Styling Xamarin.Forms apps using Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
Xamarin.Forms supports styling visual elements using Cascading Style Sheets (CSS).
Xamarin.Forms applications can be styled using CSS. A style sheet consists of a list of rules, with each rule consisting of one or more selectors and a declaration block. A declaration block consists of a list of declarations in braces, with each declaration consisting of a property, a colon, and a value. When there are multiple declarations in a block, a semi-colon is inserted as a separator. The following code example shows some Xamarin.Forms compliant CSS:
navigationpage {
-xf-bar-background-color: lightgray;
}
^contentpage {
background-color: lightgray;
}
#listView {
background-color: lightgray;
}
stacklayout {
margin: 20;
}
.mainPageTitle {
font-style: bold;
font-size: medium;
}
.mainPageSubtitle {
margin-top: 15;
}
.detailPageTitle {
font-style: bold;
font-size: medium;
text-align: center;
}
.detailPageSubtitle {
text-align: center;
font-style: italic;
}
listview image {
height: 60;
width: 60;
}
stacklayout>image {
height: 200;
width: 200;
}
In Xamarin.Forms, CSS style sheets are parsed and evaluated at runtime, rather than compile time, and style sheets are re-parsed on use.
Note
Currently, all of the styling that's possible with XAML styling cannot be performed with CSS. However, XAML styles can be used to supplement CSS for properties that are currently unsupported by Xamarin.Forms. For more information about XAML styles, see Styling Xamarin.Forms Apps using XAML Styles.
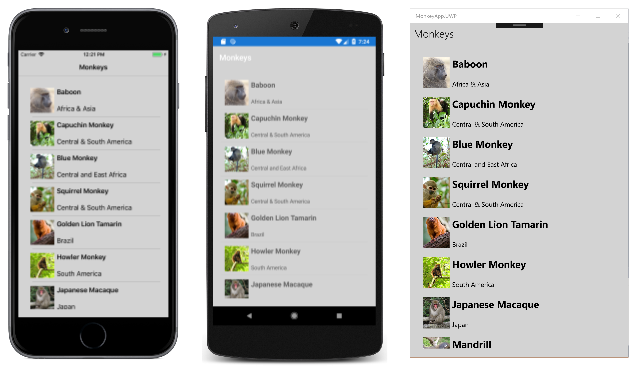
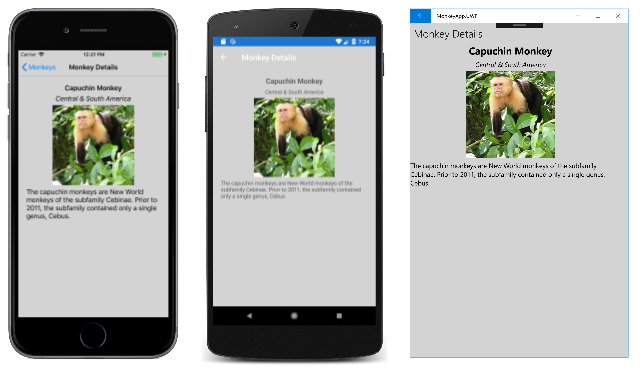
The sample demonstrates using CSS to style a simple app, and is shown in the following screenshots:
Consuming a style sheet
The process for adding a style sheet to a solution is as follows:
- Add an empty CSS file to your .NET Standard library project.
- Set the build action of the CSS file to EmbeddedResource.
Loading a style sheet
There are a number of approaches that can be used to load a style sheet.
Note
It's not currently possible to change a style sheet at runtime and have the new style sheet applied.
XAML
A style sheet can be loaded and parsed with the StyleSheet class before being added to a ResourceDictionary:
<Application ...>
<Application.Resources>
<StyleSheet Source="/Assets/styles.css" />
</Application.Resources>
</Application>
The StyleSheet.Source property specifies the style sheet as a URI relative to the location of the enclosing XAML file, or relative to the project root if the URI starts with a /.
Warning
The CSS file will fail to load if its build action is not set to EmbeddedResource.
Alternatively, a style sheet can be loaded and parsed with the StyleSheet class, before being added to a ResourceDictionary, by inlining it in a CDATA section:
<ContentPage ...>
<ContentPage.Resources>
<StyleSheet>
<![CDATA[
^contentpage {
background-color: lightgray;
}
]]>
</StyleSheet>
</ContentPage.Resources>
...
