Remarque
L’accès à cette page nécessite une autorisation. Vous pouvez essayer de vous connecter ou de modifier des répertoires.
L’accès à cette page nécessite une autorisation. Vous pouvez essayer de modifier des répertoires.
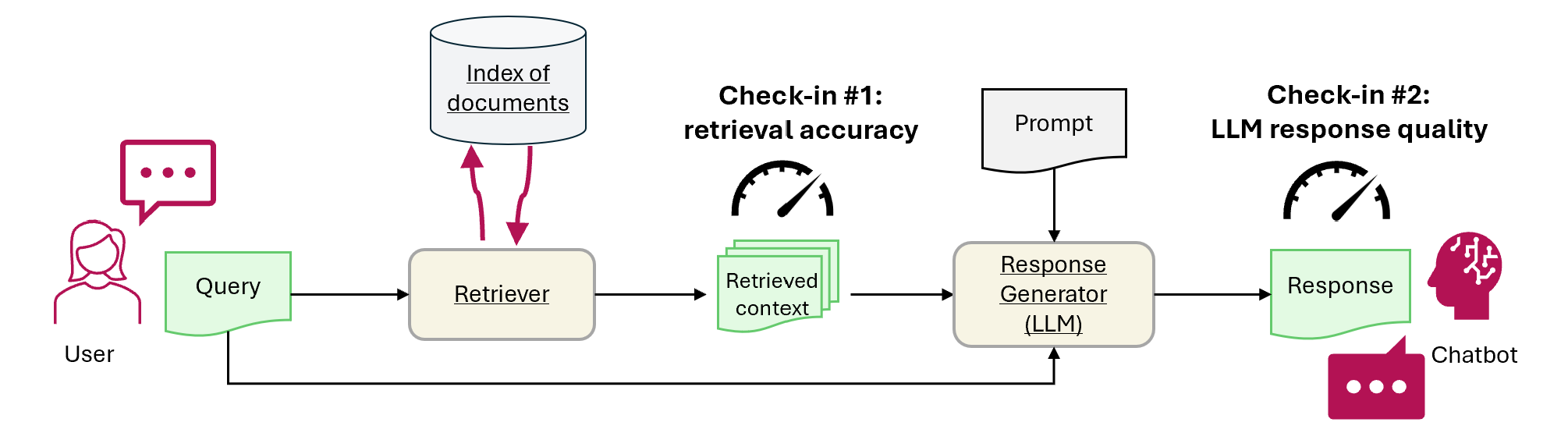
Ce tutoriel montre comment utiliser Fabric pour évaluer les performances des applications RAG. L’évaluation se concentre sur deux principaux composants RAG : le récupérateur (Recherche Azure AI) et le générateur de réponses (un LLM qui utilise la requête de l’utilisateur, le contexte récupéré et une invite pour générer une réponse). Voici les étapes principales :
- Configurer les services Azure OpenAI et Azure AI Search
- Charger des données à partir du jeu de données de questions-réponses de CMU d'articles Wikipédia pour créer un benchmark
- Exécuter un test de fumée avec une requête pour confirmer que le système RAG fonctionne de bout en bout
- Définir des métriques déterministes et assistées par l’IA pour l’évaluation
- Check-in 1 : Évaluer les performances du récupérateur à l’aide de la précision top-N
- Check-in 2 : Évaluer la performance du générateur de réponse à l’aide des métriques de plausibilité, de pertinence et de similarité.
- Visualiser et stocker les résultats d’évaluation dans OneLake pour une référence future et une évaluation en cours
Prerequisites
Avant de commencer ce tutoriel, complétez le guide étape par étape de la génération augmentée par récupération dans Fabric.
Vous avez besoin de ces services pour exécuter le notebook :
- Microsoft Fabric
- Ajoutez un Lakehouse à ce notebook (il contient les données que vous avez ajoutées dans le didacticiel précédent).
- Azure AI Studio pour OpenAI
- Recherche Azure AI (elle contient les données que vous avez indexées dans le didacticiel précédent).
Dans le tutoriel précédent, vous avez chargé des données dans votre lakehouse et créé un index de document utilisé par le système RAG. Utilisez l’index dans cet exercice pour apprendre les techniques de base pour évaluer les performances de RAG et identifier les problèmes potentiels. Si vous n’avez pas créé d’index ou supprimé, suivez le guide de démarrage rapide pour remplir la configuration requise.
Configurer l’accès à Azure OpenAI et Recherche Azure AI
Définissez les points de terminaison et les clés requises. Importez les bibliothèques et fonctions requises. Instanciez des clients pour Azure OpenAI et Azure AI Search. Définissez un wrapper de fonction avec une invite pour interroger le système RAG.
