Nota
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar iniciar sesión o cambiar directorios.
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar cambiar los directorios.
El SDK de Voz de servicios de Azure AI tiene una característica integrada para proporcionar reconocimiento de intenciones con coincidencia de patrones de idioma simples. Una intención es algo que el usuario quiere hacer: cerrar una ventana, marcar una casilla, insertar texto, etc.
En esta guía, se usará el SDK de Voz para desarrollar una aplicación de consola que derive intenciones de las expresiones de voz que se pronuncian a través del micrófono del dispositivo. Aprenderá a:
- Crear un proyecto de Visual Studio que haga referencia al paquete NuGet del SDK de Voz
- Crear una configuración de voz y obtener un reconocedor de intenciones
- Agregar intenciones y patrones a través de la API del SDK de Voz
- Agregar entidades personalizadas a través de la API del SDK de Voz
- Usar el reconocimiento asincrónico, continuo y controlado por eventos
Cuándo usar la coincidencia de patrones
Usar coincidencia de patrones si:
- Solo le interesa la coincidencia estricta de lo que ha dicho el usuario. Estos patrones coinciden de forma más agresiva que el reconocimiento del lenguaje conversacional (CLU).
- No tiene acceso a un modelo CLU, pero aun así desea usar las intenciones.
Para obtener más información, consulte la introducción a la coincidencia de patrones.
Requisitos previos
Asegúrese de disponer de los siguientes elementos antes de empezar esta guía:
- Un recurso de Azure AI Foundry o un recurso de voz unificada
- Visual Studio 2019 (cualquier edición).
Crear un proyecto
Cree un nuevo proyecto de aplicación de consola de C# en Visual Studio 2019 e instale el SDK de Voz.
Inicio con código reutilizable
Vamos abrir Program.cs y agregar código que funcione como el esqueleto del proyecto.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech;
using Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech.Intent;
namespace helloworld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IntentPatternMatchingWithMicrophoneAsync().Wait();
}
private static async Task IntentPatternMatchingWithMicrophoneAsync()
{
var config = SpeechConfig.FromSubscription("YourSpeechResourceKey", "YourSpeechResourceRegion");
}
}
}
Creación de una configuración de Voz
Para poder inicializar un objeto IntentRecognizer, es preciso crear una configuración que use la clave y la recurso para el recurso de predicción de servicios de Azure AI.
- Reemplace
"YourSpeechResourceKey"por la clave de predicción de servicios de Azure AI. - Reemplace
"YourSpeechResourceRegion"por la región de recursos de Azure AI Foundry.
En este ejemplo se usa el método FromSubscription() para compilar la clase SpeechConfig. Para ver una lista completa de los métodos disponibles, consulte Clase SpeechConfig.
Inicialización de IntentRecognizer
Ahora cree un objeto IntentRecognizer. Inserte este código justo debajo de la configuración de Voz.
using (var recognizer = new IntentRecognizer(config))
{
}
Adición de algunas intenciones
Debe asociar algunos patrones con PatternMatchingModel y aplicarlos a IntentRecognizer.
Empezaremos creando un PatternMatchingModel y le agregaremos algunas intenciones.
Nota:
Se pueden agregar varios patrones a PatternMatchingIntent.
Inserte este código dentro del bloque using:
// Creates a Pattern Matching model and adds specific intents from your model. The
// Id is used to identify this model from others in the collection.
var model = new PatternMatchingModel("YourPatternMatchingModelId");
// Creates a pattern that uses groups of optional words. "[Go | Take me]" will match either "Go", "Take me", or "".
var patternWithOptionalWords = "[Go | Take me] to [floor|level] {floorName}";
// Creates a pattern that uses an optional entity and group that could be used to tie commands together.
var patternWithOptionalEntity = "Go to parking [{parkingLevel}]";
// You can also have multiple entities of the same name in a single pattern by adding appending a unique identifier
// to distinguish between the instances. For example:
var patternWithTwoOfTheSameEntity = "Go to floor {floorName:1} [and then go to floor {floorName:2}]";
// NOTE: Both floorName:1 and floorName:2 are tied to the same list of entries. The identifier can be a string
// and is separated from the entity name by a ':'
// Creates the pattern matching intents and adds them to the model
model.Intents.Add(new PatternMatchingIntent("ChangeFloors", patternWithOptionalWords, patternWithOptionalEntity, patternWithTwoOfTheSameEntity));
model.Intents.Add(new PatternMatchingIntent("DoorControl", "{action} the doors", "{action} doors", "{action} the door", "{action} door"));
Adición de algunas entidades personalizadas
Para aprovechar al máximo el coincidencia de patrones, es posible personalizar las entidades. Convertiremos "floorName" en una lista de las plantas disponibles. También convertiremos "parkingLevel" en una entidad de entero.