</ContentPage>
For more information about resource dictionaries, see Resource Dictionaries.
C#
In C#, a style sheet can be loaded from a StringReader and added to a ResourceDictionary:
public partial class MyPage : ContentPage
{
public MyPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
using (var reader = new StringReader("^contentpage { background-color: lightgray; }"))
{
this.Resources.Add(StyleSheet.FromReader(reader));
}
}
}
The argument to the StyleSheet.FromReader method is the TextReader that has read the style sheet.
Selecting elements and applying properties
CSS uses selectors to determine which elements to target. Styles with matching selectors are applied consecutively, in definition order. Styles defined on a specific item are always applied last. For more information about supported selectors, see Selector Reference.
CSS uses properties to style a selected element. Each property has a set of possible values, and some properties can affect any type of element, while others apply to groups of elements. For more information about supported properties, see Property Reference.
Child stylesheets always override parent stylesheets if they set the same properties. Therefore, the following precedence rules are followed when applying styles that set the same properties:
- A style defined in the application resources will be overwritten by a style defined in the page resources, if they set the same properties.
- A style defined in page resources will be overwritten by a style defined in the control resources, if they set the same properties.
- A style defined in the application resources will be overwritten by a style defined in the control resources, if they set the same properties.
Important
CSS variables are unsupported.
Selecting elements by type
Elements in the visual tree can be selected by type with the case insensitive element selector:
stacklayout {
margin: 20;
}
This selector identifies any StackLayout elements on pages that consume the style sheet, and sets their margins to a uniform thickness of 20.
Note
The element selector does not identify subclasses of the specified type.
Selecting elements by base class
Elements in the visual tree can be selected by base class with the case insensitive ^base selector:
^contentpage {
background-color: lightgray;
}
This selector identifies any ContentPage elements that consume the style sheet, and sets their background color to lightgray.
Note
The ^base selector is specific to Xamarin.Forms, and isn't part of the CSS specification.
Selecting an element by name
Individual elements in the visual tree can be selected with the case sensitive #id selector:
#listView {
background-color: lightgray;
}
This selector identifies the element whose StyleId property is set to listView. However, if the StyleId property is not set, the selector will fall back to using the x:Name of the element. Therefore, in the following XAML example, the #listView selector will identify the ListView whose x:Name attribute is set to listView, and will set it's background color to lightgray.
<ContentPage ...>
<ContentPage.Resources>
<StyleSheet Source="/Assets/styles.css" />
</ContentPage.Resources>
<StackLayout>
<ListView x:Name="listView" ...>
...
</ListView>
</StackLayout>
</ContentPage>
Selecting elements with a specific class attribute
Elements with a specific class attribute can be selected with the case sensitive .class selector:
.detailPageTitle {
font-style: bold;
font-size: medium;
text-align: center;
}
.detailPageSubtitle {
text-align: center;
font-style: italic;
}
A CSS class can be assigned to a XAML element by setting the StyleClass property of the element to the CSS class name. Therefore, in the following XAML example, the styles defined by the .detailPageTitle class are assigned to the first Label, while the styles defined by the .detailPageSubtitle class are assigned to the second Label.
<ContentPage ...>
<ContentPage.Resources>
<StyleSheet Source="/Assets/styles.css" />
</ContentPage.Resources>
<ScrollView>
<StackLayout>
<Label ... StyleClass="detailPageTitle" />
<Label ... StyleClass="detailPageSubtitle"/>
...
</StackLayout>
</ScrollView>
</ContentPage>
Selecting child elements
Child elements in the visual tree can be selected with the case insensitive element element selector:
listview image {
height: 60;
width: 60;
}
This selector identifies any Image elements that are children of ListView elements, and sets their height and width to 60. Therefore, in the following XAML example, the listview image selector will identify the Image that's a child of the ListView, and sets its height and width to 60.
<ContentPage ...>
<ContentPage.Resources>
<StyleSheet Source="/Assets/styles.css" />
</ContentPage.Resources>
<StackLayout>
<ListView ...>
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<ViewCell>
<Grid>
...
<Image ... />
...
</Grid>
</ViewCell>
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
</StackLayout>
</ContentPage>
Note
The element element selector does not require the child element to be a direct child of the parent – the child element may have a different parent. Selection occurs provided that an ancestor is the specified first element.
