Nota:
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar iniciar sesión o cambiar directorios.
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar cambiar los directorios.
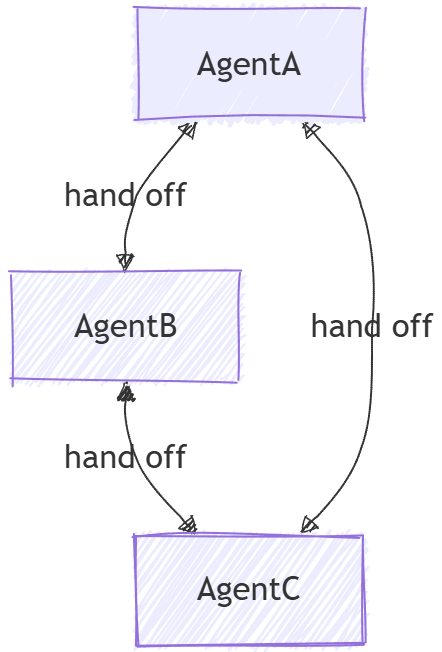
La orquestación de entrega permite a los agentes transferir el control entre sí en función del contexto o la solicitud del usuario. Cada agente puede "entregar" la conversación a otro agente con la experiencia adecuada, asegurándose de que el agente adecuado controla cada parte de la tarea. Esto es especialmente útil en el soporte al cliente, sistemas expertos o cualquier escenario que requiera delegación dinámica.
Diferencias entre transferencia y agentes como herramientas
Aunque el uso de agentes como herramientas suele considerarse un patrón multiagente y puede parecer similar al traspaso a primera vista, hay diferencias fundamentales entre ambos:
- Flujo de control: en la orquestación de transferencia, el control se pasa explícitamente entre agentes según las reglas definidas. Cada agente puede decidir entregar toda la tarea a otro agente. No hay ninguna autoridad central que administre el flujo de trabajo. En cambio, agent-as-tools implica un agente principal que delega las subtareas a otros agentes y una vez que el agente completa la subtarea, el control vuelve al agente principal.
- Propiedad de la tarea: durante la transferencia, el agente que recibe la transferencia toma completa propiedad de la tarea. En el concepto de "agentes-como-herramientas", el agente principal conserva la responsabilidad general de la tarea, y otros agentes se manejan como herramientas para asistir en tareas específicas.
- Administración de contextos: en la orquestación de entrega, la conversación se entrega a otro agente por completo. El agente receptor tiene todo el contexto de lo que se ha hecho hasta ahora. En agent-as-tools, el agente principal administra el contexto general y puede proporcionar solo información relevante a los agentes de herramientas según sea necesario.
Temas que se abordarán
- Cómo crear agentes especializados para distintos dominios
- Configuración de reglas de entrega entre agentes
- Creación de flujos de trabajo interactivos con enrutamiento dinámico de agentes
- Cómo gestionar conversaciones de múltiples turnos con cambio de agente
- Cómo implementar la aprobación de herramientas para operaciones confidenciales (HITL)
- Uso de puntos de control para flujos de trabajo de entrega duraderos
En la orquestación de traspaso, los agentes pueden transferir el control entre sí según el contexto, lo que permite un enrutamiento dinámico y la gestión de experiencia especializada.
Configuración del cliente de Azure OpenAI
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;
using Azure.Identity;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI.Workflows;
using Microsoft.Extensions.AI;
using Microsoft.Agents.AI;
// 1) Set up the Azure OpenAI client
var endpoint = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT") ??
throw new InvalidOperationException("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT is not set.");
var deploymentName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("AZURE_OPENAI_DEPLOYMENT_NAME") ?? "gpt-4o-mini";
var client = new AzureOpenAIClient(new Uri(endpoint), new AzureCliCredential())
.GetChatClient(deploymentName)
.AsIChatClient();
Definir los agentes especializados
Cree agentes específicos del dominio y un agente de evaluación de prioridades para el enrutamiento:
// 2) Create specialized agents
ChatClientAgent historyTutor = new(client,
"You provide assistance with historical queries. Explain important events and context clearly. Only respond about history.",
"history_tutor",
"Specialist agent for historical questions");
ChatClientAgent mathTutor = new(client,
"You provide help with math problems. Explain your reasoning at each step and include examples. Only respond about math.",
"math_tutor",
"Specialist agent for math questions");
ChatClientAgent triageAgent = new(client,
"You determine which agent to use based on the user's homework question. ALWAYS handoff to another agent.",
"triage_agent",
"Routes messages to the appropriate specialist agent");
Configurar reglas de entrega
Defina qué agentes pueden entregar a qué otros agentes:
// 3) Build handoff workflow with routing rules
var workflow = AgentWorkflowBuilder.StartHandoffWith(triageAgent)
.WithHandoffs(triageAgent, [mathTutor, historyTutor]) // Triage can route to either specialist
.WithHandoff(mathTutor, triageAgent) // Math tutor can return to triage
.WithHandoff(historyTutor, triageAgent) // History tutor can return to triage
.Build();
Ejecutar flujo de trabajo de entrega interactivo
Gestione conversaciones de múltiples turnos con el cambio dinámico de agente.