Inserte este código debajo de las intenciones:
// Creates the "floorName" entity and set it to type list.
// Adds acceptable values. NOTE the default entity type is Any and so we do not need
// to declare the "action" entity.
model.Entities.Add(PatternMatchingEntity.CreateListEntity("floorName", EntityMatchMode.Strict, "ground floor", "lobby", "1st", "first", "one", "1", "2nd", "second", "two", "2"));
// Creates the "parkingLevel" entity as a pre-built integer
model.Entities.Add(PatternMatchingEntity.CreateIntegerEntity("parkingLevel"));
Aplicación del modelo al reconocedor
Ahora es necesario aplicar el modelo a IntentRecognizer. Es posible usar varios modelos a la vez para que la API tome una colección de modelos.
Inserte este código debajo de las entidades:
var modelCollection = new LanguageUnderstandingModelCollection();
modelCollection.Add(model);
recognizer.ApplyLanguageModels(modelCollection);
Reconocimiento de una intención
En el objeto IntentRecognizer, va a llamar al método RecognizeOnceAsync(). Este método solicita al servicio de Voz que reconozca la voz en una sola frase y que deje de reconocer la voz una vez que la frase se haya identificado.
Inserte este código después de aplicar los modelos de lenguaje:
Console.WriteLine("Say something...");
var result = await recognizer.RecognizeOnceAsync();
Visualización de los resultados (o errores) del reconocimiento
Cuando el servicio de Voz devuelve el resultado del reconocimiento, imprimimos el resultado.
Inserte este código debajo de var result = await recognizer.RecognizeOnceAsync();:
if (result.Reason == ResultReason.RecognizedIntent)
{
Console.WriteLine($"RECOGNIZED: Text={result.Text}");
Console.WriteLine($" Intent Id={result.IntentId}.");
var entities = result.Entities;
switch (result.IntentId)
{
case "ChangeFloors":
if (entities.TryGetValue("floorName", out string floorName))
{
Console.WriteLine($" FloorName={floorName}");
}
if (entities.TryGetValue("floorName:1", out floorName))
{
Console.WriteLine($" FloorName:1={floorName}");
}
if (entities.TryGetValue("floorName:2", out floorName))
{
Console.WriteLine($" FloorName:2={floorName}");
}
if (entities.TryGetValue("parkingLevel", out string parkingLevel))
{
Console.WriteLine($" ParkingLevel={parkingLevel}");
}
break;
case "DoorControl":
if (entities.TryGetValue("action", out string action))
{
Console.WriteLine($" Action={action}");
}
break;
}
}
else if (result.Reason == ResultReason.RecognizedSpeech)
{
Console.WriteLine($"RECOGNIZED: Text={result.Text}");
Console.WriteLine($" Intent not recognized.");
}
else if (result.Reason == ResultReason.NoMatch)
{
Console.WriteLine($"NOMATCH: Speech could not be recognized.");
}
else if (result.Reason == ResultReason.Canceled)
{
var cancellation = CancellationDetails.FromResult(result);
Console.WriteLine($"CANCELED: Reason={cancellation.Reason}");
if (cancellation.Reason == CancellationReason.Error)
{
Console.WriteLine($"CANCELED: ErrorCode={cancellation.ErrorCode}");
Console.WriteLine($"CANCELED: ErrorDetails={cancellation.ErrorDetails}");
Console.WriteLine($"CANCELED: Did you set the speech resource key and region values?");
}
}
Comprobación del código
En este momento, el código debe tener esta apariencia:
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech;
using Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech.Intent;
namespace helloworld
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IntentPatternMatchingWithMicrophoneAsync().Wait();
}
private static async Task IntentPatternMatchingWithMicrophoneAsync()
{
var config = SpeechConfig.FromSubscription("YourSpeechResourceKey", "YourSpeechResourceRegion");
using (var recognizer = new IntentRecognizer(config))
{
// Creates a Pattern Matching model and adds specific intents from your model. The
// Id is used to identify this model from others in the collection.
var model = new PatternMatchingModel("YourPatternMatchingModelId");
// Creates a pattern that uses groups of optional words. "[Go | Take me]" will match either "Go", "Take me", or "".
var patternWithOptionalWords = "[Go | Take me] to [floor|level] {floorName}";
// Creates a pattern that uses an optional entity and group that could be used to tie commands together.