Selecting direct child elements
Direct child elements in the visual tree can be selected with the case insensitive element>element selector:
stacklayout>image {
height: 200;
width: 200;
}
This selector identifies any Image elements that are direct children of StackLayout elements, and sets their height and width to 200. Therefore, in the following XAML example, the stacklayout>image selector will identify the Image that's a direct child of the StackLayout, and sets its height and width to 200.
<ContentPage ...>
<ContentPage.Resources>
<StyleSheet Source="/Assets/styles.css" />
</ContentPage.Resources>
<ScrollView>
<StackLayout>
...
<Image ... />
...
</StackLayout>
</ScrollView>
</ContentPage>
Note
The element>element selector requires that the child element is a direct child of the parent.
Selector reference
The following CSS selectors are supported by Xamarin.Forms:
| Selector | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
.class |
.header |
Selects all elements with the StyleClass property containing 'header'. Note that this selector is case sensitive. |
#id |
#email |
Selects all elements with StyleId set to email. If StyleId is not set, fallback to x:Name. When using XAML, x:Name is preferred over StyleId. Note that this selector is case sensitive. |
* |
* |
Selects all elements. |
element |
label |
Selects all elements of type Label, but not subclasses. Note that this selector is case insensitive. |
^base |
^contentpage |
Selects all elements with ContentPage as the base class, including ContentPage itself. Note that this selector is case insensitive and isn't part of the CSS specification. |
element,element |
label,button |
Selects all Button elements and all Label elements. Note that this selector is case insensitive. |
element element |
stacklayout label |
Selects all Label elements inside a StackLayout. Note that this selector is case insensitive. |
element>element |
stacklayout>label |
Selects all Label elements with StackLayout as a direct parent. Note that this selector is case insensitive. |
element+element |
label+entry |
Selects all Entry elements directly after a Label. Note that this selector is case insensitive. |
element~element |
label~entry |
Selects all Entry elements preceded by a Label. Note that this selector is case insensitive. |
Styles with matching selectors are applied consecutively, in definition order. Styles defined on a specific item are always applied last.
Tip
Selectors can be combined without limitation, such as StackLayout>ContentView>label.email.
The following selectors are currently unsupported:
[attribute]@mediaand@supports:and::
Note
Specificity, and specificity overrides are unsupported.
Property reference
The following CSS properties are supported by Xamarin.Forms (in the Values column, types are italic, while string literals are gray):
| Property | Applies to | Values | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
align-content |
FlexLayout |
stretch | center | start | end | spacebetween | spacearound | spaceevenly | flex-start | flex-end | space-between | space-around | initial |
align-content: space-between; |
align-items |
FlexLayout |
stretch | center | start | end | flex-start | flex-end | initial |
align-items: flex-start; |
align-self |
VisualElement |
auto | stretch | center | start | end | flex-start | flex-end | initial |
align-self: flex-end; |
background-color |
VisualElement |
color | initial |
background-color: springgreen; |
background-image |
Page |
string | initial |
background-image: bg.png; |
border-color |
Button, Frame, ImageButton |
color | initial |
border-color: #9acd32; |
border-radius |
BoxView, Button, Frame, ImageButton |
double | initial |
border-radius: 10; |
border-width |
Button, ImageButton |
double | initial |
border-width: .5; |
color |
ActivityIndicator, BoxView, Button, CheckBox, DatePicker, Editor, Entry, Label, Picker, ProgressBar, SearchBar, Switch, TimePicker |
color | initial |
color: rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.3); |
column-gap |
Grid |
double | initial |
column-gap: 9; |
direction |
VisualElement |
ltr | rtl | inherit | initial |
direction: rtl; |
flex-direction |
FlexLayout |
column | columnreverse | row | rowreverse | row-reverse | column-reverse | initial |
flex-direction: column-reverse; |
flex-basis |
VisualElement |
