Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:
Power BI Desktop
Power BI service
Metrics in Power BI let customers curate their goals and track them against key business objectives. When choosing values for your goals, you have the choice to:
- Manually enter the current and target values.
- Connect either the current or target value to data in an existing Power BI report.
- Connect both values to data in an existing Power BI report.
This article is about connecting the values to data in an existing Power BI report. Connected values change whenever the underlying data is updated. To learn about creating manual values, see Create a manual goal in the article Create scorecards and manual goals.
Connect values to data
You can connect either the current or the target value, or both, to a value in a report.
Create a goal or edit an existing goal in a scorecard.
In the Current or Target field, select Connect to data.
In the dialog, search for the report with the data that you want to track, select it > Next.
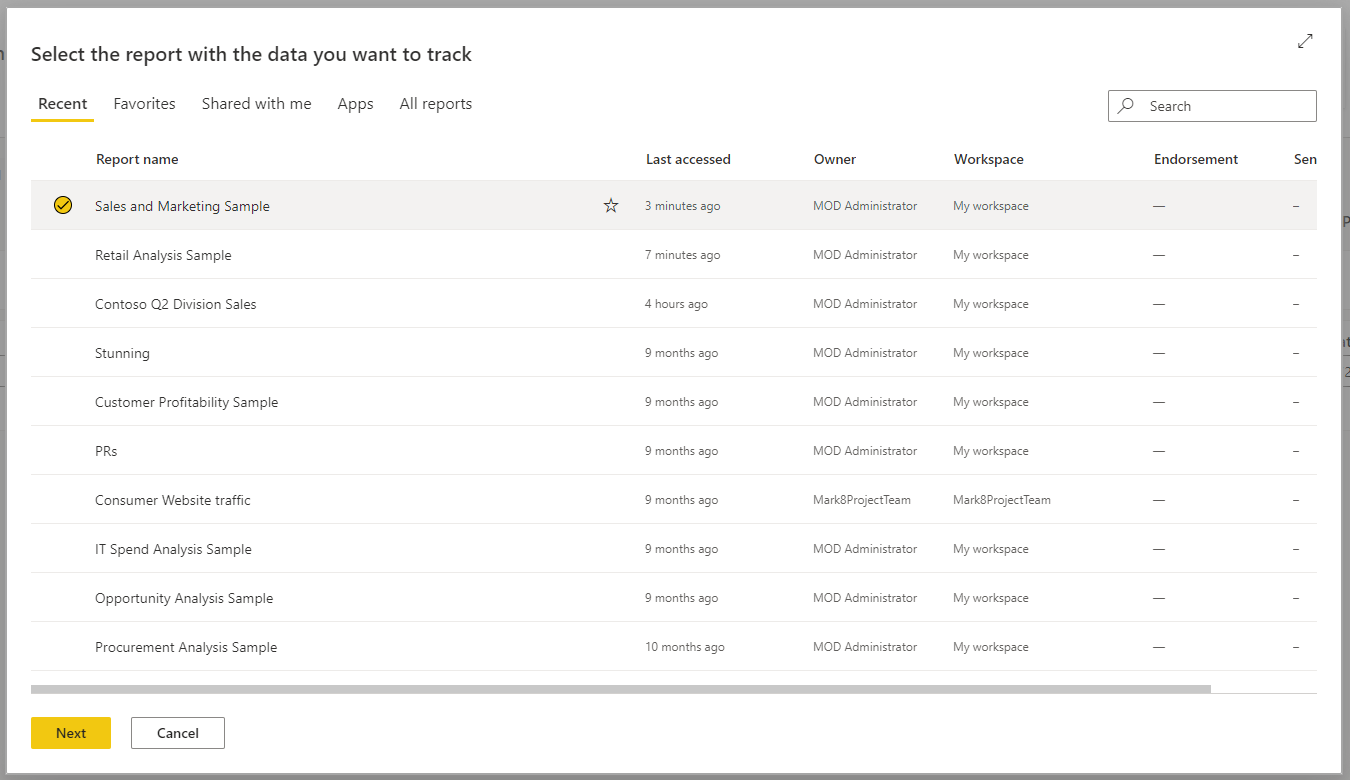
This list contains all the reports that you have access to, across all workspaces, in Power BI.
In the report that you selected, navigate to the visual that contains the data you want to track.
Select the data point or visual. Power BI displays the measure card, summarizing all the filters applied to the selection.