var patternWithOptionalEntity = "Go to parking [{parkingLevel}]";
// You can also have multiple entities of the same name in a single pattern by adding appending a unique identifier
// to distinguish between the instances. For example:
var patternWithTwoOfTheSameEntity = "Go to floor {floorName:1} [and then go to floor {floorName:2}]";
// NOTE: Both floorName:1 and floorName:2 are tied to the same list of entries. The identifier can be a string
// and is separated from the entity name by a ':'
// Adds some intents to look for specific patterns.
model.Intents.Add(new PatternMatchingIntent("ChangeFloors", patternWithOptionalWords, patternWithOptionalEntity, patternWithTwoOfTheSameEntity));
model.Intents.Add(new PatternMatchingIntent("DoorControl", "{action} the doors", "{action} doors", "{action} the door", "{action} door"));
// Creates the "floorName" entity and set it to type list.
// Adds acceptable values. NOTE the default entity type is Any and so we do not need
// to declare the "action" entity.
model.Entities.Add(PatternMatchingEntity.CreateListEntity("floorName", EntityMatchMode.Strict, "ground floor", "lobby", "1st", "first", "one", "1", "2nd", "second", "two", "2"));
// Creates the "parkingLevel" entity as a pre-built integer
model.Entities.Add(PatternMatchingEntity.CreateIntegerEntity("parkingLevel"));
var modelCollection = new LanguageUnderstandingModelCollection();
modelCollection.Add(model);
recognizer.ApplyLanguageModels(modelCollection);
Console.WriteLine("Say something...");
var result = await recognizer.RecognizeOnceAsync();
if (result.Reason == ResultReason.RecognizedIntent)
{
Console.WriteLine($"RECOGNIZED: Text={result.Text}");
Console.WriteLine($" Intent Id={result.IntentId}.");
var entities = result.Entities;
switch (result.IntentId)
{
case "ChangeFloors":
if (entities.TryGetValue("floorName", out string floorName))
{
Console.WriteLine($" FloorName={floorName}");
}
if (entities.TryGetValue("floorName:1", out floorName))
{
Console.WriteLine($" FloorName:1={floorName}");
}
if (entities.TryGetValue("floorName:2", out floorName))
{
Console.WriteLine($" FloorName:2={floorName}");
}
if (entities.TryGetValue("parkingLevel", out string parkingLevel))
{
Console.WriteLine($" ParkingLevel={parkingLevel}");
}
break;
case "DoorControl":
if (entities.TryGetValue("action", out string action))
{
Console.WriteLine($" Action={action}");
}
break;
}
}
else if (result.Reason == ResultReason.RecognizedSpeech)
{
Console.WriteLine($"RECOGNIZED: Text={result.Text}");
Console.WriteLine($" Intent not recognized.");
}
else if (result.Reason == ResultReason.NoMatch)
{
Console.WriteLine($"NOMATCH: Speech could not be recognized.");
}
else if (result.Reason == ResultReason.Canceled)
{
var cancellation = CancellationDetails.FromResult(result);
Console.WriteLine($"CANCELED: Reason={cancellation.Reason}");
if (cancellation.Reason == CancellationReason.Error)
{
Console.WriteLine($"CANCELED: ErrorCode={cancellation.ErrorCode}");
Console.WriteLine($"CANCELED: ErrorDetails={cancellation.ErrorDetails}");
Console.WriteLine($"CANCELED: Did you set the speech resource key and region values?");
}
}
}
}
}
}
Compilación y ejecución de la aplicación
Ya está listo para compilar la aplicación y probar el reconocimiento de voz con el servicio Voz.
- Compile el código: en la barra de menús de Visual Studio, elija Compilar>Compilar solución.
- Inicie la aplicación: en la barra de menús, elija Depurar>Iniciar depuración o presione F5.
- Inicie el reconocimiento: se le pedirá que diga algo. El idioma predeterminado es el inglés. La voz se envía al servicio Voz, se transcribe como texto y se representa en la consola.
Por ejemplo, si dice "Take me to floor 2", la salida debería ser:
Say something...
RECOGNIZED: Text=Take me to floor 2.
Intent Id=ChangeFloors.
FloorName=2
Como otro ejemplo, si dice "Take me to floor 7", la salida debería ser:
Say something...
RECOGNIZED: Text=Take me to floor 7.
Intent not recognized.
No se ha reconocido ninguna intención porque 7 no estaba en nuestra lista de valores válidos para floorName.
Crear un proyecto
Cree un nuevo proyecto de aplicación de consola de C++ en Visual Studio 2019 e instale el SDK de Voz.
Inicio con código reutilizable
Vamos abrir helloworld.cpp y agregar código que funcione como el esqueleto del proyecto.
