Part 6: Managing Local Administrator Passwords
Overview
This is Part 6 of a multi-part series on managing local admin passwords. In this part I will discuss how to extend the Active Directory schema to create a new confidential attribute which is where the workstation's local administrator password will be stored. In case you missed it:
Here is Part 1 - Overview
Here is Part 2 - Random Password Generation
Here is Part 3 - Secure Active Directory Attribute Update
Here is Part 4 - Update Local Account's Password
Here is Part 5 - Logging The Update Process
If you want to skip straight to the ldf file you can copy it from this post directly, or you can download the file which is attached to this post as a text file. The attached file should be renamed to a *.ldf file to properly import.
The Problem
One of the challenges associated with randomizing the local admin passwords for every workstation in a forest is how to store and retrieve the local admin workstation password when it is needed. Ideally, this scenario is not frequently needed since domain credentials will suffice for domain joined workstations, however there are times when the local admin account credentials are needed such as when the network connection to the domain controllers is unavailable.
The Solution
In this post I will show you how to create a new schema attribute, mark it as confidential, and associate it with the computer class. The new attribute will be used to store the local admin password and Part 8 of this series will show you how to securely retrieve the password when needed by using a secure XAML password viewer.
In case you are unfamiliar with confidential attributes, I suggest you review KB922836. That article goes into great detail on what a confidential attribute is, how to create it, and how to delegate permissions to users or groups of users to view its contents.
For this solution I created an ldf file with the following contents:
dn: CN=LocalAdminPWD,CN=Schema,Cn=Configuration,DC=contoso,DC=com
changetype: add
objectClass: attributeSchema
lDAPDisplayName: LocalAdminPWD
adminDescription: This attribute stores domain joined workstation's local administrator password
attributeID: 1.2.840.113556.1.8000.2554.1
attributeSyntax: 2.5.5.12
oMSyntax: 64
isSingleValued: TRUE
showInAdvancedViewOnly: TRUE
searchFlags: 128
dn:
changeType: modify
add: schemaupdatenow
schemaupdatenow: 1
-
dn: CN=Computer,CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=contoso,DC=com
changetype: modify
add: mayContain
mayContain: LocalAdminPWD
-
The preceding text, when saved to an LDF file will create a new schema single valued attribute called LocalAdminPWD and associate it with the Computer Class. I used oidgen to generate the OID used for the attribute. I do suggest that you read a bit more about OIDs and the iso.org recommended way of obtaining them here prior to deciding to use oidgen. You should also be aware that the ldf file will need to be updated to reflect your organization's schema partition prior to importing the ldf. In my sample ldf above, contoso.com was my forest root.
Update The Schema
- Create an *.ldf file and modify it to reflect the attribute name you wish to use and the path to the schema partition.
- Log into a domain controller with a user account that is a member of Schema Admins
- Copy the ldf file to the domain controller and run it with the following command: ldifde -i -f <filename.ldf>
- Go to Start > Run > adsiedit.msc
- Click Action > Connect to > Select a well-known Naming Context > Schema > OK
- Right click Schema > Update Schema Now then click Refresh
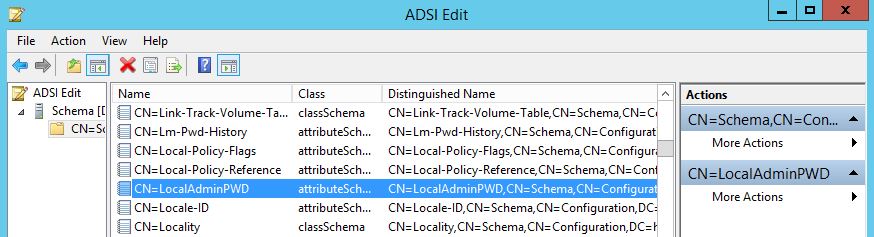
You should see a new attribute in the Schema as shown below:
It looks just like any other attribute in the Schema so to verify that it is a confidential attribute Right Click > Properties and locate the SearchFlags Attribute. It should be marked CONFIDENTIAL as shown below.
Locate a computer object in Active Directory > Properties > Attribute Editor > you should see a new Attribute for the Computer Object as shown below.
Note: if you had Active Directory Users and Computers open when you created the new attribute, you will need to close and re-open Active Directory Users and Computers before you can view the new attribute.
Delegate Permissions
For any administrators to read the contents of the new custom attribute, the following steps will configure inheritance at an OU level to allow authorized users to read the new custom attribute for each Computer object within the OU. I recommend that you create two different security groups to ensure Desktop Support admins only have the rights to read local workstation passwords and Server Support admins only have the rights to read server local admin passwords.
Note: Domain Admins will not by default have the rights needed to view the contents of the confidential attribute unless explicitly granted the permissions to do so.
The following steps are for Windows Server 2012 R2 ADDS. Windows Server 2008 R2 will require navigating slightly different dialogue boxes to achieve the same effect.
- Launch Active Directory Users and Computers using an account that has Domain Admin rights.
- Create two domain local groups, one named AD-Workstations OU-Read-Attribute-LocalAdminPWD and one named AD-MemberServers OU-Read-Attribute-LocalAdminPWD. The names here are just examples, I prefer to use descriptive names so that I can quickly identify exactly what permissions a domain local group provides.
- Locate the OU where you intend to delegate permissions to read the custom attribute. For the purposes of this example that OU is called Workstations.
- Right Click > Properties > Security Tab > Advanced > Add > Select a Principal
- Enter the AD-Workstations OU-Read-Attribute-LocalAdminPWD group as the name then click OK
- Drop down the Applies to: combo box and select Descendent Computer objects
- Scroll to the very bottom and click the Clear All button.