float | auto | initial. In addition, a percentage in the range 0% to 100% can be specified with the % sign. |
flex-basis: 25%; |
flex-grow |
VisualElement |
float | initial |
flex-grow: 1.5; |
flex-shrink |
VisualElement |
float | initial |
flex-shrink: 1; |
flex-wrap |
VisualElement |
nowrap | wrap | reverse | wrap-reverse | initial |
flex-wrap: wrap-reverse; |
font-family |
Button, DatePicker, Editor, Entry, Label, Picker, SearchBar, TimePicker, Span |
string | initial |
font-family: Consolas; |
font-size |
Button, DatePicker, Editor, Entry, Label, Picker, SearchBar, TimePicker, Span |
double | namedsize | initial |
font-size: 12; |
font-style |
Button, DatePicker, Editor, Entry, Label, Picker, SearchBar, TimePicker, Span |
bold | italic | initial |
font-style: bold; |
height |
VisualElement |
double | initial |
min-height: 250; |
justify-content |
FlexLayout |
start | center | end | spacebetween | spacearound | spaceevenly | flex-start | flex-end | space-between | space-around | initial |
justify-content: flex-end; |
letter-spacing |
Button, DatePicker, Editor, Entry, Label, Picker, SearchBar, SearchHandler, Span, TimePicker |
double | initial |
letter-spacing: 2.5; |
line-height |
Label, Span |
double | initial |
line-height: 1.8; |
margin |
View |
thickness | initial |
margin: 6 12; |
margin-left |
View |
thickness | initial |
margin-left: 3; |
margin-top |
View |
thickness | initial |
margin-top: 2; |
margin-right |
View |
thickness | initial |
margin-right: 1; |
margin-bottom |
View |
thickness | initial |
margin-bottom: 6; |
max-lines |
Label |
int | initial |
max-lines: 2; |
min-height |
VisualElement |
double | initial |
min-height: 50; |
min-width |
VisualElement |
double | initial |
min-width: 112; |
opacity |
VisualElement |
double | initial |
opacity: .3; |
order |
VisualElement |
int | initial |
order: -1; |
padding |
Button, ImageButton, Layout, Page |
thickness | initial |
padding: 6 12 12; |
padding-left |
Button, ImageButton, Layout, Page |
double | initial |
padding-left: 3; |
padding-top |
Button, ImageButton, Layout, Page |
double | initial |
padding-top: 4; |
padding-right |
Button, ImageButton, Layout, Page |
double | initial |
padding-right: 2; |
padding-bottom |
Button, ImageButton, Layout, Page |
double | initial |
padding-bottom: 6; |
position |
FlexLayout |
relative | absolute | initial |
position: absolute; |
row-gap |
Grid |
double | initial |
row-gap: 12; |
text-align |
Entry, EntryCell, Label, SearchBar |
left | top | right | bottom | start | center | middle | end | initial. left and right should be avoided in right-to-left environments. |
text-align: right; |
text-decoration |
Label, Span |
none | underline | strikethrough | line-through | initial |
text-decoration: underline, line-through; |
text-transform |
Button,Editor, Entry, Label, SearchBar, SearchHandler |
none | default | uppercase | lowercase | initial |
text-transform: uppercase; |
transform |
VisualElement |
none, rotate, rotateX, rotateY, scale, scaleX, scaleY, translate, translateX, translateY, initial |
transform: rotate(180), scaleX(2.5); |
transform-origin |
VisualElement |
double, double | initial |
transform-origin: 7.5, 12.5; |
vertical-align |
Label |
left | top | right | bottom | start | center | middle | end | initial |
vertical-align: bottom; |
visibility |
VisualElement |
true | visible | false | hidden | collapse | initial |
visibility: hidden; |
width |
VisualElement |
double | initial |
min-width: 320; |
Note
initial is a valid value for all properties. It clears the value (resets to default) that was set from another style.
The following properties are currently unsupported:
all: initial.- Layout properties (box, or grid).
- Shorthand properties, such as
font, andborder.
In addition, there's no inherit value and so inheritance isn't supported. Therefore you can't, for example, set the font-size property on a layout and expect all the Label instances in the layout to inherit the value. The one exception is the direction property, which has a default value of inherit.
Targeting Span elements has a known issue preventing spans from being the target of CSS styles by both element and name (using the # symbol). The Span element derives from GestureElement, which does not have the StyleClass property so spans do not support CSS class targeting. For more information, see Not able to apply CSS styling to Span control.