#include <iostream>
#include <speechapi_cxx.h>
using namespace Microsoft::CognitiveServices::Speech;
using namespace Microsoft::CognitiveServices::Speech::Intent;
int main()
{
std::cout << "Hello World!\n";
auto config = SpeechConfig::FromSubscription("YourSpeechResourceKey", "YourSpeechResourceRegion");
}
Creación de una configuración de Voz
Para poder inicializar un objeto IntentRecognizer, es preciso crear una configuración que use la clave y la recurso para el recurso de predicción de servicios de Azure AI.
- Reemplace
"YourSpeechResourceKey"por la clave de predicción de servicios de Azure AI. - Reemplace
"YourSpeechResourceRegion"por la región de recursos de Azure AI Foundry.
En este ejemplo se usa el método FromSubscription() para compilar la clase SpeechConfig. Para ver una lista completa de los métodos disponibles, consulte Clase SpeechConfig.
Inicialización de IntentRecognizer
Ahora cree un objeto IntentRecognizer. Inserte este código justo debajo de la configuración de Voz.
auto intentRecognizer = IntentRecognizer::FromConfig(config);
Adición de algunas intenciones
Debe asociar algunos patrones con PatternMatchingModel y aplicarlos a IntentRecognizer.
Empezaremos creando un PatternMatchingModel y le agregaremos algunas intenciones. PatternMatchingIntent es una estructura, por lo que solo usamos la sintaxis de inserción.
Nota:
Se pueden agregar varios patrones a PatternMatchingIntent.
auto model = PatternMatchingModel::FromId("myNewModel");
model->Intents.push_back({"Take me to floor {floorName}.", "Go to floor {floorName}."} , "ChangeFloors");
model->Intents.push_back({"{action} the door."}, "OpenCloseDoor");
Adición de algunas entidades personalizadas
Para aprovechar al máximo el coincidencia de patrones, es posible personalizar las entidades. Convertiremos "floorName" en una lista de las plantas disponibles.
model->Entities.push_back({ "floorName" , Intent::EntityType::List, Intent::EntityMatchMode::Strict, {"one", "1", "two", "2", "lobby", "ground floor"} });
Aplicación del modelo al reconocedor
Ahora es necesario aplicar el modelo a IntentRecognizer. Es posible usar varios modelos a la vez para que la API tome una colección de modelos.
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<LanguageUnderstandingModel>> collection;
collection.push_back(model);
intentRecognizer->ApplyLanguageModels(collection);
Reconocimiento de una intención
En el objeto IntentRecognizer, va a llamar al método RecognizeOnceAsync(). Este método solicita al servicio de Voz que reconozca la voz en una sola frase y que deje de reconocer la voz una vez que la frase se haya identificado. Por motivos de simplicidad, esperaremos a que se complete la devolución futura.
Inserte este código debajo de las intenciones:
std::cout << "Say something ..." << std::endl;
auto result = intentRecognizer->RecognizeOnceAsync().get();
Visualización de los resultados (o errores) del reconocimiento
Cuando el servicio de Voz devuelve el resultado del reconocimiento, imprimimos el resultado.
Inserte este código debajo de auto result = intentRecognizer->RecognizeOnceAsync().get();:
switch (result->Reason)
{
case ResultReason::RecognizedSpeech:
std::cout << "RECOGNIZED: Text = " << result->Text.c_str() << std::endl;
std::cout << "NO INTENT RECOGNIZED!" << std::endl;
break;
case ResultReason::RecognizedIntent:
std::cout << "RECOGNIZED: Text = " << result->Text.c_str() << std::endl;
std::cout << " Intent Id = " << result->IntentId.c_str() << std::endl;
auto entities = result->GetEntities();
if (entities.find("floorName") != entities.end())
{
std::cout << " Floor name: = " << entities["floorName"].c_str() << std::endl;
}
if (entities.find("action") != entities.end())
{
std::cout << " Action: = " << entities["action"].c_str() << std::endl;
}
break;
case ResultReason::NoMatch:
{
auto noMatch = NoMatchDetails::FromResult(result);
switch (noMatch->Reason)
{
case NoMatchReason::NotRecognized:
std::cout << "NOMATCH: Speech was detected, but not recognized." << std::endl;
break;
case NoMatchReason::InitialSilenceTimeout:
std::cout << "NOMATCH: The start of the audio stream contains only silence, and the service timed out waiting for speech." << std::endl;
break;
case NoMatchReason::InitialBabbleTimeout:
std::cout << "NOMATCH: The start of the audio stream contains only noise, and the service timed out waiting for speech." << std::endl;
break;
case NoMatchReason::KeywordNotRecognized:
std::cout << "NOMATCH: Keyword not recognized" << std::endl;
break;
}
break;
}
case ResultReason::Canceled:
{
auto cancellation = CancellationDetails::FromResult(result);
if (!cancellation->ErrorDetails.empty())
{
std::cout << "CANCELED: ErrorDetails=" << cancellation->ErrorDetails.c_str() << std::endl;
std::cout << "CANCELED: Did you set the speech resource key and region values?" << std::endl;
}
}
default:
break;
}
Comprobación del código
En este momento, el código debe tener esta apariencia:
#include <iostream>
#include <speechapi_cxx.h>
using namespace Microsoft::CognitiveServices::Speech;
using namespace Microsoft::CognitiveServices::Speech::Intent;
int main()
{
auto config = SpeechConfig::FromSubscription("YourSpeechResourceKey", "YourSpeechResourceRegion");
auto intentRecognizer = IntentRecognizer::FromConfig(config);
auto model = PatternMatchingModel::FromId("myNewModel");
model->Intents.push_back({"Take me to floor {floorName}.", "Go to floor {floorName}."} , "ChangeFloors");
model->Intents.push_back({"{action} the door."}, "OpenCloseDoor");
model->Entities.push_back({ "floorName" , Intent::EntityType::List, Intent::EntityMatchMode::Strict, {"one", "1", "two", "2", "lobby", "ground floor"} });
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<LanguageUnderstandingModel>> collection;
collection.push_back(model);
intentRecognizer->ApplyLanguageModels(collection);
std::cout << "Say something ..." << std::endl;
auto result = intentRecognizer->RecognizeOnceAsync().get();
switch (result->Reason)
{
case ResultReason::RecognizedSpeech:
std::cout << "RECOGNIZED: Text = " << result->Text.c_str() << std::endl;
std::cout << "NO INTENT RECOGNIZED!" << std::endl;
break;
case ResultReason::RecognizedIntent:
std::cout << "RECOGNIZED: Text = " << result->Text.c_str() << std::endl;
std::cout << " Intent Id = " << result->IntentId.c_str() << std::endl;
auto entities = result->GetEntities();
if (entities.find("floorName") != entities.end())
{
std::cout << " Floor name: = " << entities["floorName"].c_str() << std::endl;
}
if (entities.find("action") != entities.end())
{
std::cout << " Action: = " << entities["action"].c_str() << std::endl;
}
break;
case ResultReason::NoMatch:
{
auto noMatch = NoMatchDetails::FromResult(result);
switch (noMatch->Reason)
{
case NoMatchReason::NotRecognized:
std::cout << "NOMATCH: Speech was detected, but not recognized." << std::endl;
break;
case NoMatchReason::InitialSilenceTimeout:
std::cout << "NOMATCH: The start of the audio stream contains only silence, and the service timed out waiting for speech." << std::endl;
break;
case NoMatchReason::InitialBabbleTimeout:
std::cout << "NOMATCH: The start of the audio stream contains only noise, and the service timed out waiting for speech." << std::endl;
break;
case NoMatchReason::KeywordNotRecognized:
std::cout << "NOMATCH: Keyword not recognized." << std::endl;
break;
}
break;
}
case ResultReason::Canceled:
{
auto cancellation = CancellationDetails::FromResult(result);
if (!cancellation->ErrorDetails.empty())
{
std::cout << "CANCELED: ErrorDetails=" << cancellation->ErrorDetails.c_str() << std::endl;
std::cout << "CANCELED: Did you set the speech resource key and region values?" << std::endl;
}
}
default:
break;
}
}
Compilación y ejecución de la aplicación
Ya está listo para compilar la aplicación y probar el reconocimiento de voz con el servicio Voz.
- Compile el código: en la barra de menús de Visual Studio, elija Compilar>Compilar solución.
- Inicie la aplicación: en la barra de menús, elija Depurar>Iniciar depuración o presione F5.
- Inicie el reconocimiento: se le pedirá que diga algo. El idioma predeterminado es el inglés. La voz se envía al servicio Voz, se transcribe como texto y se representa en la consola.
Por ejemplo, si dice "Take me to floor 2", la salida debería ser:
Say something ...
RECOGNIZED: Text = Take me to floor 2.
Intent Id = ChangeFloors
Floor name: = 2
Por ejemplo, si dice "Take me to floor 7", la salida debería ser:
Say something ...
RECOGNIZED: Text = Take me to floor 7.
NO INTENT RECOGNIZED!
El identificador de intención está vacío porque el número 7 no estaba en la lista.
Documentación de referencia | Ejemplos adicionales en GitHub
En este inicio rápido, instalará la SDK de voz para Java.
Requisitos de la plataforma
Elija su ámbito objetivo:
El SDK de Voz para Java es compatible con Windows, Linux y macOS.