# Enter your Azure OpenAI service values
aoai_endpoint = "https://<your-resource-name>.openai.azure.com" # TODO: Provide the Azure OpenAI resource endpoint (replace <your-resource-name>)
aoai_key = "" # TODO: Fill in your API key from Azure OpenAI
aoai_deployment_name_embeddings = "text-embedding-ada-002"
aoai_model_name_query = "gpt-4-32k"
aoai_model_name_metrics = "gpt-4-32k"
aoai_api_version = "2024-02-01"
# Setup key accesses to Azure AI Search
aisearch_index_name = "" # TODO: Create a new index name: must only contain lowercase, numbers, and dashes
aisearch_api_key = "" # TODO: Fill in your API key from Azure AI Search
aisearch_endpoint = "https://.search.windows.net" # TODO: Provide the url endpoint for your created Azure AI Search
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=DeprecationWarning)
import os, requests, json
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential
from azure.search.documents import SearchClient
from pyspark.sql import functions as F
from pyspark.sql.functions import to_timestamp, current_timestamp, concat, col, split, explode, udf, monotonically_increasing_id, when, rand, coalesce, lit, input_file_name, regexp_extract, concat_ws, length, ceil
from pyspark.sql.types import StructType, StructField, StringType, IntegerType, TimestampType, ArrayType, FloatType
from pyspark.sql import Row
import pandas as pd
from azure.search.documents.indexes import SearchIndexClient
from azure.search.documents.models import (
VectorizedQuery,
)
from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import (
SearchIndex,
SearchField,
SearchFieldDataType,
SimpleField,
SearchableField,
SemanticConfiguration,
SemanticPrioritizedFields,
SemanticField,
SemanticSearch,
VectorSearch,
HnswAlgorithmConfiguration,
HnswParameters,
VectorSearchProfile,
VectorSearchAlgorithmKind,
VectorSearchAlgorithmMetric,
)
import openai
from openai import AzureOpenAI
import uuid
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from synapse.ml.featurize.text import PageSplitter
import ipywidgets as widgets
from IPython.display import display as w_display
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 6, Finished, Available, Finished)
# Configure access to OpenAI endpoint
openai.api_type = "azure"
openai.api_key = aoai_key
openai.api_base = aoai_endpoint
openai.api_version = aoai_api_version
# Create client for accessing embedding endpoint
embed_client = AzureOpenAI(
api_version=aoai_api_version,
azure_endpoint=aoai_endpoint,
api_key=aoai_key,
)
# Create client for accessing chat endpoint
chat_client = AzureOpenAI(
azure_endpoint=aoai_endpoint,
api_key=aoai_key,
api_version=aoai_api_version,
)
# Configure access to Azure AI Search
search_client = SearchClient(
aisearch_endpoint,
aisearch_index_name,
credential=AzureKeyCredential(aisearch_api_key)
)
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 7, Finished, Available, Finished)
Les fonctions suivantes implémentent les deux principaux composants RAG - retriever (get_context_source) et générateur de réponse (get_answer). Le code est similaire au didacticiel précédent. Le topN paramètre vous permet de définir le nombre de ressources pertinentes à récupérer (ce didacticiel utilise 3, mais la valeur optimale peut varier selon le jeu de données) :
# Implement retriever
def get_context_source(question, topN=3):
"""
Retrieves contextual information and sources related to a given question using embeddings and a vector search.
Parameters:
question (str): The question for which the context and sources are to be retrieved.
topN (int, optional): The number of top results to retrieve. Default is 3.
Returns:
List: A list containing two elements:
1. A string with the concatenated retrieved context.
2. A list of retrieved source paths.
"""
embed_client = openai.AzureOpenAI(
api_version=aoai_api_version,
azure_endpoint=aoai_endpoint,
api_key=aoai_key,
)
query_embedding = embed_client.embeddings.create(input=question, model=aoai_deployment_name_embeddings).data[0].embedding
vector_query = VectorizedQuery(vector=query_embedding, k_nearest_neighbors=topN, fields="Embedding")
results = search_client.search(
vector_queries=[vector_query],
top=topN,
)
retrieved_context = ""
retrieved_sources = []
for result in results:
retrieved_context += result['ExtractedPath'] + "\n" + result['Chunk'] + "\n\n"
retrieved_sources.append(result['ExtractedPath'])
return [retrieved_context, retrieved_sources]
# Implement response generator
def get_answer(question, context):
"""
Generates a response to a given question using provided context and an Azure OpenAI model.
