Remarque
L’accès à cette page nécessite une autorisation. Vous pouvez essayer de vous connecter ou de modifier des répertoires.
L’accès à cette page nécessite une autorisation. Vous pouvez essayer de modifier des répertoires.
S’applique à : SQL Server 2019 et versions antérieures d’Analysis Services
SQL Server 2019 et versions antérieures d’Analysis Services  Azure Analysis Services
Azure Analysis Services  Fabric/Power BI Premium
Fabric/Power BI Premium
Important
L’exploration de données a été déconseillée dans SQL Server 2017 Analysis Services et a maintenant été abandonnée dans SQL Server 2022 Analysis Services. La documentation n’est pas mise à jour pour les fonctionnalités déconseillées et abandonnées. Pour en savoir plus, consultez la compatibilité descendante des Analysis Services.
Aucune opération d’installation ou de récupération de Power Pivot pour SharePoint n’est terminée sans une passe de test de vérification solide qui confirme que vos services et données sont opérationnels. Dans cet article, nous vous montrons comment effectuer ces étapes à l’aide de Windows PowerShell. Nous mettons chaque étape dans sa propre section afin que vous puissiez accéder directement à des tâches spécifiques. Par exemple, exécutez le script dans la section Bases de données de cette rubrique pour vérifier le nom de l’application de service et des bases de données de contenu si vous souhaitez les planifier pour la maintenance ou la sauvegarde.
Un script PowerShell complet est inclus en bas de la rubrique. Utilisez le script complet comme point de départ pour créer un script personnalisé pour l’audit de votre déploiement Power Pivot complet pour SharePoint.
Préparer votre environnement PowerShell
Les étapes décrites dans cette section préparent votre environnement PowerShell. Les étapes peuvent ne pas être requises, selon la façon dont votre environnement de script est actuellement configuré.
Autorisations PowerShell
Ouvrez une fenêtre PowerShell ou PowerShell ISE (environnement de script intégré) avec des privilèges d’administration. Si vous n’avez pas de privilèges d’administration lorsque vous exécutez des commandes, un message d’erreur semblable à ce qui suit s’affiche :
Get-SPLogEvent : vous devez disposer de privilèges d’administrateur d’ordinateur pour exécuter cette applet de commande.
SharePoint et Power Pivot pour SharePoint Module
Si vous voyez un message d’erreur similaire à ce qui suit lorsque vous exécutez des applets de commande liées à SharePoint, exécutez la commande Add-PSSnapin :
Le terme « Get-PowerPivotSystemService » n’est pas reconnu comme nom d’une applet de commande, d’une fonction, d’un fichier de script ou d’un programme opérable. Vérifiez l’orthographe du nom ou, si un chemin d’accès a été inclus, vérifiez que le chemin d’accès est correct et réessayez.
Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.Sharepoint.Powershell -EA 0
Windows PowerShell
 Vous pouvez vérifier la majorité des composants dans l’Administration centrale, à l’aide du tableau de bord de gestion Power Pivot. Pour ouvrir le tableau de bord dans l’Administration centrale, cliquez sur Paramètres généraux de l’application, puis sur Tableau de bord de gestion dans Power Pivot. Pour plus d’informations sur le tableau de bord, consultez Tableau de bord de gestion Power Pivot et Données d’utilisation.
Vous pouvez vérifier la majorité des composants dans l’Administration centrale, à l’aide du tableau de bord de gestion Power Pivot. Pour ouvrir le tableau de bord dans l’Administration centrale, cliquez sur Paramètres généraux de l’application, puis sur Tableau de bord de gestion dans Power Pivot. Pour plus d’informations sur le tableau de bord, consultez Tableau de bord de gestion Power Pivot et Données d’utilisation.