En Windows debe usar la arquitectura de destino de 64 bits. Se requiere Windows 10 o posterior.
Instale el Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable para Visual Studio 2015, 2017, 2019 y 2022 para su plataforma. Durante la primera instalación del paquete, es posible que deba reiniciar.
El SDK de Voz para Java no admite Windows en ARM64.
Instale un kit de desarrollo de Java como Azul Zulu OpenJDK. La compilación de Microsoft de OpenJDK o su JDK preferido también deberían funcionar.
Instale el SDK de Voz para Java
Algunas de las instrucciones usan una versión específica del SDK, como 1.43.0. Para comprobar la versión más reciente, busque nuestro repositorio de GitHub.
Elija su ámbito objetivo:
En esta guía se muestra cómo instalar el SDK de Voz para Java en Java Runtime.
Sistemas operativos admitidos
El paquete de SDK de voz para Java está disponible en estos sistemas operativos:
- Windows: solo 64 bits.
- Mac: macOS X 10.14 o posterior.
- Linux: Consulte las distribuciones de Linux y arquitecturas de destino compatibles.
Siga estos pasos para instalar el SDK de voz para Java mediante Apache Maven:
Instalación de Apache Maven.
Abra un símbolo del sistema donde desea el nuevo proyecto, y crear un nuevo archivo pom.xml.
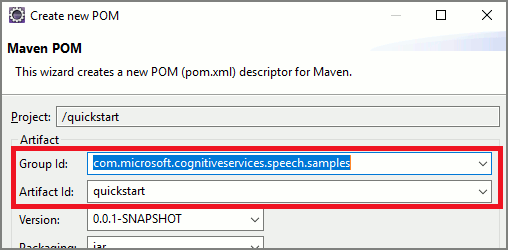
Copie el siguiente contenido XML en pom.xml:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.samples</groupId> <artifactId>quickstart-eclipse</artifactId> <version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <build> <sourceDirectory>src</sourceDirectory> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.7.0</version> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech</groupId> <artifactId>client-sdk</artifactId> <version>1.43.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>Ejecute el siguiente comando de Maven para instalar el SDK de Voz y las dependencias.
mvn clean dependency:copy-dependencies
Inicio con código reutilizable
Abra
Main.javadesde el directorio src.Reemplace el contenido del archivo por lo siguiente:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Dictionary;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.*;
import com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.intent.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
IntentPatternMatchingWithMicrophone();
}
public static void IntentPatternMatchingWithMicrophone() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
SpeechConfig config = SpeechConfig.fromSubscription("YourSpeechResourceKey", "YourSpeechResourceRegion");
}
}
Creación de una configuración de Voz
Para poder inicializar un objeto IntentRecognizer, es preciso crear una configuración que use la clave y la recurso para el recurso de predicción de servicios de Azure AI.
- Reemplace
"YourSpeechResourceKey"por la clave de predicción de servicios de Azure AI. - Reemplace
"YourSpeechResourceRegion"por la región de recursos de Azure AI Foundry.
En este ejemplo se usa el método fromSubscription() para compilar la clase SpeechConfig. Para ver una lista completa de los métodos disponibles, consulte Clase SpeechConfig.
Inicialización de IntentRecognizer
Ahora cree un objeto IntentRecognizer. Inserte este código justo debajo de la configuración de Voz. Lo hacemos en un intento para aprovechar la interfaz que se cierra de forma automática.
try (IntentRecognizer recognizer = new IntentRecognizer(config)) {
}
Adición de algunas intenciones
Debe asociar algunos patrones con PatternMatchingModel y aplicarlos a IntentRecognizer.
Para empezar, crearemos PatternMatchingModel y le agregaremos algunas intenciones.
Nota:
Se pueden agregar varios patrones a PatternMatchingIntent.
Inserte este código dentro del bloque try:
// Creates a Pattern Matching model and adds specific intents from your model. The
// Id is used to identify this model from others in the collection.
PatternMatchingModel model = new PatternMatchingModel("YourPatternMatchingModelId");
// Creates a pattern that uses groups of optional words. "[Go | Take me]" will match either "Go", "Take me", or "".
String patternWithOptionalWords = "[Go | Take me] to [floor|level] {floorName}";
// Creates a pattern that uses an optional entity and group that could be used to tie commands together.
