Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Map control is a cross-platform view for displaying and annotating maps. It uses the native map control for each platform, providing a fast and familiar maps experience for users:
The Map class defines the following properties that control map appearance and behavior:
IsShowingUser, of typebool, indicates whether the map is showing the user's current location.ItemsSource, of typeIEnumerable, which specifies the collection ofIEnumerableitems to be displayed.ItemTemplate, of typeDataTemplate, which specifies theDataTemplateto apply to each item in the collection of displayed items.ItemTemplateSelector, of typeDataTemplateSelector, which specifies theDataTemplateSelectorthat will be used to choose aDataTemplatefor an item at runtime.HasScrollEnabled, of typebool, determines whether the map is allowed to scroll.HasZoomEnabled, of typebool, determines whether the map is allowed to zoom.MapElements, of typeIList<MapElement>, represents the list of elements on the map, such as polygons and polylines.MapType, of typeMapType, indicates the display style of the map.MoveToLastRegionOnLayoutChange, of typebool, controls whether the displayed map region will move from its current region to its previously set region when a layout change occurs.Pins, of typeIList<Pin>, represents the list of pins on the map.TrafficEnabled, of typebool, indicates whether traffic data is overlaid on the map.VisibleRegion, of typeMapSpan, returns the currently displayed region of the map.
These properties, with the exception of the MapElements, Pins, and VisibleRegion properties, are backed by BindableProperty objects, which mean they can be targets of data bindings.
The Map class also defines a MapClicked event that's fired when the map is tapped. The MapClickedEventArgs object that accompanies the event has a single property named Position, of type Position. When the event is fired, the Position property is set to the map location that was tapped. For information about the Position struct, see Map Position and Distance.
For information about the ItemsSource, ItemTemplate, and ItemTemplateSelector properties, see Display a pin collection.
Display a map
A Map can be displayed by adding it to a layout or page:
<ContentPage ...
xmlns:maps="clr-namespace:Xamarin.Forms.Maps;assembly=Xamarin.Forms.Maps">
<maps:Map x:Name="map" />
</ContentPage>
Note
An additional xmlns namespace definition is required to reference the Xamarin.Forms.Maps controls. In the previous example the Xamarin.Forms.Maps namespace is referenced through the maps keyword.
The equivalent C# code is:
using Xamarin.Forms;
using Xamarin.Forms.Maps;
namespace WorkingWithMaps
{
public class MapTypesPageCode : ContentPage
{
public MapTypesPageCode()
{
Map map = new Map();
Content = map;
}
}
}
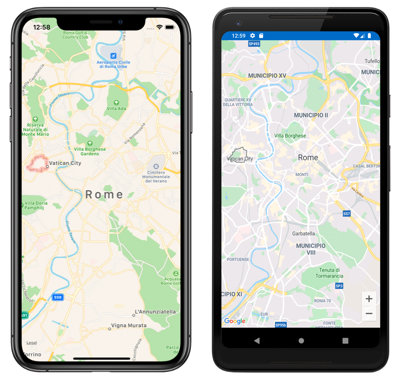
This example calls the default Map constructor, which centers the map on Rome:
Alternatively, a MapSpan argument can be passed to a Map constructor to set the center point and zoom level of the map when it's loaded. For more information, see Display a specific location on a map.
Map types
The Map.MapType property can be set to a MapType enumeration member to define the display style of the map. The MapType enumeration defines the following members:
Streetspecifies that a street map will be displayed.Satellitespecifies that a map containing satellite imagery will be displayed.Hybridspecifies that a map combining street and satellite data will be displayed.