Symptômes et actions recommandées
Le tableau suivant répertorie les symptômes ou les problèmes et la section suggérée de cette rubrique pour vous aider à résoudre le problème.
| Symptôme | Voir la section |
|---|---|
| L’actualisation des données n’est pas en cours d’exécution | Consultez la section Travaux du minuteur et vérifiez que le travail du minuteur d’actualisation des données Power Pivot en ligne est en ligne. |
| Les données du tableau de bord de gestion sont anciennes | Consultez la section Travaux du minuteur et vérifiez que le travail du minuteur de traitement du tableau de bord de gestion est en ligne. |
| Certaines parties du tableau de bord de gestion | Si vous installez Power Pivot pour SharePoint dans une batterie de serveurs disposant de la topologie de l’administration centrale, sans Excel Services ou Power Pivot pour SharePoint, vous devez télécharger et installer la bibliothèque cliente Microsoft ADOMD.NET si vous souhaitez accéder entièrement aux rapports intégrés dans le tableau de bord de gestion Power Pivot. Certains rapports du tableau de bord utilisent ADOMD.NET pour accéder aux données internes qui fournissent des données de création de rapports sur le traitement des requêtes Power Pivot et la santé du serveur dans le réseau de serveurs. |
Service Windows des services d'analyse
Le script de cette section vérifie l’instance de SQL Server Analysis Services en mode SharePoint. Vérifiez que le service est en cours d’exécution.
get-service | select name, displayname, status | where {$_.Name -eq "msolap`$powerpivot"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
Name DisplayName Status
---- ----------- ------
MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT SQL Server Analysis Services (POWERPIVOT) Running
PowerPivotSystemService et PowerPivotEngineService
Les scripts de cette section vérifient les services système Power Pivot pour SharePoint. Il existe un service système pour un déploiement SharePoint 2013 et deux services pour un déploiement SharePoint 2010.
PowerPivotSystemService
Vérifiez que l’état est en ligne.
Get-PowerPivotSystemService | select typename, status, applications, farm | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
TypeName Status Applications Farm
-------- ------ ------------ ----
SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application Online {Default PowerPivot Service Application} SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config_77d8ab0744a34e8aa27c806a2b8c760c
PowerPivotEngineService
Note
Ignorez ce script si vous utilisez SharePoint 2013. PowerPivotEngineService ne fait pas partie d’un déploiement SharePoint 2013. Si vous exécutez l’applet de commande Get-PowerPivotEngineService sur SharePoint 2013, un message d’erreur similaire à ce qui suit s’affiche. Ce message d’erreur est retourné même si vous avez exécuté la commande Add-PSSnapin décrite dans la section conditions préalables de cette rubrique.
Le terme « Get-PowerPivotEngineService » n’est pas reconnu comme nom d’une applet de commande
Dans un déploiement SharePoint 2010, vérifiez que l’état est En ligne.
Get-PowerPivotEngineService | select typename, status, name, instances, farm | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
TypeName : SQL Server Analysis Services
Status : Online
Name : MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT
Instances : {POWERPIVOT}
Farm : SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config
Application(s) de service Power Pivot et proxys
Vérifiez que l’état est En ligne. L’application Excel Services n’utilise pas de base de données d’application de service et, par conséquent, l’applet de commande ne retourne pas de nom de base de données. Notez la base de données utilisée par l’application de service Power Pivot pour vous permettre de vérifier que la base de données est en ligne dans la section de base de données plus loin dans cette rubrique.
Application(s) de service Power Pivot et Excel
Pour un déploiement SharePoint 2010, vérifiez que l’état est En ligne.
Get-PowerPivotServiceApplication | select typename,name, status, unattendedaccount, applicationpool, farm, database
Get-SPExcelServiceApplication | select typename, DisplayName, status
Exemple de sortie
TypeName : PowerPivot Service Application
Name : PowerPivotServiceApplication1
Status : Online
UnattendedAccount : PowerPivotUnattendedAccount
ApplicationPool : SPIisWebServiceApplicationPool Name=sqlbi_serviceapp
Farm : SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config
Database : GeminiServiceDatabase Name=PowerPivotServiceApplication1_19648f3f2c944e27acdc6c20aab8487a
TypeName : Excel Services Application Web Service Application
DisplayName : Excel Services Application
Status : Online
Pool d’applications de service
Note
L’exemple de code suivant retourne d’abord la propriété applicationpool de l’application de service Power Pivot pour SharePoint par défaut. Le nom est analysé à partir de la chaîne et utilisé pour obtenir l’état de l’objet du pool d’applications.
