Nota
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar iniciar sesión o cambiar directorios.
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar cambiar los directorios.
Una transformación de escalado multiplica uno o varios de los cuatro componentes de color por un número. Las entradas de matriz de colores que representan el escalado se proporcionan en la tabla siguiente.
| Componente que se va a escalar | Entrada de elemento de matriz |
|---|---|
| Rojo | [0][0] |
| Verde | [1][1] |
| Azul | [2][2] |
| Alfa | [3][3] |
Escalado de un color
En el ejemplo siguiente se construye un Image objeto a partir del archivo ColorBars2.bmp. A continuación, el código escala el componente azul de cada píxel de la imagen por un factor de 2. La imagen original se dibuja junto con la imagen transformada.
Image image = new Bitmap("ColorBars2.bmp");
ImageAttributes imageAttributes = new ImageAttributes();
int width = image.Width;
int height = image.Height;
float[][] colorMatrixElements = {
new float[] {1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
new float[] {0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
new float[] {0, 0, 2, 0, 0},
new float[] {0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
new float[] {0, 0, 0, 0, 1}};
ColorMatrix colorMatrix = new ColorMatrix(colorMatrixElements);
imageAttributes.SetColorMatrix(
colorMatrix,
ColorMatrixFlag.Default,
ColorAdjustType.Bitmap);
e.Graphics.DrawImage(image, 10, 10, width, height);
e.Graphics.DrawImage(
image,
new Rectangle(150, 10, width, height), // destination rectangle
0, 0, // upper-left corner of source rectangle
width, // width of source rectangle
height, // height of source rectangle
GraphicsUnit.Pixel,
imageAttributes);
Dim image As New Bitmap("ColorBars2.bmp")
Dim imageAttributes As New ImageAttributes()
Dim width As Integer = image.Width
Dim height As Integer = image.Height
Dim colorMatrixElements As Single()() = { _
New Single() {1, 0, 0, 0, 0}, _
New Single() {0, 1, 0, 0, 0}, _
New Single() {0, 0, 2, 0, 0}, _
New Single() {0, 0, 0, 1, 0}, _
New Single() {0, 0, 0, 0, 1}}
Dim colorMatrix As New ColorMatrix(colorMatrixElements)
imageAttributes.SetColorMatrix( _
colorMatrix, _
ColorMatrixFlag.Default, _
ColorAdjustType.Bitmap)
e.Graphics.DrawImage(image, 10, 10, width, height)
' Pass in the destination rectangle (2nd argument), the upper-left corner
' (3rd and 4th arguments), width (5th argument), and height (6th
' argument) of the source rectangle.
e.Graphics.DrawImage( _
image, _
New Rectangle(150, 10, width, height), _
0, 0, _
width, _
height, _
GraphicsUnit.Pixel, _
imageAttributes)
En la ilustración siguiente se muestra la imagen original a la izquierda y la imagen escalada a la derecha:

En la tabla siguiente se enumeran los vectores de color de las cuatro barras antes y después del escalado azul. Tenga en cuenta que el componente azul de la cuarta barra de colores pasó de 0,8 a 0,6. Esto se debe a que GDI+ conserva solo la parte fraccionaria del resultado. Por ejemplo, (2)(0,8) = 1,6 y la parte fraccionaria de 1,6 es 0,6. Conservar solo la parte fraccionaria garantiza que el resultado esté siempre en el intervalo [0, 1].
| Texto original en inglés | Redimensionado |
|---|---|
| (0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 1) | (0.4, 0.4, 0.8, 1) |
| (0.4, 0.2, 0.2, 1) | (0.4, 0.2, 0.4, 1) |
| (0.2, 0.4, 0.2, 1) | (0.2, 0.4, 0.4, 1) |
| (0.4, 0.4, 0.8, 1) | (0.4, 0.4, 0.6, 1) |
Escalado de múltiples colores
En el ejemplo siguiente se construye un Image objeto a partir del archivo ColorBars2.bmp. A continuación, el código escala los componentes rojo, verde y azul de cada píxel de la imagen. Los componentes rojos se reducen verticalmente el 25 por ciento, los componentes verdes se reducen al 35 por ciento y los componentes azules se reducen verticalmente el 50 por ciento.
Image image = new Bitmap("ColorBars.bmp");
ImageAttributes imageAttributes = new ImageAttributes();
int width = image.Width;
int height = image.Height;
float[][] colorMatrixElements = {
new float[] {.75F, 0, 0, 0, 0},
new float[] {0, .65F, 0, 0, 0},
new float[] {0, 0, .5F, 0, 0},
new float[] {0, 0, 0, 1F, 0},
new float[] {0, 0, 0, 0, 1F}};
ColorMatrix colorMatrix = new ColorMatrix(colorMatrixElements);
imageAttributes.SetColorMatrix(
colorMatrix,
ColorMatrixFlag.Default,
ColorAdjustType.Bitmap);
e.Graphics.DrawImage(image, 10, 10, width, height);
e.Graphics.DrawImage(
image,
new Rectangle(150, 10, width, height), // destination rectangle
0, 0, // upper-left corner of source rectangle
width, // width of source rectangle
height, // height of source rectangle
GraphicsUnit.Pixel,
imageAttributes);
Dim image As New Bitmap("ColorBars.bmp")
Dim imageAttributes As New ImageAttributes()
Dim width As Integer = image.Width
Dim height As Integer = image.Height
Dim colorMatrixElements As Single()() = { _
New Single() {0.75F, 0, 0, 0, 0}, _
New Single() {0, 0.65F, 0, 0, 0}, _
New Single() {0, 0, 0.5F, 0, 0}, _
New Single() {0, 0, 0, 1, 0}, _
New Single() {0, 0, 0, 0, 1}}
Dim colorMatrix As New ColorMatrix(colorMatrixElements)
imageAttributes.SetColorMatrix( _
colorMatrix, _
ColorMatrixFlag.Default, _
ColorAdjustType.Bitmap)
e.Graphics.DrawImage(image, 10, 10, width, height)
' Pass in the destination rectangle, and the upper-left corner, width,
' and height of the source rectangle as in the previous example.
e.Graphics.DrawImage( _
image, _
New Rectangle(150, 10, width, height), _
0, 0, _
width, _
height, _
GraphicsUnit.Pixel, _
imageAttributes)
En la ilustración siguiente se muestra la imagen original a la izquierda y la imagen escalada a la derecha:
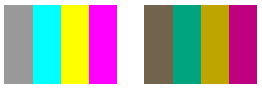
En la tabla siguiente se enumeran los vectores de color de las cuatro barras antes y después del escalado rojo, verde y azul.
| Texto original en inglés | Redimensionado |
|---|---|
| (0.6, 0.6, 0.6, 1) | (0.45, 0.39, 0.3, 1) |
| (0, 1, 1, 1) | (0, 0.65, 0.5, 1) |
| (1, 1, 0, 1) | (0.75, 0.65, 0, 1) |
| (1, 0, 1, 1) | (0.75, 0, 0.5, 1) |
Consulte también
.NET Desktop feedback