Xamarin.Forms specific properties
The following Xamarin.Forms specific CSS properties are also supported (in the Values column, types are italic, while string literals are gray):
| Property | Applies to | Values | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
-xf-bar-background-color |
NavigationPage, TabbedPage |
color | initial |
-xf-bar-background-color: teal; |
-xf-bar-text-color |
NavigationPage, TabbedPage |
color | initial |
-xf-bar-text-color: gray |
-xf-horizontal-scroll-bar-visibility |
ScrollView |
default | always | never | initial |
-xf-horizontal-scroll-bar-visibility: never; |
-xf-max-length |
Entry, Editor, SearchBar |
int | initial |
-xf-max-length: 20; |
-xf-max-track-color |
Slider |
color | initial |
-xf-max-track-color: red; |
-xf-min-track-color |
Slider |
color | initial |
-xf-min-track-color: yellow; |
-xf-orientation |
ScrollView, StackLayout |
horizontal | vertical | both | initial. both is only supported on a ScrollView. |
-xf-orientation: horizontal; |
-xf-placeholder |
Entry, Editor, SearchBar |
quoted text | initial |
-xf-placeholder: Enter name; |
-xf-placeholder-color |
Entry, Editor, SearchBar |
color | initial |
-xf-placeholder-color: green; |
-xf-spacing |
StackLayout |
double | initial |
-xf-spacing: 8; |
-xf-thumb-color |
Slider, Switch |
color | initial |
-xf-thumb-color: limegreen; |
-xf-vertical-scroll-bar-visibility |
ScrollView |
default | always | never | initial |
-xf-vertical-scroll-bar-visibility: always; |
-xf-vertical-text-alignment |
Label |
start | center | end | initial |
-xf-vertical-text-alignment: end; |
-xf-visual |
VisualElement |
string | initial |
-xf-visual: material; |
Xamarin.Forms Shell specific properties
The following Xamarin.Forms Shell specific CSS properties are also supported (in the Values column, types are italic, while string literals are gray):
| Property | Applies to | Values | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
-xf-flyout-background |
Shell |
color | initial |
-xf-flyout-background: red; |
-xf-shell-background |
Element |
color | initial |
-xf-shell-background: green; |
-xf-shell-disabled |
Element |
color | initial |
-xf-shell-disabled: blue; |
-xf-shell-foreground |
Element |
color | initial |
-xf-shell-foreground: yellow; |
-xf-shell-tabbar-background |
Element |
color | initial |
-xf-shell-tabbar-background: white; |
-xf-shell-tabbar-disabled |
Element |
color | initial |
-xf-shell-tabbar-disabled: black; |
-xf-shell-tabbar-foreground |
Element |
color | initial |
-xf-shell-tabbar-foreground: gray; |
-xf-shell-tabbar-title |
Element |
color | initial |
-xf-shell-tabbar-title: lightgray; |
-xf-shell-tabbar-unselected |
Element |
color | initial |
-xf-shell-tabbar-unselected: cyan; |
-xf-shell-title |
Element |
color | initial |
-xf-shell-title: teal; |
-xf-shell-unselected |
Element |
color | initial |
-xf-shell-unselected: limegreen; |
Color
The following color values are supported:
X11colors, which match CSS colors, UWP pre-defined colors, and Xamarin.Forms colors. Note that these color values are case insensitive.- hex colors:
#rgb,#argb,#rrggbb,#aarrggbb - rgb colors:
rgb(255,0,0),rgb(100%,0%,0%). Values are in the range 0-255, or 0%-100%. - rgba colors:
rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.8),rgba(100%, 0%, 0%, 0.8). The opacity value is in the range 0.0-1.0. - hsl colors:
hsl(120, 100%, 50%). The h value is in the range 0-360, while s and l are in the range 0%-100%. - hsla colors:
hsla(120, 100%, 50%, .8). The opacity value is in the range 0.0-1.0.
Thickness
One, two, three, or four thickness values are supported, each separated by white space:
- A single value indicates uniform thickness.
- Two values indicate vertical then horizontal thickness.
- Three values indicate top, then horizontal (left and right), then bottom thickness.
- Four values indicate top, then right, then bottom, then left thickness.
Note
CSS thickness values differ from XAML Thickness values. For example, in XAML a two-value Thickness indicates horizontal then vertical thickness, while a four-value Thickness indicates left, then top, then right, then bottom thickness. In addition, XAML Thickness values are comma delimited.
NamedSize
The following case insensitive namedsize values are supported:
defaultmicrosmallmediumlarge
The exact meaning of each namedsize value is platform-dependent and view-dependent.
Functions
Linear and radial gradients can be specified using the linear-gradient() and radial-gradient() CSS functions, respectively. The result of these functions should be assigned to the background property of a control.
CSS in Xamarin.Forms with Xamarin.University
Xamarin.Forms 3.0 CSS video