Vérifiez que le statut est en ligne. Si l’état n’est pas En ligne ou que vous voyez « erreur http » lorsque vous parcourez le site Power Pivot, vérifiez que les informations d’identification d’identité dans les pools d’applications IIS sont toujours correctes. Le nom du pool IIS correspond à la valeur de la propriété ID retournée par la commande Get-SPServiceApplicationPool.
$poolname=[string](Get-PowerPivotServiceApplication | select -property applicationpool)
$position=$poolname.lastindexof("=")
$poolname=$poolname.substring($position+1)
$poolname=$poolname.substring(0,$poolname.length-1)
Get-SPServiceApplicationPool | select name, status, processaccountname, id | where {$_.Name -eq $poolname} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
Name Status ProcessAccountName Id
---- ------ ------------------ -------
SharePoint Web Services System Online DOMAIN\account 89b50ec3-49e3-4de7-881a-2cec4b8b73ea
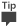 le pool d’applications peut également être vérifié dans la page Administration centrale Gérer les applications de service. Cliquez sur le nom de l’application de service, puis cliquez sur propriétés dans le ruban.
le pool d’applications peut également être vérifié dans la page Administration centrale Gérer les applications de service. Cliquez sur le nom de l’application de service, puis cliquez sur propriétés dans le ruban.
Proxys d’application Power Pivot et Excel Service
Vérifiez que l’état est En ligne.
Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy | select typename, status, unattendedaccount, displayname | where {$_.TypeName -like "*powerpivot*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*excel services*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
TypeName Status UnattendedAccount DisplayName
-------- ------ ----------------- -----------
PowerPivot Service Application Proxy Online PowerPivotUnattendedAccount PowerPivotServiceApplication1
Excel Services Application Web Service Application Proxy Online Excel Services Application
Databases
Le script suivant retourne l’état des bases de données d’application de service et de toutes les bases de données de contenu. Vérifiez que l’état est En ligne.
Get-SPDatabase | select name, status, server, typename | where {$_.TypeName -eq "content database" -or $_.TypeName -like "*Gemini*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
Name Status Server TypeName
---- ------ ------ --------
DefaultPowerPivotServiceApplicationDB-38422181-2b68-4ab2-b2bb-9c00c39e5a5e Online SPServer Name=TESTSERVER Microsoft.AnalysisServices.SPAddin.GeminiServiceDatabase
DefaultWebApplicationDB-f0db1a8e-4c22-408c-b9b9-153bd74b0312 Online TESTSERVER\POWERPIVOT Content Database
SharePoint_Admin_3cadf0b098bf49e0bb15abd487f5c684 Online TESTSERVER\POWERPIVOT Content Database
Fonctionnalités SharePoint
Vérifiez que les fonctionnalités du site, du réseau et de la batterie de serveurs sont en ligne.
Get-SPFeature | select displayname, status, scope, farm | where {$_.displayName -like "*powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
DisplayName Status Scope Farm
----------- ------ ----- ----
PowerPivotSite Online Site SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config
PowerPivotAdmin Online Web SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config
PowerPivot Online Farm SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config
Travaux du minuteur
Vérifiez que les tâches planifiées sont en ligne. Power Pivot EngineService n’est pas installé sur SharePoint 2013. Par conséquent, le script ne répertorie pas les travaux du minuteur EngineService dans un déploiement SharePoint 2013.
