Set a retention policy for untagged manifests
Azure Container Registry gives you the option to set a retention policy for stored image manifests that don't have any associated tags (untagged manifests). When a retention policy is enabled, untagged manifests in the registry are automatically deleted after a number of days you set. This feature prevents the registry from filling up with artifacts that aren't needed and helps you save on storage costs.
You can use the Azure Cloud Shell or a local installation of the Azure CLI to run the command examples in this article. If you'd like to use it locally, version 2.0.74 or later is required. Run az --version to find the version. If you need to install or upgrade, see Install Azure CLI.
A retention policy for untagged manifests is currently a preview feature of Premium container registries. For information about registry service tiers, see Azure Container Registry service tiers.
Warning
Set a retention policy with care--deleted image data is UNRECOVERABLE. If you have systems that pull images by manifest digest (as opposed to image name), you should not set a retention policy for untagged manifests. Deleting untagged images will prevent those systems from pulling the images from your registry. Instead of pulling by manifest, consider adopting a unique tagging scheme, a recommended best practice.
About the retention policy
Azure Container Registry does reference counting for manifests in the registry. When a manifest is untagged, it checks the retention policy. If a retention policy is enabled, a manifest delete operation is queued, with a specific date, according to the number of days set in the policy.
A separate queue management job constantly processes messages, scaling as needed. As an example, suppose you untagged two manifests, 1 hour apart, in a registry with a retention policy of 30 days. Two messages would be queued. Then, 30 days later, approximately 1 hour apart, the messages would be retrieved from the queue and processed, assuming the policy was still in effect.
If the delete-enabled attribute of an untagged manifest is set to false, the manifest is locked and is not deleted by the policy.
Important
The retention policy applies only to untagged manifests with timestamps after the policy is enabled. Untagged manifests in the registry with earlier timestamps aren't subject to the policy. For other options to delete image data, see examples in Delete container images in Azure Container Registry.
Set a retention policy - CLI
The following example shows you how to use the Azure CLI to set a retention policy for untagged manifests in a registry.
Enable a retention policy
By default, no retention policy is set in a container registry. To set or update a retention policy, run the az acr config retention update command in the Azure CLI. You can specify a number of days between 0 and 365 to retain the untagged manifests. If you don't specify a number of days, the command sets a default of 7 days. After the retention period, all untagged manifests in the registry are automatically deleted.
The following example sets a retention policy of 30 days for untagged manifests in the registry myregistry:
az acr config retention update --registry myregistry --status enabled --days 30 --type UntaggedManifests
The following example sets a policy to delete any manifest in the registry as soon as it's untagged. Create this policy by setting a retention period of 0 days.
az acr config retention update \
--registry myregistry --status enabled \
--days 0 --type UntaggedManifests
Validate a retention policy
If you enable the preceding policy with a retention period of 0 days, you can quickly verify that untagged manifests are deleted:
- Push a test image
hello-world:latestimage to your registry, or substitute another test image of your choice. - Untag the
hello-world:latestimage, for example, using the az acr repository untag command. The untagged manifest remains in the registry.az acr repository untag \ --name myregistry --image hello-world:latest - Within a few seconds, the untagged manifest is deleted. You can verify the deletion by listing manifests in the repository, for example, using the az acr manifest list-metadata command. If the test image was the only one in the repository, the repository itself is deleted.
Manage a retention policy
To show the retention policy set in a registry, run the az acr config retention show command:
az acr config retention show --registry myregistry
To disable a retention policy in a registry, run the az acr config retention update command and set --status disabled:
az acr config retention update \
--registry myregistry --status disabled \
--type UntaggedManifests
Set a retention policy - portal
You can also set a registry's retention policy in the Azure portal.