// 4) Process multi-turn conversations
List<ChatMessage> messages = new();
while (true)
{
Console.Write("Q: ");
string userInput = Console.ReadLine()!;
messages.Add(new(ChatRole.User, userInput));
// Execute workflow and process events
StreamingRun run = await InProcessExecution.StreamAsync(workflow, messages);
await run.TrySendMessageAsync(new TurnToken(emitEvents: true));
List<ChatMessage> newMessages = new();
await foreach (WorkflowEvent evt in run.WatchStreamAsync().ConfigureAwait(false))
{
if (evt is AgentRunUpdateEvent e)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{e.ExecutorId}: {e.Data}");
}
else if (evt is WorkflowOutputEvent outputEvt)
{
newMessages = (List<ChatMessage>)outputEvt.Data!;
break;
}
}
// Add new messages to conversation history
messages.AddRange(newMessages.Skip(messages.Count));
}
Interacción de ejemplo
Q: What is the derivative of x^2?
triage_agent: This is a math question. I'll hand this off to the math tutor.
math_tutor: The derivative of x^2 is 2x. Using the power rule, we bring down the exponent (2) and multiply it by the coefficient (1), then reduce the exponent by 1: d/dx(x^2) = 2x^(2-1) = 2x.
Q: Tell me about World War 2
triage_agent: This is a history question. I'll hand this off to the history tutor.
history_tutor: World War 2 was a global conflict from 1939 to 1945. It began when Germany invaded Poland and involved most of the world's nations. Key events included the Holocaust, Pearl Harbor attack, D-Day invasion, and ended with atomic bombs on Japan.
Q: Can you help me with calculus integration?
triage_agent: This is another math question. I'll route this to the math tutor.
math_tutor: I'd be happy to help with calculus integration! Integration is the reverse of differentiation. The basic power rule for integration is: ∫x^n dx = x^(n+1)/(n+1) + C, where C is the constant of integration.
Configurar el cliente de chat
from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIChatClient
from azure.identity import AzureCliCredential
# Initialize the Azure OpenAI chat client
chat_client = AzureOpenAIChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential())
Definir los agentes especializados
Cree agentes específicos del dominio con un coordinador para el enrutamiento:
# Create triage/coordinator agent
triage_agent = chat_client.create_agent(
instructions=(
"You are frontline support triage. Read the latest user message and decide whether "
"to hand off to refund_agent, order_agent, or support_agent. Provide a brief natural-language "
"response for the user. When delegation is required, call the matching handoff tool "
"(`handoff_to_refund_agent`, `handoff_to_order_agent`, or `handoff_to_support_agent`)."
),
name="triage_agent",
)
# Create specialist agents
refund_agent = chat_client.create_agent(
instructions=(
"You handle refund workflows. Ask for any order identifiers you require and outline the refund steps."
),
name="refund_agent",
)
order_agent = chat_client.create_agent(
instructions=(
"You resolve shipping and fulfillment issues. Clarify the delivery problem and describe the actions "
"you will take to remedy it."
),
name="order_agent",
)
support_agent = chat_client.create_agent(
instructions=(
"You are a general support agent. Offer empathetic troubleshooting and gather missing details if the "
"issue does not match other specialists."