Get-SPTimerJob | where {$_.service -like "*power*" -or $_.service -like "*mid*"} | select status, displayname, LastRunTime, service | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
Status DisplayName LastRunTime Service
------ ----------- ----------- -------
Online Health Analysis Job (Daily, SQL Server Analysis Services, All Servers) 4/9/2014 12:00:01 AM EngineService Name=MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT
Online Health Analysis Job (Hourly, SQL Server Analysis Services, All Servers) 4/9/2014 1:00:01 PM EngineService Name=MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT
Online Health Analysis Job (Weekly, SQL Server Analysis Services, All Servers) 4/6/2014 12:00:10 AM EngineService Name=MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT
Online PowerPivot Management Dashboard Processing Timer Job 4/8/2014 3:45:38 AM MidTierService
Online PowerPivot Health Statistics Collector Timer Job 4/9/2014 1:00:12 PM MidTierService
Online PowerPivot Data Refresh Timer Job 4/9/2014 1:09:36 PM MidTierService
Online Health Analysis Job (Daily, SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application, All Servers) 4/9/2014 12:00:00 AM MidTierService
Online Health Analysis Job (Daily, SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application, Any Server) 4/9/2014 12:00:00 AM MidTierService
Online Health Analysis Job (Weekly, SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application, All Servers) 4/6/2014 12:00:03 AM MidTierService
Online Health Analysis Job (Weekly, SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application, Any Server) 4/6/2014 12:00:03 AM MidTierService
Online PowerPivot Setup Extension Timer Job 4/1/2014 1:40:31 AM MidTierService
Règles de santé
Il existe moins de règles dans un déploiement SharePoint 2013. Pour obtenir la liste complète des règles pour chaque environnement SharePoint et une explication de l’utilisation des règles, consultez Configurer des règles d’intégrité Power Pivot.
Get-SPHealthAnalysisRule | select name, enabled, summary | where {$_.summary -like "*power*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
Name Enabled Summary
---- ------- -------
SecondaryLogonHealthRule True PowerPivot: Secondary Logon service (seclogon) is disabled
DataRefreshTimerJobHealthRule True PowerPivot: The PowerPivot Data Refresh timer job is disabled.
ASUsageLoadHealthRule True PowerPivot: The ratio of load events to connections is too high.
ASMiniDumpHealthRule True PowerPivot: One or more minidump files were found in the Logs directory, indicating a program crash
ASUsageCubeRule True PowerPivot: Usage data is not getting updated at the expected frequency.
ASADOMDNETHealthRule True PowerPivot: ADOMD.NET is not installed on a standalone WFE that is configured for central admin
MidTierAcctReadPermissionRule True PowerPivot: MidTier process account should have 'Full Read' permission on all associated SPWebApplications.
Journaux Windows et ULS (Service de journalisation unifié)
Journal des événements Windows
La commande suivante recherche dans le journal des événements Windows les événements liés à l’instance de SQL Server Analysis Services en mode SharePoint. Pour plus d’informations sur la désactivation des événements ou la modification du niveau d’événement, consultez Configurer et afficher les fichiers journaux SharePoint et la journalisation des diagnostics (Power Pivot pour SharePoint)
Nom du service : MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT
Nom complet dans les services Windows : SQL Server Analysis Services (POWERPIVOT)
Get-EventLog "application" | Where-Object {$_.source -like "msolap`$powerpivot*"} |select timegenerated, entrytype , source, message | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
TimeGenerated EntryType Source Message
------------- --------- ------ -------
4/16/2014 1:45:19 PM Information MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT Software usage metrics are disabled.
4/16/2014 1:45:19 PM Information MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT Service started. Microsoft SQL Server Analysis Services 64 Bit Evaluation (x64) RTM 12.0.1997.5.
4/16/2014 1:45:18 PM Information MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT The flight recorder was started.
4/14/2014 6:45:37 PM Information MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT Software usage metrics are disabled.