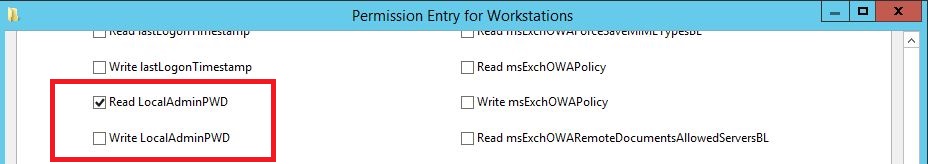
- Locate the confidential attribute that was created using the ldf file and select allow Read.
- Click OK > OK > OK
- Repeat these steps for the Member Servers OU. Ensure you select the AD-MemberServers OU-Read-Attribute-LocalAdminPWD domain local group when configuring the Member Servers OU.
The following image shows the custom attribute for descendent computer objects located in the Workstations OU.
You now have two domain local groups which give its members the rights to read the local admin passwords for their respective computer objects. Create two Domain Global groups or use two existing Domain Global groups that contain Server Admins and Workstation Admins. Make the Server Admins domain global group a member of the AD-MemberServers OU-Read-Attribute-LocalAdminPWD and make the Workstation Admins domain global group a member of the AD-Workstations OU-Read-Attribute-LocalAdminPWD. The final step is to identify your server administrators and make them a member of the Server Admins group while making the workstation administrators a member of the Workstation Admins group. This ADGLP concept can be used to scale to any organizational size, and groups can be delegated with as much granularity as you wish based on any number of factors (i.e. site, escalation model, etc.) Describing AGDLP is beyond the scope of this post but you can go here for additional reading.
So far you have created two domain local groups each of which only has rights to read the confidential attribute which stores the local admin passwords for specific types of computers; servers and workstations. Now it is time to give the computer's themselves the rights to update the confidential local admin password attribute in Active Directory.
- Launch Active Directory Users and Computers using an account that has Domain Admin rights.
- Locate the OU where you intend to store computer objects. For the purposes of this example that would be the Workstations OU and the Member Servers OU. Right Click > Properties > Security Tab > Advanced > Add > Select a Principal
- Click Add and type SELF then click OK.
- Drop down the Applies to: combo box and select Descendent Computer objects
- Scroll to the very bottom and click the Clear All button.
- Locate the confidential attribute which you created with the ldf file and select Allow Write.
- Click OK > OK > OK
- Repeat these steps for the Member Servers OU
Still To Come
The upcoming parts in this series will explain how to do the following:
- Create fnMain to control the order in which all of the functions are called and provide the completed local admin password change script
- Create a XAML based secure password viewer to retrieve the local admin password
Each portion of the solution is modularized using functions which allows the IT administrator to make use of all or just parts of the solution and allows the IT administrator to easily integrate any portion they wish into a larger script or even a different solution entirely. So stay tuned as Part 7 reveals the entire local administrator password management script. The final part of this series will provide a secure PowerShell and XAML based password viewer which could be used to securely retrieve the local admin usernames and passwords stored in Active Directory.
Comments
- Anonymous
January 01, 2003
If you already have administrative rights on the local system and have elevated to SYSTEM then you can already do anything you want including make a new user account, reset the existing local admin password, or install software. Since the password that is stored in AD is only locally relevant, obtaining it would be far less valuable than the SYSTEM rights you would already have. Additionally , encrypting the password would bring about its own challenges such as where to store the decryption key. If it is a preshared key, SYSTEM would need to have the preshared key to encrypt the password prior to storing it in AD which you would also be able to obtain by elevating to SYSTEM. - Anonymous
January 01, 2003
I’m researching whether this solution would work on our enterprise. All the parts I can see we could implement, but I wanted to know if there was a way to use an existing computer attribute to assign the confidential bit flag. From what I’ve been researching I can assign the system flag to an attribute as long as the attribute is not a base schema attribute.
What I was wondering if there is way to find an attribute I can use by searching the directory or if I am stuck having to extend the schema with a new one.
Thanks, would appreciate any guidance - Anonymous
January 01, 2003
PlatformsPFE - In regards to this comment:
Note: Domain Admins will not by default have the rights needed to view the contents of the confidential attribute unless explicitly granted the permissions to do so.
We have a test domain where we have not done many security OU changes, and this appears to be incorrrect.
It's not a big problem, but you may want to look at that. - Anonymous
January 01, 2003
thanks - Anonymous
April 02, 2014
Overview
In this multi part series I will walk you through how to manage the local admin password - Anonymous
April 27, 2014
Really interested in this. Can't wait for the full script so I can implement - Anonymous
April 27, 2014
Would it not be best practice to encrypt the string before storing the password In Active Directory for extra security?
I'm thinking that a user could use psexec -s (runs command as system account) then view the stored password in AD as the user would be logged on as the computer system account and therefore would have access to the secured attribute. You would need elevated privileges to run psexec mind in the first instance. - Anonymous
May 03, 2014
Thanks PlatformsPFE
I think this may be the solution I adopt for our Enterprise. It's simple but effective.
I like the fact it doesn't produce one password list as this would introduce more security headaches. - Anonymous
May 13, 2014
This is Part 7 of a multi-part series on managing local admin passwords. In this part I will provide - Anonymous
May 15, 2014
Pingback from Manage Local Admin Passwords – Additional Comments | JohanPersson.nu - Anonymous
August 12, 2014
This is Part 8 and the final part of a multi-part series on managing local admin passwords. In this part - Anonymous
September 12, 2014
The comment has been removed - Anonymous
October 30, 2015
Very interesting !