Kerberos Authentication in SQLServer
There are two authentication scheme which can be used by SQLserver when connecting to SQLserver using TCP/IP Protocol and windows authentication.
1. NTLM
2. Kerberos
When we use Kerberos we get ability to delegate a principal's identity and it is More efficient than NTLM - Caching mechanism and it works based on Based on encrypted tickets with client credentials
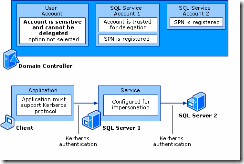
Let us take a small example to understand Double hop and delegation in simple way
====================================================================
Refer the below image
Create a linked server from SQLServer1 to SQLserver2 (in linked server security select "be made using the logins current security context")
Folow the below steps
-------------------------------
Case1
====
1. Login to the server where SQLServer1 instance is running.
2. Connect to SQLServer1 instance with windows authentication using SSMO or Query analyzer,Then run a Distributed query using the linked server to SQLserver2
It will work with both NTLM and Kerberos
Case2
====
1. Login to one of your work station (It should be different server from where SQLServer1/2 instance is running).
2. Connect to SQLServer1 instance using SSMO or Query analyzer,Then run a Distributed query using the linked server to SQLserver2.
It will Not work with NTLM.
It will work only with Kerberos.
To find which authentication scheme we are using run the below query
select net_transport,auth_scheme from sys.dm_exec_connections where session_id=@@spid
"unable to register the Service principle name." is logged in SQLerror log if the SQLServer Startup account do not have permissions to register the SPN in the active directory(SPN will registered by the SQLServer startup account every time SQLServer service is started and deleted when it is shutdown).
If we find that the Case2 did not work or Auth_scheme returned NTLM (By running select net_transport,auth_scheme from sys.dm_exec_connections where session_id=@@spid
)
Check the following check list
CLIENT ---> SQLSERVER1 ---> SQLSERVER2
User1 ---> User1(Impersonated)---> User1
Requirements
-------------------
CLIENT User Account and Startup account of SQLServer
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
If the startup account/User Account is in a Windows Server 2003 functional level domain, in active directory users and computers Right-click Startup account, and then click Propertiesclick the Delegation tab. select Trust this user for delegation to any service (Kerberos only) .
If the startup account/User account is in a Windows Server 2000 functional level domain, in active directory users and computers Right-click Startup account, and then click , In the Account options box, confirm that Account is sensitive and cannot be delegated is not selected.
BACK END SERVER
-------------------------
- SPN is registered for all the SQLServer instances.
Troubleshoot Steps
--------------------------
(1) Verify from the Client Computer that ping FQDN (SQLServer) and ping -a
IP_Address (SQLServer) return the same FQDN. Also check if this is the expected
FQDN and points to the correct SPNs
Ping MySql.Domain.Com
Result 10.10.10.1
Ping -a 10.10.10.1
Result MySQl.Domain.Com
(2) Verify that SPNs are registered for the middle and back end servers
MSSQLSvc/HostComputer_FQDN:PORTNUMBER SQLServer_ServiceAccount
OR
MSSQLSvc/HostComputer_FQDN:PORTNUMBER HostComputer_ComputerAccount
AND for cluster installation (SQL Virtual Server)
MSSQLSvc/SQLVirtualServer_FQDN SQLServer_ServiceAccount
MSSQLSvc/SQLVirtualServer_FQDN:PORTNUMBER SQLServer_ServiceAccount
To add an SPN Use
setspn -A "MSSQLSvc/MySql.Domain.Com:1433" "DOMAIN\sqlsvc"
To delete an SPN use
setspn -D "MSSQLSvc/MySql.Domain.Com:1433" "DOMAIN\sqlsvc"
To List SPN for a specific account use
setspn -L "DOMAIN\sqlsvc"
setspn can be downloaded from MSN site.