Parameters:
question (str): The question that needs to be answered.
context (str): The contextual information related to the question that will help generate a relevant response.
Returns:
str: The response generated by the Azure OpenAI model based on the provided question and context.
"""
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a chat assistant. Use provided text to ground your response. Give a one-word answer when possible ('yes'/'no' is OK where appropriate, no details). Unnecessary words incur a $500 penalty."
}
]
messages.append(
{
"role": "user",
"content": question + "\n" + context,
},
)
chat_client = openai.AzureOpenAI(
azure_endpoint=aoai_endpoint,
api_key=aoai_key,
api_version=aoai_api_version,
)
chat_completion = chat_client.chat.completions.create(
model=aoai_model_name_query,
messages=messages,
)
return chat_completion.choices[0].message.content
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 8, Finished, Available, Finished)
Dataset
La version 1.2 du jeu de données de l’Université Carnegie Mellon Question-Answer est un corpus d’articles Wikipédia avec des questions factuelles et des réponses écrites manuellement. Il est hébergé dans le Stockage Blob d'Azure sous licence GFDL. Le jeu de données utilise une table avec ces champs :
-
ArticleTitle: Nom de l’article Wikipédia les questions et réponses proviennent de -
Question: question écrite manuellement sur l’article -
Answer: réponse écrite manuellement en fonction de l’article -
DifficultyFromQuestioner: Évaluation de la difficulté attribuée par l'auteur de la question -
DifficultyFromAnswerer: évaluation de la difficulté que l’évaluateur assigne ; peut différer deDifficultyFromQuestioner -
ExtractedPath: Chemin d’accès à l’article d’origine (un article peut avoir plusieurs paires question-réponse) -
text: Texte de l’article Wikipédia nettoyé
Téléchargez les fichiers LICENSE-S08 et LICENSE-S09 à partir du même emplacement pour obtenir les détails de la licence.
Historique et citation
Utilisez cette citation pour le jeu de données :
CMU Question/Answer Dataset, Release 1.2
August 23, 2013
Noah A. Smith, Michael Heilman, and Rebecca Hwa
Question Generation as a Competitive Undergraduate Course Project
In Proceedings of the NSF Workshop on the Question Generation Shared Task and Evaluation Challenge, Arlington, VA, September 2008.
Available at http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~nasmith/papers/smith+heilman+hwa.nsf08.pdf.
Original dataset acknowledgments:
This research project was supported by NSF IIS-0713265 (to Smith), an NSF Graduate Research Fellowship (to Heilman), NSF IIS-0712810 and IIS-0745914 (to Hwa), and Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education R305B040063 (to Carnegie Mellon).
cmu-qa-08-09 (modified version)
June 12, 2024
Amir Jafari, Alexandra Savelieva, Brice Chung, Hossein Khadivi Heris, Journey McDowell
This release uses the GNU Free Documentation License (GFDL) (http://www.gnu.org/licenses/fdl.html).
The GNU license applies to all copies of the dataset.
Créer un benchmark
Importez le benchmark. Pour cette démonstration, utilisez un sous-ensemble de questions provenant des compartiments S08/set1 et S08/set2. Pour conserver une question par article, appliquez df.dropDuplicates(["ExtractedPath"]). Supprimez les questions dupliquées. Le processus de curation ajoute des étiquettes de difficulté ; cet exemple les limite à medium.
df = spark.sql("SELECT * FROM data_load_tests.cmu_qa")
# Filter the DataFrame to include the specified paths
df = df.filter((col("ExtractedPath").like("S08/data/set1/%")) | (col("ExtractedPath").like("S08/data/set2/%")))
# Keep only medium-difficulty questions.
df = df.filter(col("DifficultyFromQuestioner") == "medium")
# Drop duplicate questions and source paths.
df = df.dropDuplicates(["Question"])
df = df.dropDuplicates(["ExtractedPath"])
num_rows = df.count()
num_columns = len(df.columns)
print(f"Number of rows: {num_rows}, Number of columns: {num_columns}")
# Persist the DataFrame
df.persist()
display(df)
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 9, Finished, Available, Finished)Number of rows: 20, Number of columns: 7SynapseWidget(Synapse.DataFrame, 47aff8cb-72f8-4a36-885c-f4f3bb830a91)
Le résultat est un DataFrame avec 20 lignes : le benchmark de démonstration. Les champs clés sont Question, Answer (réponse de vérité au sol organisée par l’homme) et ExtractedPath (document source). Ajustez les filtres pour inclure d’autres questions et modifiez la difficulté d’un exemple plus réaliste. Essaie.