Journal ULS SharePoint, dernières 48 heures
Les messages Power Pivot du journal ULS créés au cours des 48 dernières heures seront retournés par la commande suivante. Ajustez le paramètre addhours pour vos besoins.
Get-SPLogEvent -starttime(get-date).addhours(-48) | Where-Object {$_.Area -eq "powerpivot service" -and $_.level -eq "high"} | select timestamp, area, category, eventid,level, message| format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
La variante suivante de la commande retourne uniquement les événements de journal pour la catégorie d’actualisation des données .
Get-SPLogEvent -starttime(get-date).addhours(-48) | Where-Object {$_.category -eq "data refresh" -and $_.level -eq "high"} | select timestamp, area, category, eventid, level, correlation, message
Exemple de sortie
Timestamp : 4/14/2014 7:15:01 PM
Area : PowerPivot Service
Category : Data Refresh
EventID : 43
Level : High
Correlation : 5755879c-7cab-e097-8f80-f27895d44a77
Message : The following error occured when working with the service application, Default PowerPivot Service Application. Skipping the service application..
Timestamp : 4/14/2014 7:15:02 PM
Area : PowerPivot Service
Category : Data Refresh
EventID : 99
Level : High
Correlation : 5755879c-7cab-e097-8f80-f27895d44a77
Message : EXCEPTION: System.TimeoutException: The request channel timed out while waiting for a reply after 00:00:47.0625313. Increase the timeout value passed to
the call to Request or increase the SendTimeout value on the Binding. The time allotted to this operation may have been a portion of a longer timeout.
---> System.TimeoutException: The HTTP request to 'http://localhost:32843/SecurityTokenServiceApplication/securitytoken.svc/actas' has exceeded the
allotted timeout of 00:00:54.5930000. The time allotted to this operation may have been a portion of a longer timeout. ---> System.Net.WebException: The
operation has timed out at System.Net.HttpWebRequest.GetResponse() at
System.ServiceModel.Channels.HttpChannelFactory`1.HttpRequestChannel.HttpChannelRequest.WaitForReply(TimeSpan timeout...
Fournisseur MSOLAP
Vérifiez le fournisseur MSOLAP. SQL Server 2012 (11.x) et SQL Server 2014 (12.x) Power Pivot nécessitent MSOLAP.5.
$excelApp=Get-SPExcelServiceApplication
get-spexceldataprovider -ExcelServiceApplication $excelApp |select providerid,providertype,description | where {$_.providerid -like "msolap*" } | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
ProviderId ProviderType Description
---------- ------------ -----------
MSOLAP Oledb Microsoft OLE DB Provider for OLAP Services
MSOLAP.3 Oledb Microsoft OLE DB Provider for OLAP Services 9.0
MSOLAP.4 Oledb Microsoft OLE DB Provider for OLAP Services 10.0
MSOLAP.5 Oledb Microsoft OLE DB Provider for OLAP Services 11.0
bibliothèque cliente ADOMD.Net
get-wmiobject -class win32_product | Where-Object {$_.name -like "*ado*"} | select name, version, vendor | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
name version vendor
---- ------- ------
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services ADOMD.NET 10.1.2531.0 Microsoft Corporation
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Analysis Services ADOMD.NET 9.00.1399.06 Microsoft Corporation
Règles de collecte des données de santé
Vérifiez que l’état est En Ligne et Activé est Vrai.
get-spusagedefinition | select name, status, enabled, tablename, DaysToKeepDetailedData | where {$_.name -like "powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie
Name Status Enabled TableName DaysToKeepDetailedData
---- ------ ------- --------- ----------------------
PowerPivot Connections OnlineTrue AnalysisServicesConnections 14
PowerPivot Load Data Usage Online True AnalysisServicesLoads 14
PowerPivot Query Usage Online True AnalysisServicesRequests 14
PowerPivot Unload Data Usage Online True AnalysisServicesUnloads 14
Pour plus d’informations, consultez La collecte de données d’utilisation de Power Pivot.