String patternWithOptionalEntity = "Go to parking [{parkingLevel}]";
// You can also have multiple entities of the same name in a single pattern by adding appending a unique identifier
// to distinguish between the instances. For example:
String patternWithTwoOfTheSameEntity = "Go to floor {floorName:1} [and then go to floor {floorName:2}]";
// NOTE: Both floorName:1 and floorName:2 are tied to the same list of entries. The identifier can be a string
// and is separated from the entity name by a ':'
// Creates the pattern matching intents and adds them to the model
model.getIntents().put(new PatternMatchingIntent("ChangeFloors", patternWithOptionalWords, patternWithOptionalEntity, patternWithTwoOfTheSameEntity));
model.getIntents().put(new PatternMatchingIntent("DoorControl", "{action} the doors", "{action} doors", "{action} the door", "{action} door"));
Adición de algunas entidades personalizadas
Para aprovechar al máximo el coincidencia de patrones, es posible personalizar las entidades. Convertiremos "floorName" en una lista de las plantas disponibles. También convertiremos "parkingLevel" en una entidad de entero.
Inserte este código debajo de las intenciones:
// Creates the "floorName" entity and set it to type list.
// Adds acceptable values. NOTE the default entity type is Any and so we do not need
// to declare the "action" entity.
model.getEntities().put(PatternMatchingEntity.CreateListEntity("floorName", PatternMatchingEntity.EntityMatchMode.Strict, "ground floor", "lobby", "1st", "first", "one", "1", "2nd", "second", "two", "2"));
// Creates the "parkingLevel" entity as a pre-built integer
model.getEntities().put(PatternMatchingEntity.CreateIntegerEntity("parkingLevel"));
Aplicación del modelo al reconocedor
Ahora es necesario aplicar el modelo a IntentRecognizer. Es posible usar varios modelos a la vez para que la API tome una colección de modelos.
Inserte este código debajo de las entidades:
ArrayList<LanguageUnderstandingModel> modelCollection = new ArrayList<LanguageUnderstandingModel>();
modelCollection.add(model);
recognizer.applyLanguageModels(modelCollection);
Reconocimiento de una intención
En el objeto IntentRecognizer, va a llamar al método RecognizeOnceAsync(). Este método solicita al servicio de Voz que reconozca la voz en una sola frase y que deje de reconocer la voz una vez que la frase se haya identificado.
Inserte este código después de aplicar los modelos de lenguaje:
System.out.println("Say something...");
IntentRecognitionResult result = recognizer.recognizeOnceAsync().get();
Visualización de los resultados (o errores) del reconocimiento
Cuando el servicio de Voz devuelva el resultado del reconocimiento, imprimiremos el resultado.
Inserte este código debajo de IntentRecognitionResult result = recognizer.recognizeOnceAsync.get();:
if (result.getReason() == ResultReason.RecognizedSpeech) {
System.out.println("RECOGNIZED: Text= " + result.getText());
System.out.println(String.format("%17s", "Intent not recognized."));
}
else if (result.getReason() == ResultReason.RecognizedIntent)
{
System.out.println("RECOGNIZED: Text= " + result.getText());
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "Intent Id=", result.getIntentId() + "."));
Dictionary<String, String> entities = result.getEntities();
switch (result.getIntentId())
{
case "ChangeFloors":
if (entities.get("floorName") != null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "FloorName=", entities.get("floorName")));
}
if (entities.get("floorName:1") != null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "FloorName:1=", entities.get("floorName:1")));
}
if (entities.get("floorName:2") != null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "FloorName:2=", entities.get("floorName:2")));
}
if (entities.get("parkingLevel") != null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "ParkingLevel=", entities.get("parkingLevel")));
}
break;
case "DoorControl":
if (entities.get("action") != null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "Action=", entities.get("action")));
}
break;
}
}
else if (result.getReason() == ResultReason.NoMatch) {
System.out.println("NOMATCH: Speech could not be recognized.");
}
else if (result.getReason() == ResultReason.Canceled) {
CancellationDetails cancellation = CancellationDetails.fromResult(result);
System.out.println("CANCELED: Reason=" + cancellation.getReason());
if (cancellation.getReason() == CancellationReason.Error)
{
System.out.println("CANCELED: ErrorCode=" + cancellation.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("CANCELED: ErrorDetails=" + cancellation.getErrorDetails());
System.out.println("CANCELED: Did you update the Speech resource info?");
}
}
Comprobación del código
En este momento, el código debe tener esta apariencia:
package quickstart;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.Dictionary;
import com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.*;
import com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.intent.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
IntentPatternMatchingWithMicrophone();
}
public static void IntentPatternMatchingWithMicrophone() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
SpeechConfig config = SpeechConfig.fromSubscription("YourSpeechResourceKey", "YourSpeechResourceRegion");
try (IntentRecognizer recognizer = new IntentRecognizer(config)) {
// Creates a Pattern Matching model and adds specific intents from your model. The
// Id is used to identify this model from others in the collection.