By default, a Map will display a street map if the MapType property is undefined. Alternatively, the MapType property can be set to one of the MapType enumeration members:
<maps:Map MapType="Satellite" />
The equivalent C# code is:
Map map = new Map
{
MapType = MapType.Satellite
};
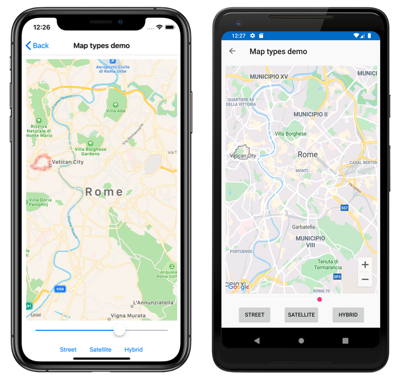
The following screenshots show a Map when the MapType property is set to Street:
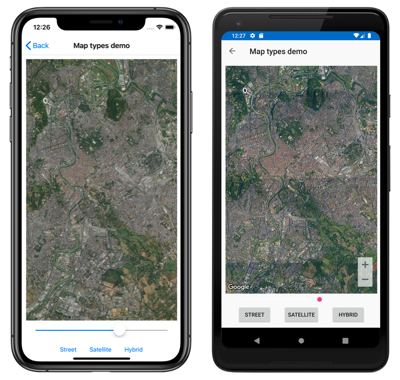
The following screenshots show a Map when the MapType property is set to Satellite:
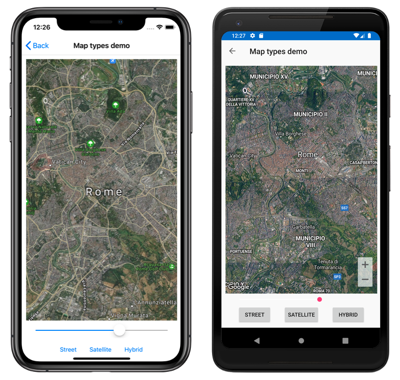
The following screenshots show a Map when the MapType property is set to Hybrid:
Display a specific location on a map
The region of a map to display when a map is loaded can be set by passing a MapSpan argument to the Map constructor:
<maps:Map>
<x:Arguments>
<maps:MapSpan>
<x:Arguments>
<maps:Position>
<x:Arguments>
<x:Double>36.9628066</x:Double>
<x:Double>-122.0194722</x:Double>
</x:Arguments>
</maps:Position>
<x:Double>0.01</x:Double>
<x:Double>0.01</x:Double>
</x:Arguments>
</maps:MapSpan>
</x:Arguments>
</maps:Map>
The equivalent C# code is:
Position position = new Position(36.9628066, -122.0194722);
MapSpan mapSpan = new MapSpan(position, 0.01, 0.01);
Map map = new Map(mapSpan);
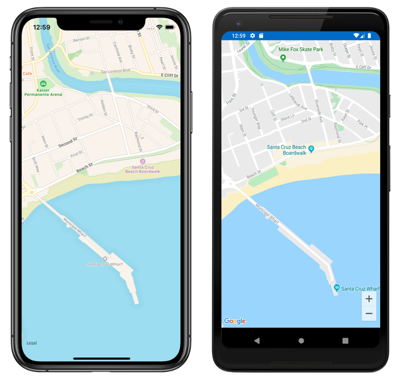
This example creates a Map object that shows the region that is specified by the MapSpan object. The MapSpan object is centered on the latitude and longitude represented by a Position object, and spans 0.01 latitude and 0.01 longitude degrees. For information about the Position struct, see Map Position and Distance. For information about passing arguments in XAML, see Passing Arguments in XAML.
The result is that when the map is displayed, it's centered on a specific location, and spans a specific number of latitude and longitude degrees:
Create a MapSpan object
There are a number of approaches for creating MapSpan objects. A common approach is supply the required arguments to the MapSpan constructor. These are a latitude and longitude represented by a Position object, and double values that represent the degrees of latitude and longitude that are spanned by the MapSpan. For information about the Position struct, see Map Position and Distance.
Alternatively, there are three methods in the MapSpan class that return new MapSpan objects:
ClampLatitudereturns aMapSpanwith the sameLongitudeDegreesas the method's class instance, and a radius defined by itsnorthandsoutharguments.FromCenterAndRadiusreturns aMapSpanthat is defined by itsPositionandDistancearguments.WithZoomreturns aMapSpanwith the same center as the method's class instance, but with a radius multiplied by itsdoubleargument.
For information about the Distance struct, see Map Position and Distance.
Once a MapSpan has been created, the following properties can be accessed to retrieve data about it:
Center, which represents thePositionin the geographical center of theMapSpan.LatitudeDegrees, which represents the degrees of latitude that are spanned by theMapSpan.LongitudeDegrees, which represents the degrees of longitude that are spanned by theMapSpan.Radius, which represents theMapSpanradius.