Solutions
Si les autres composants sont en ligne, vous pouvez ignorer la vérification des solutions. Si toutefois les règles de santé sont manquantes, vérifiez que les deux solutions existent et que les deux solutions Power Pivot sont en ligne et déployées.
get-spsolution | select name, status, deployed, DeploymentState, DeployedServers | where {$_.Name -like "*powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Exemple de sortie SharePoint 2013
Name Status Deployed DeploymentState DeployedServers
---- ------ -------- --------------- ---------------
powerpivotfarm14solution.wsp Online True GlobalDeployed {UETESTA00}
powerpivotfarmsolution.wsp Online True GlobalDeployed {UETESTA00}
powerpivotwebapplicationsolution.wsp Online True WebApplicationDeployed {UETESTA00}
Exemple de sortie SharePoint 2010
Name Status Deployed DeploymentState DeployedServers
---- ------ -------- --------------- ---------------
powerpivotfarm.wsp Online True GlobalDeployed {uesql11spoint2}
powerpivotwebapp.wsp Online True WebApplicationDeployed {uesql11spoint2}
Pour plus d’informations sur le déploiement de solutions SharePoint, consultez Déployer des packages de solutions (SharePoint Server 2010).
Étapes de vérification manuelle
Cette section décrit les étapes de vérification qui ne peuvent pas être effectuées avec les applets de commande PowerShell.
Actualisation planifiée des données : Configurez la planification de l’actualisation pour qu’un classeur soit également actualisé dès que possible. Pour plus d’informations, consultez la section « Vérifier l’actualisation des données » de la planification de l’actualisation des données et des sources de données qui ne prennent pas en charge l’authentification Windows (Power Pivot pour SharePoint).
Autres ressources
Applets de commande d’administration de serveur web (IIS) dans Windows PowerShell.
Informations de référence sur Windows PowerShell pour SharePoint 2013
Informations de référence sur Windows PowerShell pour SharePoint Foundation 2010
Gérer Excel Services avec Windows PowerShell (SharePoint Server 2010)
Afficher et lire les fichiers journaux d’installation de SQL Server
Utiliser l’applet de commande Get-EvenLog
Script PowerShell complet
Le script suivant contient toutes les commandes des sections précédentes. Le script exécute les commandes dans le même ordre qu’elles sont présentées dans cette rubrique. Le script contient certaines variantes facultatives des commandes indiquées dans cette rubrique dans le cas où vous avez besoin d’un filtrage supplémentaire. Les variantes sont désactivées avec un caractère de commentaire (#). Le script inclut également des instructions pour vérifier le mode SharePoint de Reporting Services. Les déclarations Reporting Services sont désactivées avec un caractère de commentaire (#).
# This script audits services related to PowerPivot for SharePoint
$starttime=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime $starttime
Write-Host "Import the SharePoint PowerShell snappin"
Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.Sharepoint.Powershell -EA 0
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Analysis Services Windows Service"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
get-service | select name, displayname, status | where {$_.Name -eq "msolap`$powerpivot"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "PowerPivotEngineService and PowerPivotSystemService"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-PowerPivotSystemService | select typename, status, applications, farm | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
# If needed, you can run the following to compare job definitions specific to the service against the results of the timer job definition section
#Get-PowerPivotSystemService | select -ExpandProperty jobdefinitions | select displayname, schedule, service | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Get-PowerPivotEngineService | select typename, status, name, instances, farm | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
# If needed, you can run the following to compare job definitions specific to the service against the results of the timer job definition section
#Get-PowerPivotEngineService | select -ExpandProperty jobdefinitions | select displayname, schedule, service | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
#Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Service Instances - optional if you want to associate services with the server"
#Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
#Get-SPServiceInstance | select typename, status, server, service, instance | where {$_.TypeName -like "*powerpivot*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*excel*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*Analysis Services*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Get-PowerPivotEngineServiceInstance | select typename, ASServername, status, server, service, instance
#Get-PowerPivotSystemServiceInstance | select typename, ASSServerName, status, server, service, instance
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "PowerPivot And Excel Service Applications"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-PowerPivotServiceApplication | select typename,name, status, unattendedaccount, applicationpool, farm, database
Get-SPExcelServiceApplication | select typename, DisplayName, status
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "PowerPivot Service Application pool"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