Enable a retention policy
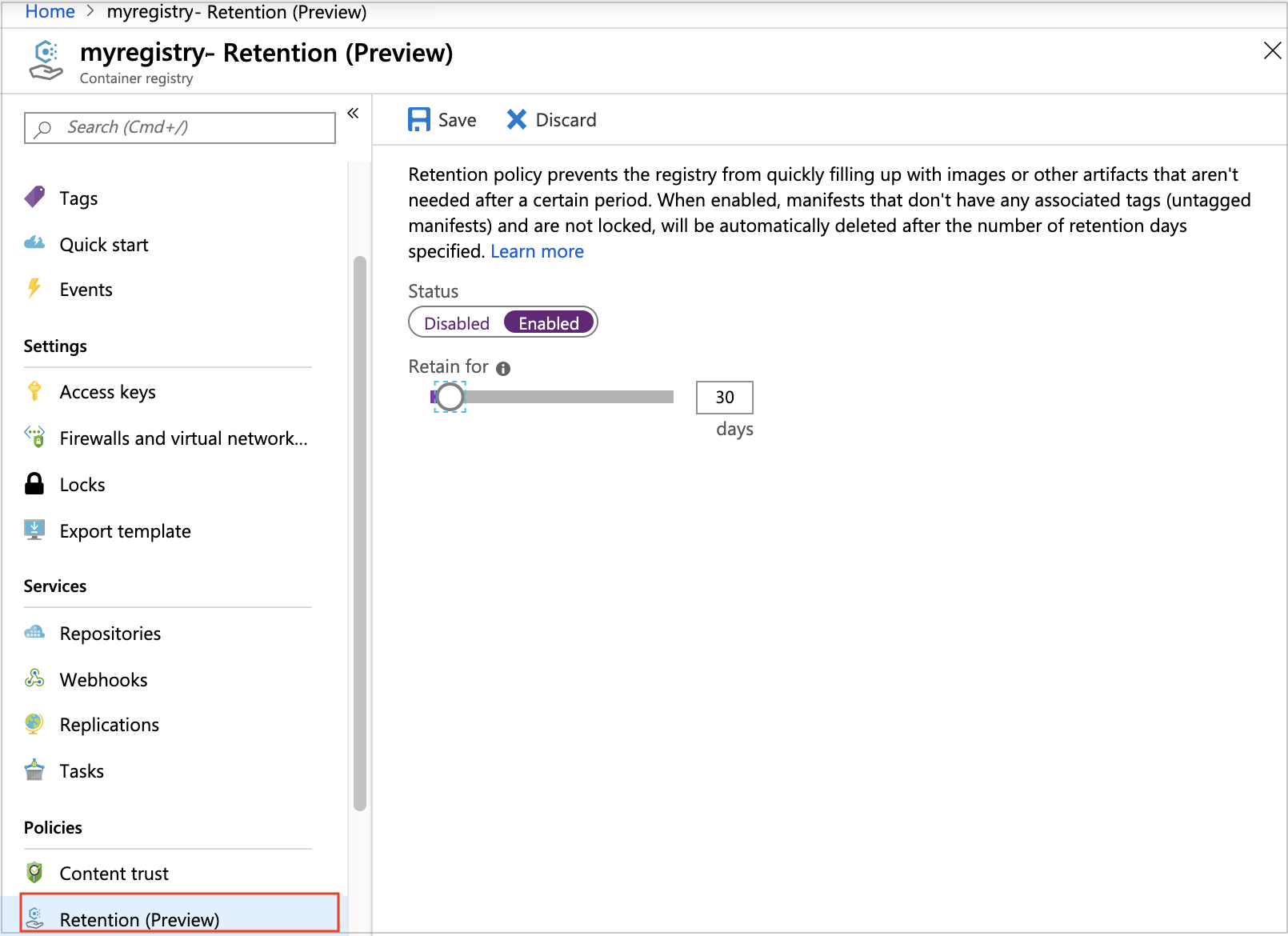
- Navigate to your Azure container registry. Under Policies, select Retention (Preview).
- In Status, select Enabled.
- Select a number of days between 0 and 365 to retain the untagged manifests. Select Save.
Disable a retention policy
- Navigate to your Azure container registry. Under Policies, select Retention (Preview).
- In Status, select Disabled. Select Save.
Next steps
Learn more about options to delete images and repositories in Azure Container Registry
Learn how to automatically purge selected images and manifests from a registry
Learn more about options to lock images and manifests in a registry