Move the map
The Map.MoveToRegion method can be called to change the position and zoom level of a map. This method accepts a MapSpan argument that defines the region of the map to display, and its zoom level.
The following code shows an example of moving the displayed region on a map:
MapSpan mapSpan = MapSpan.FromCenterAndRadius(position, Distance.FromKilometers(0.444));
map.MoveToRegion(mapSpan);
Zoom the map
The zoom level of a Map can be changed without altering its location. This can be accomplished using the map UI, or programatically by calling the MoveToRegion method with a MapSpan argument that uses the current location as the Position argument:
double zoomLevel = 0.5;
double latlongDegrees = 360 / (Math.Pow(2, zoomLevel));
if (map.VisibleRegion != null)
{
map.MoveToRegion(new MapSpan(map.VisibleRegion.Center, latlongDegrees, latlongDegrees));
}
In this example, the MoveToRegion method is called with a MapSpan argument that specifies the current location of the map, via the Map.VisibleRegion property, and the zoom level as degrees of latitude and longitude. The overall result is that the zoom level of the map is changed, but its location isn't. An alternative approach for implementing zoom on a map is to use the MapSpan.WithZoom method to control the zoom factor.
Important
Zooming a map, whether via the map UI or programatically, requires that the Map.HasZoomEnabled property is true. For more information about this property, see Disable zoom.
Customize map behavior
The behavior of a Map can be customized by setting some of its properties, and by handling the MapClicked event.
Note
Additional map behavior customization can be achieved by creating a map custom renderer. For more information, see Customizing a Xamarin.Forms Map.
Show traffic data
The Map class defines a TrafficEnabled property of type bool. By default this property is false, which indicates that traffic data won't be overlaid on the map. When this property is set to true, traffic data is overlaid on the map. The following example shows setting this property:
<maps:Map TrafficEnabled="true" />
The equivalent C# code is:
Map map = new Map
{
TrafficEnabled = true
};
Disable scroll
The Map class defines a HasScrollEnabled property of type bool. By default this property is true, which indicates that the map is allowed to scroll. When this property is set to false, the map will not scroll. The following example shows setting this property:
<maps:Map HasScrollEnabled="false" />
The equivalent C# code is:
Map map = new Map
{
HasScrollEnabled = false
};
Disable zoom
The Map class defines a HasZoomEnabled property of type bool. By default this property is true, which indicates that zoom can be performed on the map. When this property is set to false, the map can't be zoomed. The following example shows setting this property:
<maps:Map HasZoomEnabled="false" />
The equivalent C# code is:
Map map = new Map
{
HasZoomEnabled = false
};
Show the user's location
The Map class defines a IsShowingUser property of type bool. By default this property is false, which indicates that the map is not showing the user's current location. When this property is set to true, the map shows the user's current location. The following example shows setting this property:
<maps:Map IsShowingUser="true" />
The equivalent C# code is:
Map map = new Map
{
IsShowingUser = true
};
Important
On iOS, Android, and the Universal Windows Platform, accessing the user's location requires location permissions to have been granted to the application. For more information, see Platform configuration.
Maintain map region on layout change
The Map class defines a MoveToLastRegionOnLayoutChange property of type bool. By default this property is true, which indicates that the displayed map region will move from its current region to its previously set region when a layout change occurs, such as on device rotation. When this property is set to false, the displayed map region will remain centered when a layout change occurs. The following example shows setting this property:
<maps:Map MoveToLastRegionOnLayoutChange="false" />
The equivalent C# code is:
Map map = new Map
{
MoveToLastRegionOnLayoutChange = false
};
Map clicks
The Map class defines a MapClicked event that's fired when the map is tapped. The MapClickedEventArgs object that accompanies the event has a single property named Position, of type Position. When the event is fired, the Position property is set to the map location that was tapped. For information about the Position struct, see Map Position and Distance.
The following code example shows an event handler for the MapClicked event:
void OnMapClicked(object sender, MapClickedEventArgs e)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"MapClick: {e.Position.Latitude}, {e.Position.Longitude}");
}
In this example, the OnMapClicked event handler outputs the latitude and longitude that represents the tapped map location. The event handler can be registered with the MapClicked event as follows:
<maps:Map MapClicked="OnMapClicked" />
The equivalent C# code is:
Map map = new Map();
map.MapClicked += OnMapClicked;