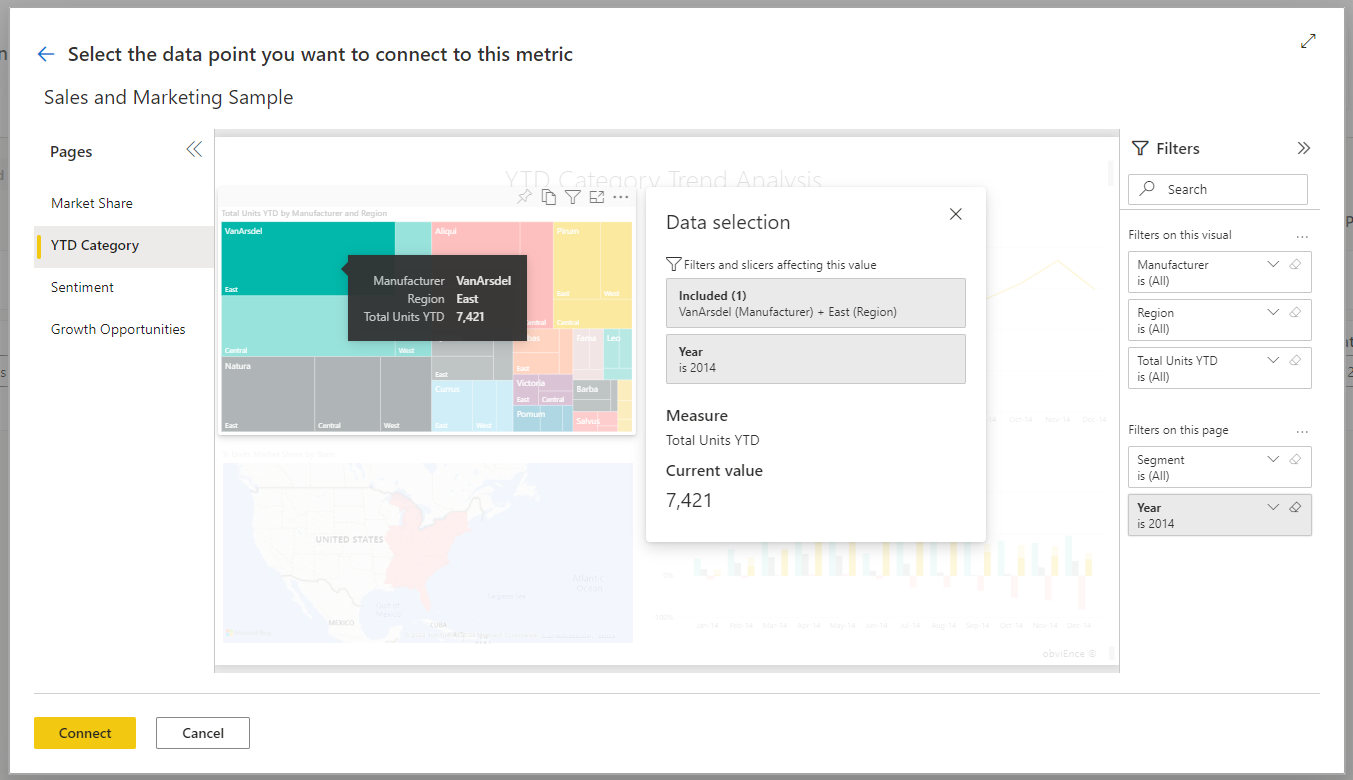
Currently there are some limitations on the values you can select. See the Considerations and limitations section in this article for details.
Select Connect.
Power BI automatically represents values in numeric notation. For example, 2044 is represented as 2 K.
Select Save.
Choose measures for connected goals
The Connect to data experience makes it easy for scorecard authors to automate goals. You can select and calculate measures at the following levels:
- Visual
- Legend
- Data point
- Axis value
To break this down further, there are two main types of cases for connecting to data in goals and subgoals:
- Categorical data
- Time-series data
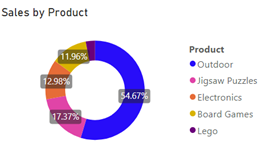
Categorical data
Categorical data refers to cases where you are connecting a goal or subgoal to data other than time-series data. For example, connecting to the total sales of the Outdoor product category:
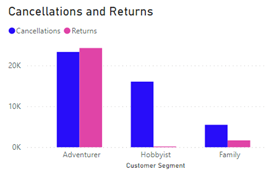
Or connecting to the total number of results in the Family customer segment:
In these cases, depending on what you select, Power BI calculates the measures as follows:
- Visual – measure is calculated at the aggregate level.
- Legend – measure is filtered to the selected legend.
- Data point – measure is filtered to the selected data point.
- Axis value – measure is filtered to the category selected in the axis.
Time-series data
The time series refers to cases where you have a Date/Time field in the axis. In these cases, Power BI calculates the measures as follows:
- Visual – measure is calculated at the last data point in time series and history is pulled in.
- Legend – measure is calculated at the last data point in time series and history is pulled in.
- Data point – measure is calculated at the last data point in time series and history is pulled in.
- Axis value – measure is calculated at the last data point in time series and history is pulled in.
Considerations and limitations
The following list describes the current limitations on the values you can choose in a visual:
- In a 100% stacked bar or column chart, Power BI will pull in the measure value rather than the percentage.
- In a multi-row card, Power BI will pull in the first measure in the card.
- Multi-Geo is currently not supported.
- In gauges and KPI tiles, Power BI will pull in the value, but not the target, or the min or max value in the gauge.
- In a table with more than one column of measures, Power BI selects the first measure in the row.
- Connected goal values will not automatically update when connected to data from a datamart using DQ/Live connection.
Related content
- Get started with goals in Power BI
- Create scorecards and manual goals in Power BI
- Stay on top of your goals in Power BI
More questions? Try the Power BI Community.