# the following assumes there is only 1 PowerPivot Service Application, and returns that applicaitons pool name. if you have more than one, use the 2nd version
$poolname=[string](Get-PowerPivotServiceApplication | select -property applicationpool)
$position=$poolname.lastindexof("=")
$poolname=$poolname.substring($position+1)
$poolname=$poolname.substring(0,$poolname.length-1)
Get-SPServiceApplicationPool | select name, status, processaccountname, id | where {$_.Name -eq $poolname} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "PowerPivot and Excel Service Application Proxy"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy | select typename, status, unattendedaccount, displayname | where {$_.TypeName -like "*powerpivot*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*excel services*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy | select typename, status, unattendedaccount, displayname | where {$_.TypeName -like "*powerpivot*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*Reporting Services*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*excel services*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "DATABASES"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPDatabase | select name, status, server, typename | where {$_.TypeName -eq "content database" -or $_.TypeName -like "*Gemini*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Get-SPDatabase | select name, status, server, typename | where {$_.TypeName -eq "content database" -or $_.TypeName -like "*Gemini*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*ReportingServices*"}
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "features"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPFeature | select displayname, status, scope, farm| where {$_.displayName -like "*powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Get-SPFeature | select displayname, status, scope, farm | where {$_.displayName -like "*powerpivot*" -or $_.displayName -like "*ReportServer*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Timer Jobs (Job Definitions) -- list is the same as seen in the 'Review timer job definitions' section of the management dashboard"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPTimerJob | where {$_.service -like "*power*" -or $_.service -like "*mid*"} | select status, displayname, LastRunTime, service | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "health rules"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPHealthAnalysisRule | select name, enabled, summary | where {$_.summary -like "*power*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
$time=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime $starttime
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray EndTime $time
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Windows Event Log data MSSQL$POWERPIVOT and "
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-EventLog "application" | Where-Object {$_.source -like "msolap`$powerpivot*"} |select timegenerated, entrytype , source, message | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#The following is the same command but with the Inforamtion events filtered out.
#Get-EventLog "application" | Where-Object {$_.source -like "msolap`$powerpivot*" -and ($_.entrytype -match "error" -or $_.entrytype -match "critical" -or $_.entrytype -match "warning")} |select timegenerated, entrytype , source, message | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "ULS Log data"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPLogEvent -starttime(get-date).addhours(-48) | Where-Object {$_.Area -eq "powerpivot service" -and $_.level -eq "high"} | select timestamp, area, category, eventid,level, correlation, message| format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#the following example filters for the category 'data refresh'
#Get-SPLogEvent -starttime(get-date).addhours(-48) | Where-Object {$_.category -eq "data refresh" -and $_.level -eq "high"} | select timestamp, area, category, eventid, level, correlation, message
$time=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime $starttime
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray EndTime $time
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "MSOLAP data provider for Excel Servivces, service application"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
$excelApp=Get-SPExcelServiceApplication
get-spexceldataprovider -ExcelServiceApplication $excelApp |select providerid,providertype,description | where {$_.providerid -like "msolap*" } | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "ADOMD.net client library"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
get-wmiobject -class win32_product | Where-Object {$_.name -like "*ado*"} | select name, version, vendor | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Usage Data Rules"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
get-spusagedefinition | select name, status, enabled, tablename, DaysToKeepDetailedData | where {$_.name -like "powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Solutions"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
get-spsolution | select name, status, deployed, DeploymentState, DeployedServers | where {$_.Name -like "*powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
$time=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime $starttime
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray EndTime $time