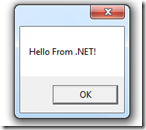
Using .NET library in VBA
Three easy steps for exporting .NET functionality to VBA:
1. Write a source file:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace InteropTest
{
[Guid("BEB2C62D-5646-4B08-81DF-670314BFEE4A")]
public class InteropTestClass
{
public void Help()
{
MessageBox.Show("Hello From .NET!");
}
}
}
The GUID needs to be unique.
2. Generate a strong key to sign the assembly:
sn -k MyKey.snk
3. Compile the C# file using CSC:
csc /target:library /out:tstint.dll MyClass.cs /keyfile:MyKey.snk
We now have a DLL that can be exported to another machine with the .NET Framework installed. On the target machnie, the assembly needs to be registered:
regasm tstint.dll /codebase /tlb:tstint.tlb
Now the library can be used in Office by selecting it from the list of references in VBA:
Comments
- Anonymous
November 13, 2015
But I want to use .NET just because I don't want the final user install anithing apart from Office!