Exécuter un test simple de bout en bout
Commencez par un test de fumée de bout en bout de la génération d’extraction augmentée (RAG).
question = "How many suborders are turtles divided into?"
retrieved_context, retrieved_sources = get_context_source(question)
answer = get_answer(question, retrieved_context)
print(answer)
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 10, Finished, Available, Finished)Three
Ce test de fumée vous aide à trouver des problèmes dans l’implémentation RAG, tels que des informations d’identification incorrectes, un index vectoriel manquant ou vide ou des interfaces de fonction incompatibles. Si le test échoue, vérifiez les problèmes. Sortie attendue : Three. Si le test de fumée réussit, accédez à la section suivante pour évaluer RAG plus loin.
Établir des métriques
Définissez une métrique déterministe pour évaluer le récupérateur. Il est inspiré par les moteurs de recherche. Elle vérifie si la liste des sources récupérées inclut la source de vérité de base. Cette métrique est un score de précision N supérieur, car le topN paramètre définit le nombre de sources récupérées.
def get_retrieval_score(target_source, retrieved_sources):
if target_source in retrieved_sources:
return 1
else:
return 0
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 11, Finished, Available, Finished)
Selon le benchmark, la réponse est contenue dans la source avec l’ID "S08/data/set1/a9". Test de la fonction sur l’exemple que nous avons exécuté ci-dessus retourne 1, comme prévu, car elle se trouvait dans les trois premiers blocs de texte pertinents.
print("Retrieved sources:", retrieved_sources)
get_retrieval_score("S08/data/set1/a9", retrieved_sources)
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 12, Finished, Available, Finished)Retrieved sources: ['S08/data/set1/a9', 'S08/data/set1/a9', 'S08/data/set1/a5']1
Cette section définit les métriques assistées par l’IA. Le modèle d’invite comprend quelques exemples d'input (CONTEXTE et RÉPONSE) et une sortie suggérée, également appelé modèle few-shot. Il s’agit de la même invite utilisée dans Azure AI Studio. En savoir plus sur les métriques d’évaluation intégrées. Cette démonstration utilise les métriques groundedness et relevance - elles sont généralement les plus utiles et fiables pour l'évaluation des modèles GPT. D’autres métriques peuvent être utiles, mais fournissent moins d’intuition, par exemple, les réponses n’ont pas besoin d’être similaires pour être correctes, de sorte que les scores similarity peuvent être trompeurs. L’échelle pour toutes les métriques est de 1 à 5. Plus élevé est meilleur. Groundedness ne prend que deux entrées (contexte et réponse générée), tandis que les deux autres métriques utilisent également la vérité de base pour l’évaluation.
def get_groundedness_metric(context, answer):
"""Get the groundedness score from the LLM using the context and answer."""
groundedness_prompt_template = """
You are presented with a CONTEXT and an ANSWER about that CONTEXT. Decide whether the ANSWER is entailed by the CONTEXT by choosing one of the following ratings:
1. 5: The ANSWER follows logically from the information contained in the CONTEXT.
2. 1: The ANSWER is logically false from the information contained in the CONTEXT.
3. an integer score between 1 and 5 and if such integer score does not exist, use 1: It is not possible to determine whether the ANSWER is true or false without further information. Read the passage of information thoroughly and select the correct answer from the three answer labels. Read the CONTEXT thoroughly to ensure you know what the CONTEXT entails. Note the ANSWER is generated by a computer system, it can contain certain symbols, which should not be a negative factor in the evaluation.
Independent Examples:
## Example Task #1 Input:
"CONTEXT": "Some are reported as not having been wanted at all.", "QUESTION": "", "ANSWER": "All are reported as being completely and fully wanted."
## Example Task #1 Output:
1
## Example Task #2 Input:
"CONTEXT": "Ten new television shows appeared during the month of September. Five of the shows were sitcoms, three were hourlong dramas, and two were news-magazine shows. By January, only seven of these new shows were still on the air. Five of the shows that remained were sitcoms.", "QUESTION": "", "ANSWER": "At least one of the shows that were cancelled was an hourlong drama."
## Example Task #2 Output:
5
## Example Task #3 Input:
"CONTEXT": "In Quebec, an allophone is a resident, usually an immigrant, whose mother tongue or home language is neither French nor English.", "QUESTION": "", "ANSWER": "In Quebec, an allophone is a resident, usually an immigrant, whose mother tongue or home language is not French."
