Debugging services..
How to debug Windows services covers the main points – but I think a common issue is debugging why a service won’t start.
When the service is failing on start – you can’t simply start it and then quickly attach the debugger – you need to have the debugger attach to it on start.
I like to do this via gflags.exe which is included with the debugger package when you install it. Here is an example of connecting to spoolsv.exe when you start the spooler service:
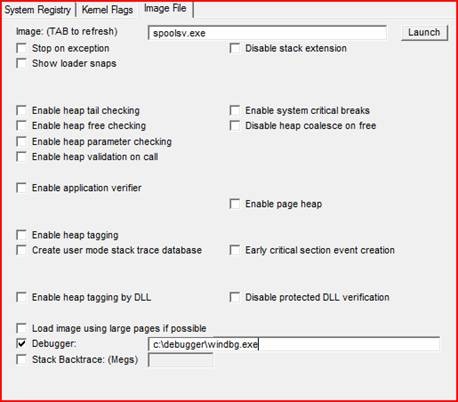
On any services General tab, you can see the path to the .exe ..in this case spoolsv.exe, which you place in the image file.
This will also create a registry key such as HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Image File Execution

Options\spoolsv.exe with the “debugger” value set to the value you placed in gflags.exe
One of the big problems is the SCM timeout when you launch the service under the debugger the service times out – the ServicesPipeTimeout reg value will get around that.
The next problem you may run into is that the debugger is not visible when the service launches.
This is because the service is not configured to interact with the desktop:
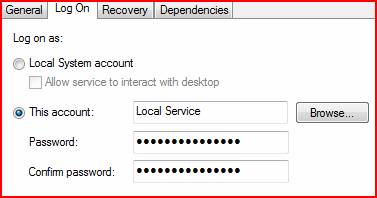
Many services run as Local Service or Network Service or some other account and will not be able to interact with the desktop. In these cases I like to do something a little more complex.
First, I change the debugger to cdb.exe and set it up to immediately start a server which I can attach to remotely.

Then, I create a batch file like so:
It’s all a one liner.
Debug_svc.bat
C:\debugger\windbg.exe -remote tcp:server=localhost,port=1234 -g –c “$$< :c\debugger\commands.txt” -y srv*c:\symbols*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols |
The switches are summarized below:
-remote : Connect to the server which was kicked off when the service started via cdb.exe
-g : Ignores the initial breakpoint in target application. This option will cause the target application to continue running after it is started or WinDbg attaches to it.
-c : Specifies the initial debugger command to run at start-up. The $$< basically says look to this script file and do what it says.
-y : The symbol path.
The c:\debugger\commands .txt looks like this:
Bp advapi32!regqueryvalue Bp foo!func1 Bd* Bp foo!func2 G |
I like to do this to save time from resetting breakpoints each time I need to try and start the service, as well as the flexibility of easy changes and a history of my breaks. The file above shows that I set some BP’s , then when I wanted to add\remove etc… So, I set a breakpoint on regqueryvalue(), and Func1(), decided I didn’t need them disabled all previous bp’s and set a bp on func2() then did a “go”
You then can do a “net start service” and then “debug_svc.bat”.
You will basically see the windbg.exe GUI come up and then hit your breakpoint at the exact spot you want to start debugging at, and it wont time out on you since you set ServicesPipeTimeout.
The last thing which could cause you some pain is the fact that many services run under svchost.exe.
Debugging an instance of svchost with 10 other dependant services in it, well it’s not always acceptable to put them all on hold J
Like the CertPropSvc
You can split it out into its own service by running:
“sc config <service> type= own”
And revert it via
“sc config <service> type= share”
Here we can see that it is in a shared svchost:
C:\debugger>tasklist /svc
Image Name ====================== System Idle Process System <snip> svchost.exe svchost.exe Ati2evxx.exe svchost.exe svchost.exe svchost.exe audiodg.exe SLsvc.exe |
PID ======= 0 4 972 1004 1100 1116 1148 1164 1260 1316 |
Services ============================================ N/A N/A RpcSs WinDefend Ati External Event Utility Audiosrv, Dhcp, Eventlog, lmhosts, wscsvc AudioEndpointBuilder, CscService, EMDMgmt, hidserv, Irmon, Netman, PcaSvc, SysMain, TabletInputService, TrkWks, UxSms, WdiSystemHost, Wlansvc, WPDBusEnum, wudfsvc AeLookupSvc, BITS, CertPropSvc, EapHost, gpsvc, IKEEXT, iphlpsvc, LanmanServer, MMCSS, ProfSvc, RasMan, Schedule, seclogon, SENS, ShellHWDetection, Themes, Winmgmt, wuauserv N/A slsvc |
We will change it like so:
C:\debugger>sc config CertPropSvc type= own
[SC] ChangeServiceConfig SUCCESS
Make sure you get that space in the after the ='s sign
Then you restart the service..and note that it’s in it’s own instance of svchost.exe
C:\debugger>tasklist /svc
Image Name ======================= System Idle Process System smss.exe csrss.exe csrss.exe wininit.exe services.exe winlogon.exe <snip> WmiPrvSE.exe svchost.exe tasklist.exe |
PID ====== 0 4 396 528 576 584 632 660 1672 5680 2032 |
Services ============== N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A CertPropSvc N/A |
When you are done – revert it via:
C:\debugger>sc config CertPropSvc type= share
[SC] ChangeServiceConfig SUCCESS
If you want to break it into its own svchost but named something unique so you can use image file executions on it
See https://support.microsoft.com/kb/934650
Basic steps are - copy svchost.exe to a unique name ( like svchost_1.exe ) , find the service's and modify the imagepath to use your svchost_1.exe and restart the service.
Have a great day!
Spat
Comments
Anonymous
September 17, 2007
With admin privileges, you can also attach to the services.exe process and then enable child debugging.Anonymous
July 22, 2013
Awesome article.