Promote an Agile culture within your team
TFS 2017 | TFS 2015 | TFS 2013
Note
Are you new to Agile? Learn more about Agile Culture and Scaling Agile to Large Teams.
As your team grows, you want your tools to grow with it. And, if you're an enterprise adopting Agile methodologies, you want your Agile tools to support the business goals of your enterprise.
However, to successfully scale Agile requires addressing both the culture and tools within your organization.
Alignment enables autonomy
Organizations that aspire to be agile need to consider the twin obligations of creating alignment across the enterprise and supporting team autonomy. Teams need autonomy to be efficient. And, enterprises need alignment across teams and the organization to be efficient.
Too much alignment with insufficient team autonomy leads doesn't support innovation or agility of teams to get things done. Too little alignment with each team running their own program doesn't provide the insight and coordination required to meet business goals.
With the right level of alignment across the organization and team autonomy, individuals are empowered to innovate and inspired to collaborate to meet business goals.
Create alignment and support autonomy
As you plan how you want to grow your Agile tool set, consider the following areas. These areas are key to creating enterprise alignment while developing team autonomy.
Area
Create alignment
Support autonomy
Product vision
The organization defines the goals and roadmap for the organization. Goals can be defined as epics and features that show up on the portfolio backlog.
Teams determine how to best meet the roadmap. Teams break down goals into user stories or product backlog items using their team backlogs.
Team structure
Based on business goals, organizations determine the number and size of teams. Vertically structured feature teams lead to greater autonomy and efficiency.
With teams, there should be some established roles, such as product owner and development leads, but also room to rotate roles. For example, team members can take turns acting as Scrum Master, developing sprint demos, running sprint retrospectives, or crafting sprint emails.
Development cadence
Agile organizations need to release products and feature updates at regular intervals. Establishing regular release and sprint schedules promotes the rhythm of the business.
Each sprint--a time boxed iteration of constant duration between two and four weeks—includes planning, executing, delivering value, reflecting, and engaging in continuous improvement.
All teams manage their work within the set sprint cadence. Teams provide input into the length of sprint that works best for them.
Teams choose the Agile methods that work for them, Scrum, Kanban, or a mix of both. Teams also take ownership of starting and acting on their own set of continuous improvement practices.
It's possible for some teams to execute in shorter sprints. For example, if an organization sets a 2-week sprint cadence, some teams may choose to operate in 1-week sprints, while still aligning with the organizational schedule.
Communication cadence
Just as sprints bring a natural rhythm to the flow of work, so too do regular communications. By setting expectations for the types of communications they want to see to stay aligned and how often they occur, organizations naturally create alignment across teams and the enterprise.
Team sprint emails, bug bar status, and release team feature delivery status are examples of such regular communications.
Teams determine the details that they communicate and who will develop the communication. Their sprint emails may contain a summary of previous sprint accomplishments and next sprint plans or include a demo of recently completed features.
Quality
Each organization needs to set the criteria and standards by which they assess quality and set expectations for quality standards. A few ways they define the criteria is to set exit criteria for new feature development, standards to manage technical debt, and bug caps for teams or individuals.
Also, they can monitor bug status and trends by creating bug dashboards.
Teams choose how they meet the quality standards. They may stage bug bashes for new features or at the end of each sprint. They may choose an individual to act as a bug shield on a rotating basis.
Manage risk, track work
The organization determines how each functional unit will communicate status and risk. They establish a "contract of communication" as to the minimum required information the organization needs.
Also, the organization provides the infrastructure to reduce risks. The organization owes the teams anything they can do to reduce risks that are common across teams.
Beyond meeting the needs set by the organization, teams determine any other details they need to manage and track to reduce their risks. Whether they use a white board with sticky notes or a full Gantt chart, they manage the details.
For example, teams may add a backlog item to track a dependency they have on another team. Or, they may track their risks via a list of issues or impediments. Also, teams regularly contribute to improving the process and infrastructure to support the organizations ability to manage risk and gain insights.
Feature teams
As you scale, one of the most important tasks to consider is how you structure your teams. Traditionally, horizontal team structures divide teams according to the software architecture: user interface, service-oriented architecture, and data teams.