5
## Example Task #4 Input:
"CONTEXT": "Some are reported as not having been wanted at all.", "QUESTION": "", "ANSWER": "All are reported as being completely and fully wanted."
## Example Task #4 Output:
1
## Actual Task Input:
"CONTEXT": {context}, "QUESTION": "", "ANSWER": {answer}
Reminder: The return values for each task should be correctly formatted as an integer between 1 and 5. Do not repeat the context and question. Don't explain the reasoning. The answer should include only a number: 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5.
Actual Task Output:
"""
metric_client = openai.AzureOpenAI(
api_version=aoai_api_version,
azure_endpoint=aoai_endpoint,
api_key=aoai_key,
)
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are an AI assistant. You will be given the definition of an evaluation metric for assessing the quality of an answer in a question-answering task. Your job is to compute an accurate evaluation score using the provided evaluation metric."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": groundedness_prompt_template.format(context=context, answer=answer)
}
]
metric_completion = metric_client.chat.completions.create(
model=aoai_model_name_metrics,
messages=messages,
temperature=0,
)
return metric_completion.choices[0].message.content
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 13, Finished, Available, Finished)
def get_relevance_metric(context, question, answer):
relevance_prompt_template = """
Relevance measures how well the answer addresses the main aspects of the question, based on the context. Consider whether all and only the important aspects are contained in the answer when evaluating relevance. Given the context and question, score the relevance of the answer between one to five stars using the following rating scale:
One star: the answer completely lacks relevance
Two stars: the answer mostly lacks relevance
Three stars: the answer is partially relevant
Four stars: the answer is mostly relevant
Five stars: the answer has perfect relevance
This rating value should always be an integer between 1 and 5. So the rating produced should be 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5.
context: Marie Curie was a Polish-born physicist and chemist who pioneered research on radioactivity and was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize.
question: What field did Marie Curie excel in?
answer: Marie Curie was a renowned painter who focused mainly on impressionist styles and techniques.
stars: 1
context: The Beatles were an English rock band formed in Liverpool in 1960, and they are widely regarded as the most influential music band in history.
question: Where were The Beatles formed?
answer: The band The Beatles began their journey in London, England, and they changed the history of music.
stars: 2
context: The recent Mars rover, Perseverance, was launched in 2020 with the main goal of searching for signs of ancient life on Mars. The rover also carries an experiment called MOXIE, which aims to generate oxygen from the Martian atmosphere.
question: What are the main goals of Perseverance Mars rover mission?
answer: The Perseverance Mars rover mission focuses on searching for signs of ancient life on Mars.
stars: 3
context: The Mediterranean diet is a commonly recommended dietary plan that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Studies have shown that it offers numerous health benefits, including a reduced risk of heart disease and improved cognitive health.
question: What are the main components of the Mediterranean diet?
answer: The Mediterranean diet primarily consists of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
stars: 4
context: The Queen's Royal Castle is a well-known tourist attraction in the United Kingdom. It spans over 500 acres and contains extensive gardens and parks. The castle was built in the 15th century and has been home to generations of royalty.
question: What are the main attractions of the Queen's Royal Castle?
answer: The main attractions of the Queen's Royal Castle are its expansive 500-acre grounds, extensive gardens, parks, and the historical castle itself, which dates back to the 15th century and has housed generations of royalty.
stars: 5
Don't explain the reasoning. The answer should include only a number: 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5.
context: {context}
question: {question}
answer: {answer}
stars:
"""
metric_client = openai.AzureOpenAI(
api_version=aoai_api_version,
azure_endpoint=aoai_endpoint,
api_key=aoai_key,
)
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are an AI assistant. You are given the definition of an evaluation metric for assessing the quality of an answer in a question-answering task. Compute an accurate evaluation score using the provided evaluation metric."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": relevance_prompt_template.format(context=context, question=question, answer=answer)
}
]
metric_completion = metric_client.chat.completions.create(
model=aoai_model_name_metrics,
messages=messages,
temperature=0,
)
return metric_completion.choices[0].message.content
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 14, Finished, Available, Finished)
def get_similarity_metric(question, ground_truth, answer):
similarity_prompt_template = """
Equivalence, as a metric, measures the similarity between the predicted answer and the correct answer. If the information and content in the predicted answer is similar or equivalent to the correct answer, then the value of the Equivalence metric should be high, else it should be low. Given the question, correct answer, and predicted answer, determine the value of Equivalence metric using the following rating scale:
One star: the predicted answer is not at all similar to the correct answer
Two stars: the predicted answer is mostly not similar to the correct answer
Three stars: the predicted answer is somewhat similar to the correct answer
Four stars: the predicted answer is mostly similar to the correct answer
Five stars: the predicted answer is completely similar to the correct answer
This rating value should always be an integer between 1 and 5. So the rating produced should be 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5.
