Layered security model in Business Central
Note
Azure Active Directory is now Microsoft Entra ID. Learn more
This section helps you understand and improve the security of your Business Central installation regardless of where it's hosted. In the sections listed below, you'll find guidance and recommended practices related to authentication, authorization, and auditing, in addition to data encryption and secure development practices that can be applied to any Business Central environment.
Business Central uses a layered approach to application security, as outlined in the following diagram.
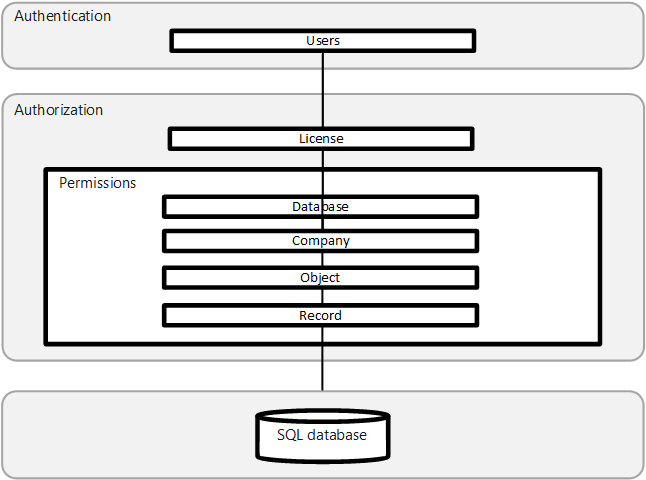
Authentication
Before users can sign in to the Business Central application, they must be authenticated as a valid user in the system. Business Central (on-premises) supports several authentication methods, such as Windows and Microsoft Entra ID . Business Central online deployments use Microsoft Entra ID only. For more information, see the following articles:
Managing Users and Permissions
Set up Business Central Access with Microsoft 365 Licenses
Authentication and Credential Types (on-premises only)
Set up Multifactor Authentication (MFA)
The authentication method configured for Business Central Server is also used to access web services. For more information, see Web Services Authentication.
Authorization
After a user is authenticated, authorization determines which areas the user can access, such as the pages and reports they can open and the permissions they have on associated data. For more information, see the following articles:
User Permissions in the Application
Analyzing Permission Changes Trace Telemetry
Removing Elements from the User Interface According to Permissions
Analyzing Authorization Telemetry
Using OAuth to Authorize Business Central Web Services
Data encryption
You can encrypt data on the Business Central server by generating new encryption keys—or importing existing ones—that you enable on the Business Central server instance that connects to the database. For more information, see Encrypting Data in Dynamics 365 Business Central.
Security development lifecycle
The Microsoft Security Development Lifecycle (SDL) is a software development process that helps developers build more secure software and address security compliance requirements while reducing development cost. For more information, see Security Development Lifecycle.
See Also
Security and Protection
Security Tips for Business Users
Online Security
On-Premises Security