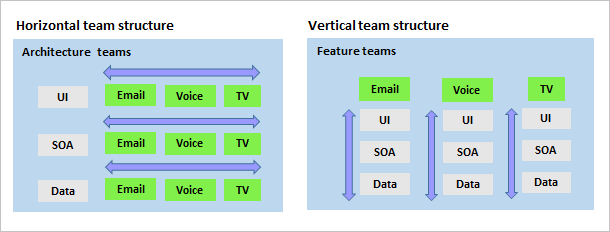
However, with the adoption of Agile practices, vertical team structures that span the architecture have been shown to provide greater team autonomy. Vertical teams can deliver on the features they own by working across the software architecture. They also spread the knowledge needed to work at all architecture levels throughout all the teams.
Configure your teams along the value streams your organization wants to deliver. For example, Fabrikam Fiber, organizes their teams into the following seven feature teams.
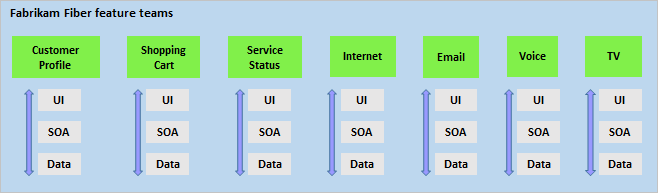
Each team plans the features they'll deliver. They have the autonomy to determine how they'll structure the data, architect the services, and design of the web and mobile user interfaces. They plan in adherence with the quality standards set by the organization and to which all teams contribute.
Configure your Agile tools to scale
As your organization grows, you can scale your Agile tools in the following ways.
Add teams and filtered backlog views: You add teams to support team autonomy and provide them with the tools they can configure and manage that supports how they want to work. These tools include product backlogs, Kanban boards, sprint backlogs and taskboards, and many others.
Also, you can configure teams to support a hierarchy of backlogs and portfolio backlogs so that portfolio managers can review priority and progress across several teams.
Set up sprints and releases: You can structure your iterations to support a flat set of sprints, or a set of sprints embedded within scheduled releases. Each team activates the set of sprints and releases that they need to participate in.
Manage portfolios: by setting up a hierarchy of teams and backlogs and activating portfolio backlogs. Feature teams focused on a subset of the product backlog can remain focused on just their backlog. Portfolio managers who want to view and organize backlogs to track progress and dependencies can manage portfolio backlogs of Features and Epics.
If other portfolio backlogs are needed--for example, Scenarios or Initiatives--you can add them as well.
Configure dashboards: With team dashboards, you can configure many charts that track progress within a team or across teams. Specifically, you can add status and trend charts based on queries you create.
Group or categorize work: There are several ways to group work that you want to track. Backlogs filter work items based on team area assignments. And, portfolio backlogs allow you to group backlog items under Features and Epics.
If you want to track and report on work items based on other groupings, you can. You can add tags to work items and then filter backlogs or queries based on tags. Also, you can add subarea paths to represent more granular feature areas.
Add folders and use team favorites: As your teams grow, you'll see a growing list of work item queries, build definitions, and source code folders. By using folders, subfolders, and team favorites, you can manage many of these lists more easily. You can add team favorites for shared queries, source code, and build definitions.
Related articles
Before you can create or work with any of the Agile tools, you need a project. If you don't have one yet, you can create one.
If you're ready to move from one team to two teams, or configure several teams, see Add teams. To add a team administrator or configure team assets, see Manage teams and configure team tools.
For more information, see these articles:
- Practices that scale
- Visibility across teams
- Review team delivery plans
- Implement Scaled Agile Framework® to support epics, release trains, and multiple backlogs.
Agile culture industry resources
- Nexus, the Exoskeleton of Scaled Scrum
- Culture over process
- The Culture Game - Tools for the Agile Manager
- Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
- Scaling Agile Software Development, - Disciplined Agility at Scale (White Paper)
Scale with teams and not projects
Often, organizations look at adding a project for each software development project.
Adding teams to scale your tools rather than adding projects is recommended for the following reasons:
- Visibility: It's much easier to view progress across all teams
- Tracking and auditing: It's easier to link work items and other objects for tracking and auditing purposes
- Maintainability: You minimize the maintenance of security groups and process updates.
To learn more, see About projects and scaling your organization.