The examples below show the Equivalence score for a question, a correct answer, and a predicted answer.
question: What is the role of ribosomes?
correct answer: Ribosomes are cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis. They interpret the genetic information carried by messenger RNA (mRNA) and use it to assemble amino acids into proteins.
predicted answer: Ribosomes participate in carbohydrate breakdown by removing nutrients from complex sugar molecules.
stars: 1
question: Why did the Titanic sink?
correct answer: The Titanic sank after it struck an iceberg during its maiden voyage in 1912. The impact caused the ship's hull to breach, allowing water to flood into the vessel. The ship's design, lifeboat shortage, and lack of timely rescue efforts contributed to the tragic loss of life.
predicted answer: The sinking of the Titanic was a result of a large iceberg collision. This caused the ship to take on water and eventually sink, leading to the death of many passengers due to a shortage of lifeboats and insufficient rescue attempts.
stars: 2
question: What causes seasons on Earth?
correct answer: Seasons on Earth are caused by the tilt of the Earth's axis and its revolution around the Sun. As the Earth orbits the Sun, the tilt causes different parts of the planet to receive varying amounts of sunlight, resulting in changes in temperature and weather patterns.
predicted answer: Seasons occur because of the Earth's rotation and its elliptical orbit around the Sun. The tilt of the Earth's axis causes regions to be subjected to different sunlight intensities, which leads to temperature fluctuations and alternating weather conditions.
stars: 3
question: How does photosynthesis work?
correct answer: Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants and some other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy. This occurs as light is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules, and then carbon dioxide and water are converted into glucose and oxygen through a series of reactions.
predicted answer: In photosynthesis, sunlight is transformed into nutrients by plants and certain microorganisms. Light is captured by chlorophyll molecules, followed by the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen through multiple reactions.
stars: 4
question: What are the health benefits of regular exercise?
correct answer: Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight, increase muscle and bone strength, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. It also promotes mental well-being by reducing stress and improving overall mood.
predicted answer: Routine physical activity can contribute to maintaining ideal body weight, enhancing muscle and bone strength, and preventing chronic illnesses. In addition, it supports mental health by alleviating stress and augmenting general mood.
stars: 5
Don't explain the reasoning. The answer should include only a number: 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5.
question: {question}
correct answer:{ground_truth}
predicted answer: {answer}
stars:
"""
metric_client = openai.AzureOpenAI(
api_version=aoai_api_version,
azure_endpoint=aoai_endpoint,
api_key=aoai_key,
)
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are an AI assistant. You will be given the definition of an evaluation metric for assessing the quality of an answer in a question-answering task. Your job is to compute an accurate evaluation score using the provided evaluation metric."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": similarity_prompt_template.format(question=question, ground_truth=ground_truth, answer=answer)
}
]
metric_completion = metric_client.chat.completions.create(
model=aoai_model_name_metrics,
messages=messages,
temperature=0,
)
return metric_completion.choices[0].message.content
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 15, Finished, Available, Finished)
Testez la métrique de pertinence :
get_relevance_metric(retrieved_context, question, answer)
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 16, Finished, Available, Finished)'2'
Un score de 5 signifie que la réponse est pertinente. Le code suivant obtient la métrique de similarité :
get_similarity_metric(question, 'three', answer)
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 17, Finished, Available, Finished)'5'
Un score de 5 signifie que la réponse correspond à la réponse de base organisée par un expert humain. Les scores de métriques assistés par l’IA peuvent varier avec la même entrée. Ils sont plus rapides que d’utiliser des juges humains.
Évaluer la performance de RAG sur le benchmark de Q&A
Créez des enveloppes de fonctions pour les exécuter à grande échelle. Encapsulez chaque fonction qui se termine par _udf (court pour user-defined function) afin qu’elle soit conforme aux exigences Spark (@udf(returnType=StructType([ ... ]))) et exécute des calculs sur des données volumineuses plus rapidement sur le cluster.
