Hierarchy model in Azure Data Manager for Agriculture
Note
Microsoft Azure Data Manager for Agriculture is currently in preview. For legal terms that apply to features that are in beta, in preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
Microsoft Azure Data Manager for Agriculture requires registration and is available to only approved customers and partners during the preview period. To request access to Microsoft Data Manager for Agriculture during the preview period, use this form.
To generate actionable insights, data related to growers, farms, and fields should be organized in a well-defined way. Firms that operate in the agriculture industry often perform longitudinal studies and need high-quality data to generate insights. Azure Data Manager for Agriculture organizes agronomic data in the following hierarchy.
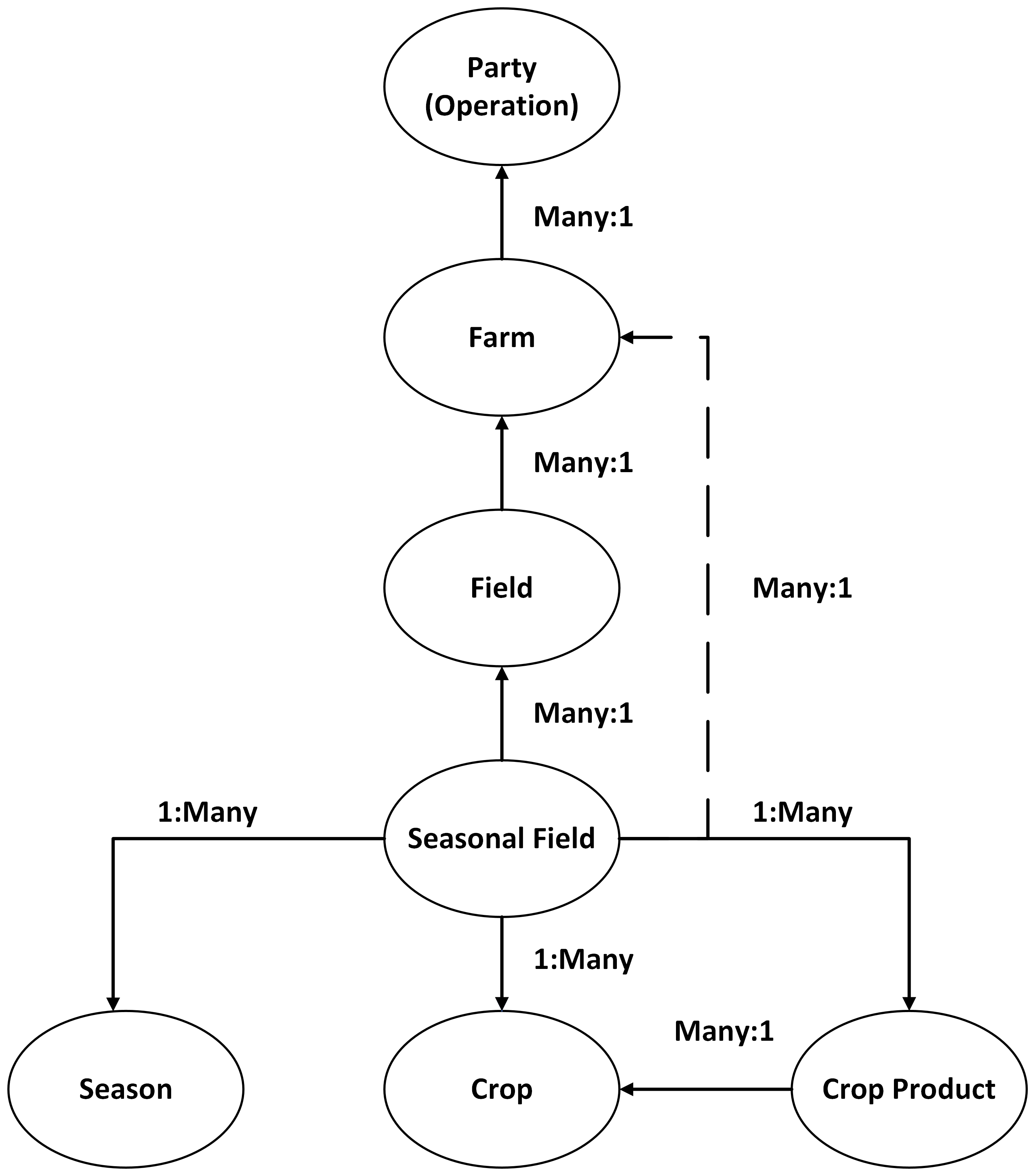

Farm hierarchy
Party
A party is the owner and custodian of any data related to a farm. You can think of a party as the legal entity that runs the business.
The customer who sets up Azure Data Manager for Agriculture defines the party entity.
Farm
Farms are logical entities. A farm is a collection of fields.
Farms don't have any geometry associated with them. A farm entity helps you organize your growing operations. For example, Contoso Ltd. is the party that has farms in Oregon and Idaho.
Field
Fields denote a stable geometry that's generally agnostic to seasons and other temporal constructs. For example, a field could be the geometry denoted in government records.
Fields are multipolygons. For example, a road might divide the farm into two or more parts.
Seasonal field
A seasonal field is the most important construct in the farming world. A seasonal field's definition includes:
- Geometry
- Season
- Crop
A seasonal field is:
- Associated with a field or a farm.
- A monocrop entity in Azure Data Manager for Agriculture. If farmers cultivate multiple crops simultaneously, they have to create one seasonal field per crop.
- Associated with one season. If farmers cultivate across multiple seasons, they have to create one seasonal field per season.
- A multipolygon. The same crop can be planted in various areas within the farm.
Season
The season represents the temporal aspect of farming. It's a function of local agronomic practices, procedures, and weather.
Crop
A crop entity provides the phenotypic details of the planted crop.
Crop product
A crop product is the commercial variety (brand and product) of the planted seeds. A seasonal field can contain information about varieties of seeds planted in the same crop.