- Also use SPN Query to search for duplicate spns under different accounts (This
is very common)
https://www.microsoft.com/technet/scriptcenter/solutions/spnquery.mspx
(3) SQL Server Service will automatically register its required SPN if the account
running the service has these rights in AD: Read servicePrincipalName and Write
servicePrincipalName
Read topic: How to configure the SQL Server service to create SPNs dynamically
for the SQL Server instances in KB 811889
(4) For the Client account, Verify that "Account is sensitive and cannot be
delegated is NOT selected"
Open Active Directory Users and Computers; Right-click the user account, and
then click Properties; Click the Account tab; In the Account options box, confirm
that Account is sensitive and cannot be delegated is not selected.
(5) For the Middle Server, account verify that Account is trusted for delegation or
computer is trusted for delegation is set
If middle tier service is using the computer account: Open Active Directory
Users and Computers; Right-click the computer account, and then click Properties
If the account is in a Windows 2000 functional level domain, verify that
the Account is trusted for delegation option is selected.
If the account is in a Windows Server 2003 functional level domain,
configure options on the Delegation tab.
If middle tier service is using a domain user account: Open Active Directory
Users and Computers; Right-click the service account, and then click Properties.
If the service account is in a Windows 2000 functional level domain, the
Account is trusted for delegation option on the Account tab should be selected.
If the computer account is in a Windows Server 2003 functional level
domain, configure options on the Delegation tab.
(6)For the Middle Server, verify that the account that is running SQL Server is
member of "Impersonate a client after authentication". If the client account has
not been authenticated yet (at the front line server) we need to add the "Act as
part of the operating system" policy as well.
Open the domain security policy by clicking Start, Programs, Administrative
Tools, and then Domain Security Policy; Click Local Policies, and then click User
Rights Assignment; verify that the account that is running SQL Server is member of
"Impersonate a client after authentication". If the client account has not been
authenticated yet (at the front line server) we need to add the "Act as part of the
operating system" policy as well.
Test
----
- If we are using SQL2005 from a workstation you may query the sys.dm_exec_connections DMV
and look under the auth_scheme column:
select auth_scheme from sys.dm_exec_connections where session_id=@@spid
If Kerberos is being used, then it will display "KERBEROS".
Tools
-----
- To setup account permissions you can use "Active Directory Users and Computers"
- To manage SPNs you can use SETSPN.exe or ADSIEDIT.msc
- To manage policy use "Domain Security Policy Group Policy" or "Local Security
Policy" editors
Notes
-----
- Pre-Windows 2000 cannot use Kerberos natively
- TCP/IP is required for Kerberos
- Kerberos ports must be open in the Firewall (88/TCP, 88/UDP)
- DNS Must be working in the client to obtain the FQDN
- Time on computers must be synchronized
-SQLServer Service startup account should have Read servicePrincipalName and Write servicePrincipalName in AD to create SPN's Dyanamically
Common Error Messages
---------------------
- Cannot generate SSPI context
- Login failed for user '(null)'. Reason: Not associated with a trusted SQL Server
connection.
- Logon failed for null user
- Login failed for user 'NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGON'
- Cannot generate SSPI Context
- Login failed for user NULL Reason not associated with a trusted SQL server
connection
References
----------
How to troubleshoot the "Cannot generate SSPI context" error message
< https://support.microsoft.com/kb/811889 >
How to use Kerberos authentication in SQL Server
< https://support.microsoft.com/?id=319723 >
1.When we are using the named pipe Protocol it will not use Kerberos authentication and can overcome any of above issues.
2.In windows 2003 and named instance of SQLserver2005 there is a problem occurs during the discovery phase of the connection. The IPSec policy on the client drops packets from the server when the source IP changes. This happens if the IPSec policy is enabled on client domain and TCP/IP sockets are used for connection.
Regards
Karthick PK
Comments
Anonymous
January 22, 2009
PingBack from http://blog.a-foton.ru/index.php/2009/01/23/kerberos-authentication-in-sqlserver/Anonymous
June 26, 2012
An excellent article ( a pity i have discovered it only today , it would have been useful for me in the SQL Server Data Access Forum ) Some remarks i hope they will not vexate you At the beginning of your article , you wrote
- SSMO . Please, could you explain what it does mean ? If SQL Server Management Objects, i think that the "official" shortcut is SMO
- "Service principle name" . Maybe Service PrinciPal Name (SPN) Already put in my favorites ( i am sure to use it in less than 4 months ) Thanks