# UDF wrappers for RAG components
@udf(returnType=StructType([
StructField("retrieved_context", StringType(), True),
StructField("retrieved_sources", ArrayType(StringType()), True)
]))
def get_context_source_udf(question, topN=3):
return get_context_source(question, topN)
@udf(returnType=StringType())
def get_answer_udf(question, context):
return get_answer(question, context)
# UDF wrapper for retrieval score
@udf(returnType=StringType())
def get_retrieval_score_udf(target_source, retrieved_sources):
return get_retrieval_score(target_source, retrieved_sources)
# UDF wrappers for AI-assisted metrics
@udf(returnType=StringType())
def get_groundedness_metric_udf(context, answer):
return get_groundedness_metric(context, answer)
@udf(returnType=StringType())
def get_relevance_metric_udf(context, question, answer):
return get_relevance_metric(context, question, answer)
@udf(returnType=StringType())
def get_similarity_metric_udf(question, ground_truth, answer):
return get_similarity_metric(question, ground_truth, answer)
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 18, Finished, Available, Finished)
Suivi n° 1 : performance du module de récupération
Le code suivant crée les colonnes result et retrieval_score dans le DataFrame de référence. Ces colonnes incluent la réponse générée par RAG et un indicateur indiquant si le contexte fourni au LLM inclut l’article sur lequel repose la question.
df = df.withColumn("result", get_context_source_udf(df.Question)).select(df.columns+["result.*"])
df = df.withColumn('retrieval_score', get_retrieval_score_udf(df.ExtractedPath, df.retrieved_sources))
print("Aggregate Retrieval score: {:.2f}%".format((df.where(df["retrieval_score"] == 1).count() / df.count()) * 100))
display(df.select(["question", "retrieval_score", "ExtractedPath", "retrieved_sources"]))
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 19, Finished, Available, Finished)Aggregate Retrieval score: 100.00%SynapseWidget(Synapse.DataFrame, 14efe386-836a-4765-bd88-b121f32c7cfc)
** Pour toutes les questions, l'extracteur récupère le contexte correct et, dans la plupart des cas, c'est la première entrée. La recherche Azure AI fonctionne bien. Vous pouvez vous demander pourquoi, dans certains cas, le contexte a deux ou trois valeurs identiques. Ce n’est pas une erreur : cela signifie que le récupérateur extrait des fragments du même article qui ne tiennent pas dans un bloc lors du fractionnement.
Suivi n° 2 : performance du générateur de réponses
Passez la question et le contexte au LLM pour générer une réponse. Stockez-la dans la generated_answer colonne dans le DataFrame :
df = df.withColumn('generated_answer', get_answer_udf(df.Question, df.retrieved_context))
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 20, Finished, Available, Finished)
Utilisez la réponse générée, la réponse de base, la question et le contexte pour calculer les métriques. Affichez les résultats de l’évaluation pour chaque paire question-réponse :
df = df.withColumn('gpt_groundedness', get_groundedness_metric_udf(df.retrieved_context, df.generated_answer))
df = df.withColumn('gpt_relevance', get_relevance_metric_udf(df.retrieved_context, df.Question, df.generated_answer))
df = df.withColumn('gpt_similarity', get_similarity_metric_udf(df.Question, df.Answer, df.generated_answer))
display(df.select(["question", "answer", "generated_answer", "retrieval_score", "gpt_groundedness","gpt_relevance", "gpt_similarity"]))
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 21, Finished, Available, Finished)SynapseWidget(Synapse.DataFrame, 22b97d27-91e1-40f3-b888-3a3399de9d6b)
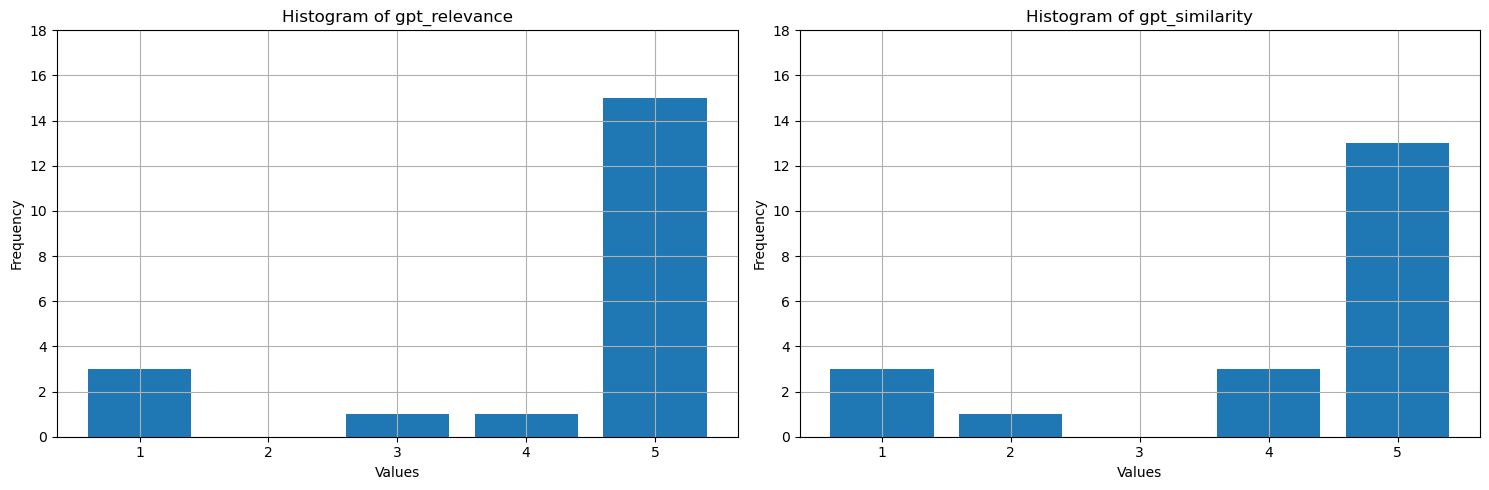