),
name="support_agent",
)
Configurar reglas de entrega
Compile el flujo de trabajo de entrega mediante HandoffBuilder:
from agent_framework import HandoffBuilder
# Build the handoff workflow
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="customer_support_handoff",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent, support_agent],
)
.set_coordinator("triage_agent")
.with_termination_condition(
# Terminate after a certain number of user messages
lambda conv: sum(1 for msg in conv if msg.role.value == "user") >= 10
)
.build()
)
Para un enrutamiento más avanzado, puede configurar entregas especializadas a especialistas:
# Enable return-to-previous and add specialist-to-specialist handoffs
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="advanced_handoff",
participants=[coordinator, technical, account, billing],
)
.set_coordinator(coordinator)
.add_handoff(coordinator, [technical, account, billing]) # Coordinator routes to all specialists
.add_handoff(technical, [billing, account]) # Technical can route to billing or account
.add_handoff(account, [technical, billing]) # Account can route to technical or billing
.add_handoff(billing, [technical, account]) # Billing can route to technical or account
.enable_return_to_previous(True) # User inputs route directly to current specialist
.build()
)
Ejecutar flujo de trabajo de entrega interactivo
Gestione conversaciones de múltiples turnos con solicitudes de entrada de usuario:
from agent_framework import RequestInfoEvent, HandoffUserInputRequest, WorkflowOutputEvent
# Start workflow with initial user message
events = [event async for event in workflow.run_stream("I need help with my order")]
# Process events and collect pending input requests
pending_requests = []
for event in events:
if isinstance(event, RequestInfoEvent):
pending_requests.append(event)
request_data = event.data
print(f"Agent {request_data.awaiting_agent_id} is awaiting your input")
for msg in request_data.conversation[-3:]:
print(f"{msg.author_name}: {msg.text}")
# Interactive loop: respond to requests
while pending_requests:
user_input = input("You: ")
# Send responses to all pending requests
responses = {req.request_id: user_input for req in pending_requests}
events = [event async for event in workflow.send_responses_streaming(responses)]
# Process new events
pending_requests = []
for event in events:
if isinstance(event, RequestInfoEvent):
pending_requests.append(event)
elif isinstance(event, WorkflowOutputEvent):
print("Workflow completed!")
conversation = event.data
for msg in conversation:
print(f"{msg.author_name}: {msg.text}")
Avanzado: Aprobación de herramientas en flujos de trabajo de entrega
Los flujos de trabajo de transferencia pueden incluir agentes con herramientas que requieren aprobación humana antes de su ejecución. Esto resulta útil para operaciones confidenciales, como el procesamiento de reembolsos, la realización de compras o la ejecución de acciones irreversibles.
Definición de herramientas con aprobación requerida
from typing import Annotated
from agent_framework import ai_function
@ai_function(approval_mode="always_require")
def submit_refund(
refund_description: Annotated[str, "Description of the refund reason"],
amount: Annotated[str, "Refund amount"],
order_id: Annotated[str, "Order ID for the refund"],
) -> str:
"""Submit a refund request for manual review before processing."""
return f"Refund recorded for order {order_id} (amount: {amount}): {refund_description}"
Crear agentes con herramientas que requieren aprobación
from agent_framework import ChatAgent
from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIChatClient
from azure.identity import AzureCliCredential
client = AzureOpenAIChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential())
triage_agent = client.create_agent(
name="triage_agent",
instructions=(
"You are a customer service triage agent. Listen to customer issues and determine "
"if they need refund help or order tracking. Use handoff_to_refund_agent or "
"handoff_to_order_agent to transfer them."
),
)
refund_agent = client.create_agent(
name="refund_agent",
instructions=(
"You are a refund specialist. Help customers with refund requests. "
"When the user confirms they want a refund and supplies order details, "
"call submit_refund to record the request."
),
tools=[submit_refund],
)
order_agent = client.create_agent(
name="order_agent",
instructions="You are an order tracking specialist. Help customers track their orders.",
)
Gestionar tanto las solicitudes de input de usuario como las solicitudes de aprobación de herramientas
from agent_framework import (
FunctionApprovalRequestContent,
HandoffBuilder,
HandoffUserInputRequest,
RequestInfoEvent,
WorkflowOutputEvent,
)
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="support_with_approvals",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent],
)
.set_coordinator("triage_agent")
.build()
)
pending_requests: list[RequestInfoEvent] = []
# Start workflow
async for event in workflow.run_stream("My order 12345 arrived damaged. I need a refund."):
if isinstance(event, RequestInfoEvent):
pending_requests.append(event)
# Process pending requests - could be user input OR tool approval
while pending_requests:
responses: dict[str, object] = {}
for request in pending_requests:
if isinstance(request.data, HandoffUserInputRequest):
# Agent needs user input
print(f"Agent {request.data.awaiting_agent_id} asks:")
for msg in request.data.conversation[-2:]:
print(f" {msg.author_name}: {msg.text}")
user_input = input("You: ")
responses[request.request_id] = user_input
elif isinstance(request.data, FunctionApprovalRequestContent):
# Agent wants to call a tool that requires approval
func_call = request.data.function_call
args = func_call.parse_arguments() or {}
print(f"\nTool approval requested: {func_call.name}")
print(f"Arguments: {args}")
approval = input("Approve? (y/n): ").strip().lower() == "y"
responses[request.request_id] = request.data.create_response(approved=approval)
# Send all responses and collect new requests
pending_requests = []
async for event in workflow.send_responses_streaming(responses):
if isinstance(event, RequestInfoEvent):
pending_requests.append(event)
elif isinstance(event, WorkflowOutputEvent):
print("\nWorkflow completed!")
