file systems (NTFS, FAT, exFAT, and UDFS) while supporting standard disk and file operations. VHD API support allows management of the virtual disks. Virtual disks created with the VHD API can function as boot disks.
An example of how VHD files are used is the Hyper-V feature in Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, Virtual Server, and Windows Virtual PC. These products use the VHD API to contain the Windows operating system image utilized by a virtual machine as its system boot disk.
The Microsoft Windows Software Development Kit (SDK) integrates Native VHD support for working with virtual disks, making it easier for developers and administrators to create, manage, and deploy Windows images in VHD files using either the platform API support or management tools. It is not necessary to install separate applications or implement a VHD format parser to enable these operations. These APIs allow for generic use of virtual disks independent of any other virtualization technologies.
Terminology
The term backing store is used to refer to the physical file that exists on the actual hard disk. The backing store is represented by a VHD image file.
The terms dynamic, expandable, and sparse are often used interchangeably when referring to dynamically expandable virtual disks. For VHD technology, these terms are identical.
VHD System Features Overview
The following diagram presents an overview of the VHD features and their relationships.
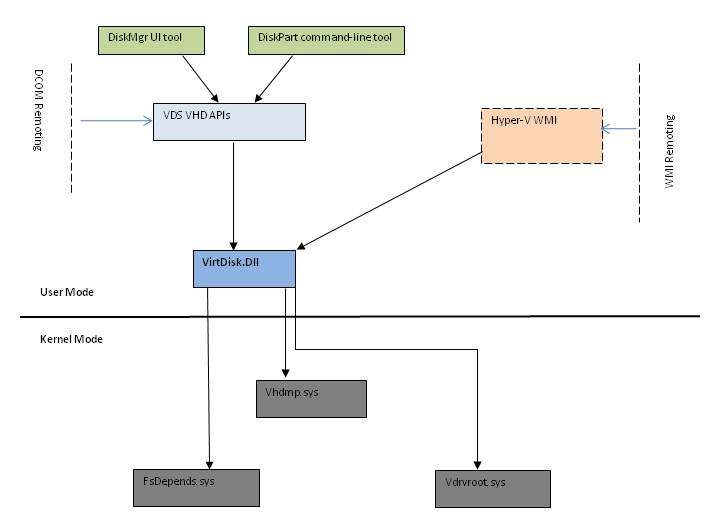
The following is a summary explanation of the previously described features.
User Mode Native Windows APIs:
- VirtDisk.dll - Common library for VHD management APIs.
User Mode Domain-specific Management Wrappers:
- VDS VHD APIs - VDS Object Model wrappers for the VHD Windows APIs.
Kernel Mode Drivers:
- VDrvRoot.sys - Root virtual drive enumerator.
- FsDepends.sys - Nested volume dependency management.
- Vhdmp.sys - VHD parser and dependency property provider.
The SDK documentation in this section covers the user-mode native Windows VHD APIs.
Virtual Disk Types
There are considerations for using virtual disks, and what types of virtual disks are available:
Fixed—The VHD image file is pre-allocated on the backing store for the maximum size requested.
Expandable—Also known as "dynamic", "dynamically expandable", and "sparse", the VHD image file uses only as much space on the backing store as needed to store the actual data the virtual disk currently contains. When creating this type of virtual disk, the VHD API does not test for free space on the physical disk based on the maximum size requested, therefore it is possible to successfully create a dynamic virtual disk with a maximum size larger than the available physical disk free space. For more information, see ExpandVirtualDisk. Note The maximum size of a dynamic virtual disk is 2,040 GB.
Differencing—A parent virtual disk is used as the basis of this type, with any subsequent writes written to the virtual disk as differences to the new differencing VHD image file, and the parent VHD image file is not modified. For example, if you have a clean-install system boot operating system virtual disk as a parent and designate the differencing virtual disk as the current virtual disk for the system to use, then the operating system on the parent virtual disk stays in its original state for quick recovery or for quickly creating more boot images based on additional differencing virtual disks. For more information, see MergeVirtualDisk. Note The maximum size of a differencing virtual disk is 2,040 GB.
All virtual disk types have a minimum size of 3 MB.
Related topics
Virtual Hard Disk Image Format Specification