Que montrent ces valeurs ? Pour faciliter leur interprétation, tracez des histogrammes de fiabilité, de pertinence et de similarité. Le LLM est plus détaillé que les réponses humaines, ce qui diminue la métrique de similarité - environ la moitié des réponses sont sémantiquement correctes, mais reçoivent quatre étoiles en tant que principalement similaires. La plupart des valeurs pour les trois métriques sont 4 ou 5, ce qui suggère que les performances RAG sont bonnes. Il existe quelques valeurs hors norme (par exemple, pour la question How many species of otter are there?, le modèle a généré There are 13 species of otter, qui est correct avec une pertinence élevée et une similarité (5). Pour une raison quelconque, GPT considérait qu’il était mal ancré dans le contexte fourni et lui a donné une étoile. Dans les trois autres cas, où il existe au moins une métrique d'une étoile assistée par l'IA, le faible score indique une mauvaise réponse. Le LLM évalue parfois incorrectement, mais évalue généralement avec précision.
# Convert Spark DataFrame to Pandas DataFrame
pandas_df = df.toPandas()
selected_columns = ['gpt_groundedness', 'gpt_relevance', 'gpt_similarity']
trimmed_df = pandas_df[selected_columns].astype(int)
# Define a function to plot histograms for the specified columns
def plot_histograms(dataframe, columns):
# Set up the figure size and subplots
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
for i, column in enumerate(columns, 1):
plt.subplot(1, len(columns), i)
# Filter the dataframe to only include rows with values 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
filtered_df = dataframe[dataframe[column].isin([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])]
filtered_df[column].hist(bins=range(1, 7), align='left', rwidth=0.8)
plt.title(f'Histogram of {column}')
plt.xlabel('Values')
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.xticks(range(1, 6))
plt.yticks(range(0, 20, 2))
# Call the function to plot histograms for the specified columns
plot_histograms(trimmed_df, selected_columns)
# Show the plots
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 24, Finished, Available, Finished)
En guise d'étape finale, sauvegardez les résultats du benchmark dans une table de votre lakehouse. Cette étape est facultative mais fortement recommandée : elle rend vos résultats plus utiles. Lorsque vous modifiez un élément dans le RAG (par exemple, modifiez l’invite, mettez à jour l’index ou utilisez un autre modèle GPT dans le générateur de réponse), mesurez l’impact, quantifiez les améliorations et détectez les régressions.
# create name of experiment that is easy to refer to
friendly_name_of_experiment = "rag_tutorial_experiment_1"
# Note the current date and time
time_of_experiment = current_timestamp()
# Generate a unique GUID for all rows
experiment_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
# Add two new columns to the Spark DataFrame
updated_df = df.withColumn("execution_time", time_of_experiment) \
.withColumn("experiment_id", lit(experiment_id)) \
.withColumn("experiment_friendly_name", lit(friendly_name_of_experiment))
# Store the updated DataFrame in the default lakehouse as a table named 'rag_experiment_runs'
table_name = "rag_experiment_run_demo1"
updated_df.write.format("parquet").mode("append").saveAsTable(table_name)
Sortie de cellule :StatementMeta(, 21cb8cd3-7742-4c1f-8339-265e2846df1d, 28, Finished, Available, Finished)
Revenez aux résultats de l’expérience à tout moment pour les examiner, comparer avec de nouvelles expériences et choisir la configuration qui fonctionne le mieux pour la production.
Résumé
Utilisez les métriques assistées par IA et le taux de récupération top-N pour créer votre solution de génération d’extraction augmentée (RAG).