Con puntos de control para flujos de trabajo duraderos
Para los flujos de trabajo de ejecución prolongada en los que las aprobaciones de herramientas puedan ocurrir horas o días después, utilice el checkpoint:
from agent_framework import FileCheckpointStorage
storage = FileCheckpointStorage(storage_path="./checkpoints")
workflow = (
HandoffBuilder(
name="durable_support",
participants=[triage_agent, refund_agent, order_agent],
)
.set_coordinator("triage_agent")
.with_checkpointing(storage)
.build()
)
# Initial run - workflow pauses when approval is needed
pending_requests = []
async for event in workflow.run_stream("I need a refund for order 12345"):
if isinstance(event, RequestInfoEvent):
pending_requests.append(event)
# Process can exit here - checkpoint is saved automatically
# Later: Resume from checkpoint and provide approval
checkpoints = await storage.list_checkpoints()
latest = sorted(checkpoints, key=lambda c: c.timestamp, reverse=True)[0]
# Step 1: Restore checkpoint to reload pending requests
restored_requests = []
async for event in workflow.run_stream(checkpoint_id=latest.checkpoint_id):
if isinstance(event, RequestInfoEvent):
restored_requests.append(event)
# Step 2: Send responses
responses = {}
for req in restored_requests:
if isinstance(req.data, FunctionApprovalRequestContent):
responses[req.request_id] = req.data.create_response(approved=True)
elif isinstance(req.data, HandoffUserInputRequest):
responses[req.request_id] = "Yes, please process the refund."
async for event in workflow.send_responses_streaming(responses):
if isinstance(event, WorkflowOutputEvent):
print("Refund workflow completed!")
## Sample Interaction
```plaintext
User: I need help with my order
triage_agent: I'd be happy to help you with your order. Could you please provide more details about the issue?
User: My order 1234 arrived damaged
triage_agent: I'm sorry to hear that your order arrived damaged. I will connect you with a specialist.
support_agent: I'm sorry about the damaged order. To assist you better, could you please:
- Describe the damage
- Would you prefer a replacement or refund?
User: I'd like a refund
triage_agent: I'll connect you with the refund specialist.
refund_agent: I'll process your refund for order 1234. Here's what will happen next:
1. Verification of the damaged items
2. Refund request submission
3. Return instructions if needed
4. Refund processing within 5-10 business days
Could you provide photos of the damage to expedite the process?
Conceptos clave
- Enrutamiento dinámico: los agentes pueden decidir qué agente debe controlar la siguiente interacción en función del contexto.
- AgentWorkflowBuilder.StartHandoffWith(): define el agente inicial que inicia el flujo de trabajo.
- WithHandoff() y WithHandoffs():configura reglas de entrega entre agentes específicos
- Conservación del contexto: se mantiene el historial de conversaciones completo en todas las transferencias
- Compatibilidad con varios turnos: admite conversaciones en curso con cambio de agente sin problemas
- Experiencia especializada: Cada agente se centra en su dominio mientras colabora a través de transiciones
- Enrutamiento dinámico: los agentes pueden decidir qué agente debe controlar la siguiente interacción en función del contexto.
- HandoffBuilder: crea flujos de trabajo con registro automático de herramientas de entrega
- set_coordinator(): define qué agente recibe primero la entrada del usuario.
- add_handoff(): configura relaciones de entrega específicas entre agentes
- enable_return_to_previous():enruta las entradas de usuario directamente al especialista actual, omitiendo la reevaluación del coordinador.
- Conservación del contexto: se mantiene el historial de conversaciones completo en todas las transferencias
- Ciclo de solicitud y respuesta: el flujo de trabajo solicita la entrada del usuario, procesa las respuestas y continúa hasta que se cumpla la condición de terminación.
-
Aprobación de herramientas: uso
@ai_function(approval_mode="always_require")para operaciones confidenciales que necesitan aprobación humana -
FunctionApprovalRequestContent: emitido cuando un agente llama a una herramienta que requiere aprobación; usar
create_response(approved=...)para responder -
Checkpointing: Utilice
with_checkpointing()para flujos de trabajo duraderos que pueden pausarse y reanudarse tras reinicios del proceso. - Experiencia especializada: Cada agente se centra en su dominio mientras colabora a través de transiciones