PatternMatchingModel model = new PatternMatchingModel("YourPatternMatchingModelId");
// Creates a pattern that uses groups of optional words. "[Go | Take me]" will match either "Go", "Take me", or "".
String patternWithOptionalWords = "[Go | Take me] to [floor|level] {floorName}";
// Creates a pattern that uses an optional entity and group that could be used to tie commands together.
String patternWithOptionalEntity = "Go to parking [{parkingLevel}]";
// You can also have multiple entities of the same name in a single pattern by adding appending a unique identifier
// to distinguish between the instances. For example:
String patternWithTwoOfTheSameEntity = "Go to floor {floorName:1} [and then go to floor {floorName:2}]";
// NOTE: Both floorName:1 and floorName:2 are tied to the same list of entries. The identifier can be a string
// and is separated from the entity name by a ':'
// Creates the pattern matching intents and adds them to the model
model.getIntents().put(new PatternMatchingIntent("ChangeFloors", patternWithOptionalWords, patternWithOptionalEntity, patternWithTwoOfTheSameEntity));
model.getIntents().put(new PatternMatchingIntent("DoorControl", "{action} the doors", "{action} doors", "{action} the door", "{action} door"));
// Creates the "floorName" entity and set it to type list.
// Adds acceptable values. NOTE the default entity type is Any and so we do not need
// to declare the "action" entity.
model.getEntities().put(PatternMatchingEntity.CreateListEntity("floorName", PatternMatchingEntity.EntityMatchMode.Strict, "ground floor", "lobby", "1st", "first", "one", "1", "2nd", "second", "two", "2"));
// Creates the "parkingLevel" entity as a pre-built integer
model.getEntities().put(PatternMatchingEntity.CreateIntegerEntity("parkingLevel"));
ArrayList<LanguageUnderstandingModel> modelCollection = new ArrayList<LanguageUnderstandingModel>();
modelCollection.add(model);
recognizer.applyLanguageModels(modelCollection);
System.out.println("Say something...");
IntentRecognitionResult result = recognizer.recognizeOnceAsync().get();
if (result.getReason() == ResultReason.RecognizedSpeech) {
System.out.println("RECOGNIZED: Text= " + result.getText());
System.out.println(String.format("%17s", "Intent not recognized."));
}
else if (result.getReason() == ResultReason.RecognizedIntent)
{
System.out.println("RECOGNIZED: Text= " + result.getText());
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "Intent Id=", result.getIntentId() + "."));
Dictionary<String, String> entities = result.getEntities();
switch (result.getIntentId())
{
case "ChangeFloors":
if (entities.get("floorName") != null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "FloorName=", entities.get("floorName")));
}
if (entities.get("floorName:1") != null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "FloorName:1=", entities.get("floorName:1")));
}
if (entities.get("floorName:2") != null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "FloorName:2=", entities.get("floorName:2")));
}
if (entities.get("parkingLevel") != null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "ParkingLevel=", entities.get("parkingLevel")));
}
break;
case "DoorControl":
if (entities.get("action") != null) {
System.out.println(String.format("%17s %s", "Action=", entities.get("action")));
}
break;
}
}
else if (result.getReason() == ResultReason.NoMatch) {
System.out.println("NOMATCH: Speech could not be recognized.");
}
else if (result.getReason() == ResultReason.Canceled) {
CancellationDetails cancellation = CancellationDetails.fromResult(result);
System.out.println("CANCELED: Reason=" + cancellation.getReason());
if (cancellation.getReason() == CancellationReason.Error)
{
System.out.println("CANCELED: ErrorCode=" + cancellation.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("CANCELED: ErrorDetails=" + cancellation.getErrorDetails());
System.out.println("CANCELED: Did you update the Speech resource info?");
}
}
}
}
}
Compilación y ejecución de la aplicación
Ya está listo para compilar la aplicación y probar el reconocimiento de la intención con el servicio de voz y el buscador de coincidencias de patrones insertados.
Seleccione el botón Ejecutar en Eclipse o presione Ctrl+F11 y vea la salida del mensaje "Diga algo...". Cuando aparezca, pronuncie la expresión y observe la salida.
Por ejemplo, si dice "Take me to floor 2", la salida debería ser:
Say something...
RECOGNIZED: Text=Take me to floor 2.
Intent Id=ChangeFloors.
FloorName=2
Como otro ejemplo, si dice "Take me to floor 7", la salida debería ser:
Say something...
RECOGNIZED: Text=Take me to floor 7.
Intent not recognized.
No se ha reconocido ninguna intención porque 7 no estaba en nuestra lista de valores válidos para floorName.